|
 |
- Search
| Intest Res > Volume 16(4); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
NOTES
FINANCIAL SUPPORT
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Katsuyoshi Matsuoka received lecture fees from Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., AbbVie GK, Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., and Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. Tadakazu Hisamatsu received research grants from Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., EA pharma Co. Ltd., AbbVie GK, JIMRO Co. Ltd., Asahi Kasei Kuraray Medical Co. Ltd., Zeria Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd., Kyorin Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Nippon Kayaku Co. Ltd., Astellas Pharma Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Pfizer Inc., and Mochida Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., serves as a consultant to EA pharma Co. Ltd., AbbVie GK, Celgene K.K., Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Pfizer Inc., Nichi-Iko Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., and received lecture fees from Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Abbvie GK, EA pharma Co. Ltd., Kyorin Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., and JIMRO Co. Toshifumi Hibi received lecture fees from Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co. Takanori Kanai received research grants from Miyarisan Pharmaceutical Co., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Ezaki Glico Co. Ltd., and Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. and lecture fees from Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., AstraZeneca K.K., Miyarisan Pharmaceutical Co., and Zeria Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: JM, KM, TH, TK. Methodology: JM, KM. Formal analysis: JM, KM, AY, MN, TH, TY, NI, SO, YI, HO, FU, TH, TK. Project administration: JM, KM. Visualization: JM, KM. Writing-original draft: JM. Writing-review and editing: KM, AY, MN, TH, TY, NI, SO, YI, HO, FU, TH, TK. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Fig. 1.
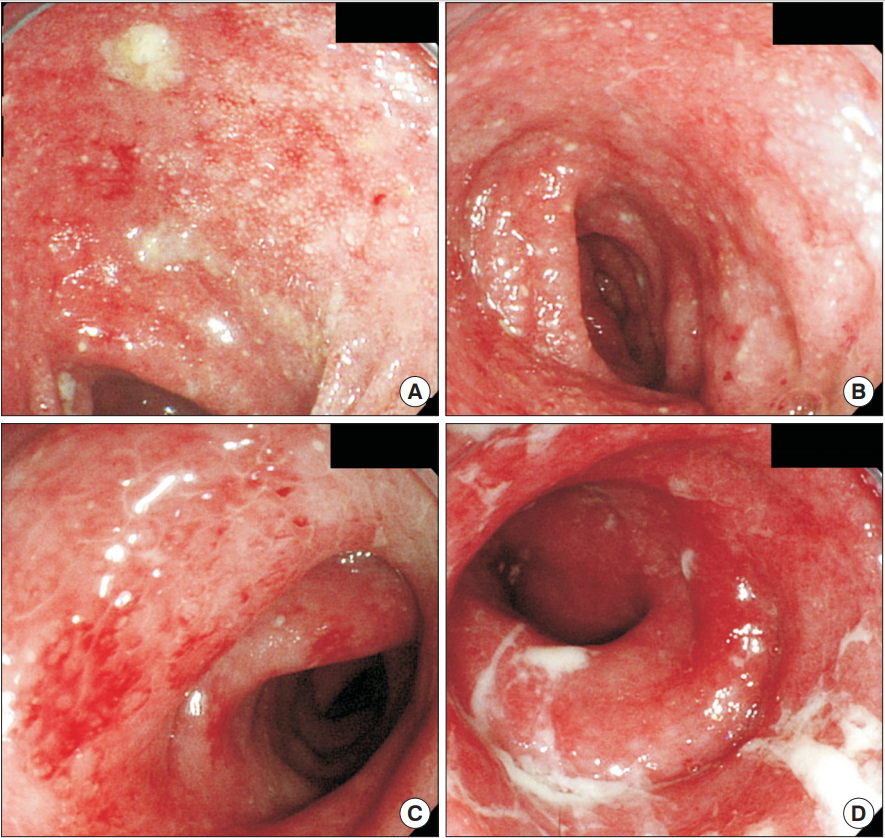
Fig. 2.
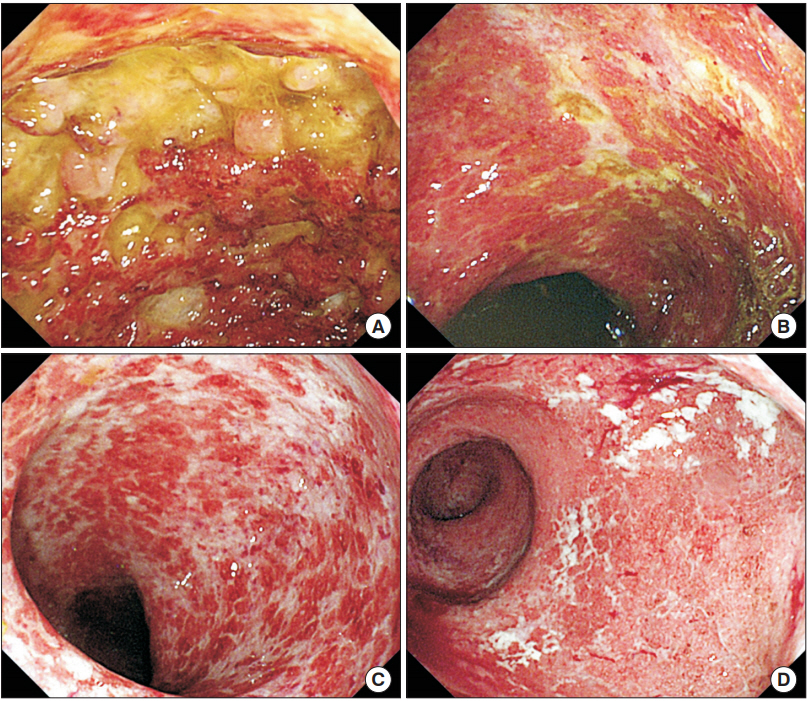
Table 1.
REFERENCES
- TOOLS