 |
 |
- Search
| Intest Res > Volume 21(2); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
After oncologic resection, histological grading and staging of the tumor give important prognostic information about the future risk of recurrence and hence influence the subsequent management plan. Several studies and their meta-analysis have shown that various histological features (e.g., microscopic positive resection margins, plexitis, granuloma, mesenteric inflammatory activity) can predict postoperative clinical/endoscopic/surgical recurrence after resection in Crohn’s disease (CD). Inclusion of mesentery in surgical resection specimens has been shown to reduce surgical recurrence after ileocolonic resection in CD. However, there is no uniform histopathological staging system for risk stratification in postoperative CD to systematically predict postoperative recurrence. This is because the prediction to date is based on clinical characteristics (smoking status, disease phenotype, surgical history). Histopathological predictors are still not adopted in routine clinical practice due to the lack of a uniform staging system, heterogeneity of published studies and lack of standardized definition of histological features. In this article, we attempted to incorporate all such histological features in a single histological staging system CNM (Crohn’s primary site [resection margin positivity, plexitis, granuloma, depth of infiltration], nodes [presence of granuloma], mesentery [involved or not]) in surgical resection specimen in CD. The proposed CNM classification would help to enable systematic reporting, design future clinical trials, stratify postoperative recurrence risk and choose appropriate postoperative prophylaxis.
The term “recurrence” in oncology denotes that cancer has recurred after some time during which it could not be detected. Postoperative recurrence (POR) in Crohn’s disease (CD) is not truly recurrence as the original disease persists microscopically because most of the resections are limited and not radical as in oncological practice. This later manifests as endoscopic/clinical/surgical recurrence. So, recurrence in postoperative CD is primarily “relapse” or “persistent CD” rather than true recurrence. Among the histological features predicting recurrence in postoperative CD, the most commonly studied factor is positive resection margins. Microscopic positive resection margin increases the risk of clinical, surgical, and early recurrence (<12 months) by 2-, 9-, and 6-fold, respectively (Table 1) [1]. Similarly, a retrospective study has shown that the inclusion of mesentery at ileocolonic resection in CD reduces the surgical recurrence rate substantially (40% to 2.9%) [2]. However, the study results are confounded by different follow-up times and concerns regarding a higher risk of postoperative complications due to vascular compromise [3]. Hence, this is currently studied in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) [4]. Myenteric plexitis (MP) is associated with a 30% higher risk of clinical but not surgical recurrence. Granulomas in resected mesenteric lymph nodes and in the intestine were associated with a higher risk of both surgical and endoscopic recurrence [1]. Apart from these factors, depth of infiltration (e.g., transmural involvement) can also be predictive of POR. We incorporated all these factors in our proposed Crohn’s primary site, nodes, mesentery (CNM) staging to systematically evaluate and histopathological report resected surgical specimens in CD. This could potentially help to risk stratify postoperative CD and plan controlled trials studying histological factors for predicting POR in CD along with other clinical predictors.
For ease of classification, under the heading “C” we have included predictive factors which are within the intestine wall like resection margin, inflammation in the neural plexus (plexitis), granuloma and depth of infiltration. Under heading “N,” we have included factors within lymph nodes (e.g., granuloma) and in “M” we have included mesenteric involvement (Table 2).
By far, the strongest evidence for predicting POR in CD is present for positive microscopic resection margins on surgical biopsies. An earlier RCT concluded that recurrence in CD is unaffected by resection margins influencing the guidelines to recommend bowel sparing surgery in CD [5,6]. But a current meta-analysis including 21 studies with over 2,000 patients showed that the risk of clinical and surgical risk was nearly 1.26- and 1.87-fold in patients with positive resection margin with a trend towards endoscopic recurrence. Similar results were seen including studies that only evaluated ileocecal resection [1]. A single study performing multivariate analysis reported 2-, 9-, and 4-fold higher odds of clinical, endoscopic, and surgical recurrence [7]. Studies performing time to event analysis showed approximately 3-fold higher hazard of endoscopic recurrence, 2-fold higher hazard of clinical recurrence, and 3- to 9.6-fold higher hazard of surgical recurrence with active disease margin [8-11]. Early recurrence (<12 months) was primarily endoscopic as expected and not clinical or surgical. The risk of endoscopic recurrence was 6-fold in persons with a positive resection margin compared to those who have a negative margin [1]. Based on the above findings, active disease margin at the resection site is undoubtedly one of the most important factors predicting recurrence in postoperative CD. Whether recurrence can be reduced by extended bowel resection or early, aggressive medical prophylaxis remains to be determined in properly designed studies. Nonetheless, we have included this in the proposed CNM classification given the robust evidence present so far (Fig. 1).
Inflammatory cell infiltration in the nerve bundles and ganglion cells (plexitis) at the margins of resection was associated with a 70% higher risk of endoscopic recurrence with a trend toward clinical recurrence based on a recent meta-analysis based on 10 studies involving more than 700 patients [1]. Similar results were replicated in the ileocecal resection subgroup. Most recurrences at ileal anastomosis after ileocolic resection can be explained by uniform involvement of proximal rather than distal resection margin across the studies [12,13]. Plexitis can be subdivided into MP (between circular and longitudinal muscles) and submucosal plexitis (SMP). Earlier studies evaluated both MP and SMP and have used both hematoxylin and eosin staining and immunohistochemistry (CD117 and CD3 for mastocytes and lymphocytes respectively) [11,13-18]. On multivariate analysis, plexitis was associated with 10-fold higher risk of endoscopic recurrence and a 30% higher risk of surgical recurrence [12,19]. Plexitis in MP and not SMP was associated with an increased risk of endoscopic recurrence when assessed by hematoxylin and eosin staining alone [17]. Studies have shown that at least 1 eosinophil and 6 lymphocytes in SMP predicted surgical recurrence whereas at least 1 lymphocyte in SMP or MP predict endoscopic, clinical and surgical recurrence [19-22].
The hazard ratio of surgical, endoscopic, and clinical recurrence were 9, 6, and 4, respectively, in the presence of plexitis on time to event analysis [1]. Overall 4 studies also reported a 30% higher risk of early endoscopic recurrence (<12 months) with plexitis [12,13,23,24]. The severity of plexitis (mild: < 4/high-power field [HPF], moderate: 4-9/HPF, severe: > 9/HPF) correlates with the risk of endoscopic recurrence, although similar endoscopic recurrence rates have been reported with both moderate and severe plexitis [12,15,17].
On recent meta-analysis based upon a total of 19 studies with more than 1,700 patients showed a significantly increased risk (~30%) of endoscopic and clinical recurrence with a trend towards higher surgical recurrence in CD [1]. In studies performing multivariate analysis, the odds of surgical recurrence were 2-fold in the presence of granulomas whereas only one study evaluated endoscopic recurrence (adjusted odds ratio, 1.63) [7,25].
On survival analysis, the hazard ratio for endoscopic, clinical and surgical recurrence were approximately 2, 3, and 2, respectively [10,26,27]. A higher risk (80%) of early endoscopic recurrence was noted in presence of granulomas [15,28].
Among all the studies, some had studied resection margin as well as from remaining specimen for granuloma while others studied only margin [1]. Hence, in the CNM classification, we considered granulomas in the resection margin as well as in the resected specimen. It is important to consider that granulomas are less commonly seen compared to features such as active margins/plexitis (more in young and long-standing/severe diseases) and its detection can have significant interobserver variability [16,29,30]. However, granulomas are one of the important risk factors for POR in CD [31].
A recent multicenter study has also shown that transmural CD lesions (involving mucosa: cryptitis, mucosal inflammation; submucosa: fibrosis; subserosa: lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate) at the ileal resection margin increased the risk of clinical and early endoscopic recurrence (assessed at 6 months) [15]. It is known that disease severity and penetrating complications go hand in hand with increasing depth of infiltration in CD. So, further studies are required to establish whether the depth of infiltration at the resection margin or specimen influences POR in CD. This is the reason why we included this in the CNM classification (Table 2).
Mesenteric lymph nodes act as a driver for POR in CD as memory T- lymphocytes migrate from the lymph nodes to the anastomotic site after resection to initiate inflammation leading to future recurrence [32]. Hence resection of all draining lymph nodes along with affected bowel is termed as “patho-physiological excision of CD.”
Recent studies have shown that mesenteric lymph nodal granulomas increased the risk of endoscopic and surgical recurrence by 2-fold. These studies highlighted that granulomas in the mesenteric lymph nodes and not those in the intestine increase the risk of surgical or endoscopic recurrence [26,27]. Hence mesenteric and intestinal granulomas should be differentiated in histopathology reports [27]. Spread of intestinal inflammation into adjacent mesentery and lymph nodes leads to the formation of granulomatous reaction in mesenteric lymph nodes and indicates severe disease. Mesenteric lymph nodes provide immunological inputs to the adjacent intestine which could explain why the presence of mesenteric granuloma is an independent predictive factor of POR in CD [27]. We included mesenteric nodal granuloma as a separate entity from intestinal granuloma in the CNM classification.
Mesenteric adipose tissue migrates to the site of intestinal inflammation in CD which leads to the fat wrapping of the inflamed intestine. Recent studies have highlighted the interconnection of mesentery with other abdominal organs [33]. In a retrospective study, it was shown that mesenteric resection substantially reduced POR rates (40% to 3%) [2].
However, block resection and mesenteric inclusion surgeries were performed at different points in the time frame leading to variation in flow up time and postoperative prophylactic therapy which could influence the results of the aforementioned study. Another cohort study has shown that limited mesenteric excision was an independent risk factor of POR after colorectal resection in CD [34]. RCTs are being performed in this regard, results of which are awaited [4].
Macroscopically, the degree of fat wrapping and mesenteric thickening determines the degree of mesenteric involvement (the mesenteric disease activity index) which correlates microscopically with the thickening of surface mesothelium/submesothelial connective tissue complex, increasing connective tissue septations, and adipose tissue number [2]. The mesenteric disease activity index, on the other hand, correlated with mucosal disease activity, Crohn’s Disease Activity Index, and circulating white cells fibrocyte percentage [2]. Mesenteric excision removes mesenteric mesenchymal inputs along with immunological inputs from mesenteric lymph nodes to the inflamed intestine and also hinders fibrocyte recruitment. The mesorectal tissue in CD expresses high numbers of tumor necrosis factor α-producing CD14+ macrophages with reduced expression of markers of wound-healing (e.g., CD206). Hence, excision of the mesolectal tissue after close rectal dissection reduces perineal complications. This highlights the pathophysiological role of the mesentery in CD recurrence [3].
We have included mesenteric involvement in our proposed classification as it is proven to have some role in POR and disease activity. Mesenteric involvement is defined as the thickening of the surface mesothelium/submesothelial/interlobular connective tissue with or without the presence of connective tissue septations extending from the submesothelium.
The authors realized the need for a uniform classification in postoperative CD based on histopathological examination of the resection specimen which could be helpful to predict recurrence. This was based on the realization that recurrence in CD might not be true recurrence as in oncological resections as it was increasingly evident that microscopic persistence of disease at the margins of resection increase the possibility of endoscopic, clinical, and surgical recurrence in CD [1]. Recurrence in CD is multifaceted and occur in the sequence of endoscopic, clinical and surgical recurrence with a strong correlation between each of them (Fig. 2) [35]. Recent studies have shown that radiological evidence of recurrence could precede endoscopic recurrence as endoscopy only evaluate the mucosal aspect of transmural CD [36]. It became increasingly evident that factors other than active microscopic disease margins like depth of infiltration (transmural and extramural), granuloma and plexitis at Crohn’s primary resection site could predict recurrence [7,12,15,19,25]. Apart from the primary site of involvement, involvement of the adjacent structures like nodes (specially granuloma) and mesentery predict recurrence. This could be due to the fact mesenteric adipose tissue and lymph nodes help in mediating immunological, inflammatory and fibrotic signals in the intestine [2]. This is substantiated by the fact that circulating lymphocytes are incapable of producing recurrent lesions after a small bowel transplant in CD if mesenteric lymph nodes were removed fully along with the whole bowel [37]. As conceptualized, the authors reviewed the literature for all the relevant literature on the histological prediction of recurrence in CD. Previous pathology reports of postoperative patients with CD were reviewed and most of the above -mentioned factors were described except for plexitis. With the help of an expert pathologist and based on published literature, we developed the various components of the classification. The CNM staging was developed keeping in mind all these factors with emphasis on simplicity and practical applicability without putting an additional burden on the reporting pathologist.
The effectiveness of postoperative prophylactic therapy in CD in the future would depend on risk stratification based on clinical as well as histopathological predictors. The POR in CD is a complex phenomenon affected by a multitude of factors other than clinical and histologic predictors such as luminal microbiota (depletion of butyrate-producing Lachnospiraceae and abundance of Enterobacteriaceae) and cytokine profile (interleukin 6 and interferon-gamma) [38,39]. A complete “pathophysiological excision of Crohn’s” removing microscopically involved bowel along with mesentery and draining lymph nodes can reduce the risk of POR. Systematic reporting of such factors in the pathological report of surgical resection based on the proposed CNM classification would enable the study of the histopathological factors systematically.
Examples of staging according to the CNM system are given in Table 2. The capital letters signify Crohn’s primary site, draining mesenteric lymph nodes, and mesenteric involvement. In “C” category (Crohn’s primary site), there are 4 subcategories designated by capital letters (GRIP): G, granuloma; R, resection margin; I, infiltration depth; P, plexitis. In these subcategories, increasing involvement is designated by the addition of a number (1, 2, 3, 4) and various types within the subcategory are designated by capital letters (A, B, C) following the number (Table 2). Final C staging is based on the presence increasing number of the following factors: granuloma, positive resection margin, moderate to severe plexitis or transmural involvement (Table 2). Granuloma (G) is kept at the beginning so that the “GRIP” mnemonic is easy to remember. In the “N” (node) category, Nx indicates that regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed, N0 indicates no granulomas in resected regional lymph nodes, N1 indicates granulomas in the resected lymph nodes. In “M” category, M0 denotes no involvement of adjacent mesentery in the form of thickening of the surface mesothelium/submesothelial/interlobular connective tissue with or without the presence of connective tissue septations. M1 indicates mesenteric involvement microscopically without grossly visible fat wrapping or mesenteric thickening. M2 indicates grossly visible fat wrapping or mesenteric thickening. M2 can be further divided into A, B, C according to the mesenteric disease activity index [2].
For example, a 25-year-old female with 8 years history of CD, who underwent right hemicolectomy 9 months back presented with diarrhea and abdominal pain. Hence, she had an early (<12 visible months) clinical and endoscopic recurrence as colonoscopy revealed deep ulceration at the anastomotic site as well as neoterminal ileum (along with wall thickening in mid ileum on computed tomography: computed tomography enterography). She was started on azathioprine immediately postoperatively. Later biologics were started due to early recurrence along with oral steroids. A review of her operative specimen showed no granuloma in the resection specimen (G0), positive resection margins (R1), transmural infiltration (I3), no plexitis (P0), no nodal granuloma (N0), and gross mesenteric involvement (M2). So, the final staging would is C2 N0 M2.
Apart from the above mentioned histological factors predicting POR of CD, other factors such as microbiota recolonization after surgery, gene expression profile of ileal mucosa and various blood-based biomarkers are shown to predict POR in CD [40-42]. Fusobacteria is the most important microbial driver or POR, whereas expression of JAK-STAT at the ileal margin and mitochondrial dysfunction inside foci of chronic inflammation is associated with a higher probability of POR [40,41]. Markers of memory T cell response like CXCR3 ligands are also associated with higher POR in CD [42]. Future staging systems may incorporate these factors for prediction of POR in CD.
There is growing evidence that many histological factors in the resected intestinal specimen in CD (C), mesenteric lymph nodes (N) and mesentery involvement (M) predict POR in CD. Most of the evidence is based mainly on retrospective studies without adjusting for confounding factors like disease severity and postoperative prophylaxis. Hence there is a need for future prospective studies evaluating all these factors. However, such a study is challenging given the various factors that need to be studied. We have attempted to incorporate all the histologic factors in the proposed CNM classification to enable systematic reporting which will help design such studies. However, the individual weightage of each component of the CNM classification needs to be evaluated based on validation using multivariate analysis in future prospective studies. Until such studies are published, further refinements of the classification are warranted based on expert consensus development before its routine clinical use [43,44]. Nevertheless, the CNM classification is the first attempt to systemically report and study these predictive factors for POR. The CNM classification along with existing clinical predictors (e.g., smoking, history of intestinal resection) could help to predict recurrence effectively and more accurately. Moreover, like the TNM classification for malignancy, the CNM classification for CD has the potential to not only predict “recurrence” systematically but also influence postoperative surveillance and prophylactic therapy.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Funding Source
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Rao GV, Pal P. Data curation: Pal P. Formal analysis: Pal P. Investigation: Pal P, Sekaran A. Methodology: Rao GV, Pal P. Project administration: Rao GV, Tandan M. Supervision: Rebala P, Tandan M, Reddy DN. Visualization: Rao GV, Rebala P, Tandan M, Reddy DN. Writing - original draft: Pal P. Writing - review & editing: all authors. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the proposed the CNM (Crohn’s primary site, nodes, mesentery) classification.

Fig. 2.
Implications of proposed the CNM (Crohn’s primary site, nodes, mesentery) classification on postoperative Crohn’s disease.
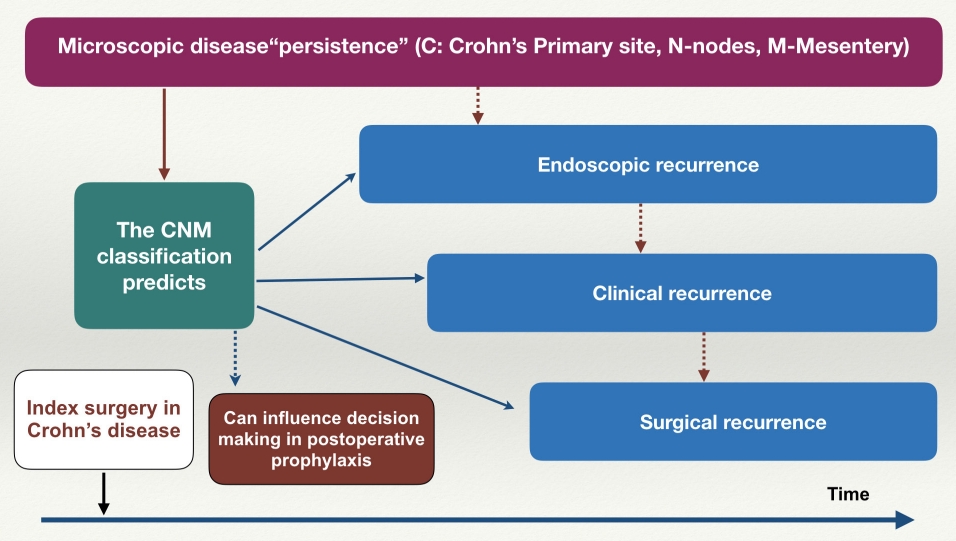
Table 1.
Definitions of Various Factors in the CNM (Crohn’s Primary Site, Nodes, Mesentery) Classification
Table 2.
Proposed Staging to Predict Postoperative Recurrence in Crohn’s Disease Based on Histopathological Factors in Resected Specimen
REFERENCES
1. Tandon P, Malhi G, Abdali D, et al. Active margins, plexitis, and granulomas increase postoperative Crohn’s recurrence: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;19:451-462.


2. Coffey CJ, Kiernan MG, Sahebally SM, et al. Inclusion of the mesentery in ileocolic resection for Crohn’s disease is associated with reduced surgical recurrence. J Crohns Colitis 2018;12:1139-1150.



3. de Groof EJ, van der Meer JH, Tanis PJ, et al. Persistent mesorectal inflammatory activity is associated with complications after proctectomy in Crohn’s disease. J Crohns Colitis 2019;13:285-293.


4. Li Y, Mohan H, Lan N, et al. Mesenteric excision surgery or conservative limited resection in Crohn’s disease: study protocol for an international, multicenter, randomized controlled trial. Trials 2020;21:210.




5. Fazio VW, Marchetti F, Church M, et al. Effect of resection margins on the recurrence of Crohn’s disease in the small bowel: a randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg 1996;224:563-573.


6. Bemelman WA, Warusavitarne J, Sampietro GM, et al. ECCOESCP consensus on surgery for Crohn’s disease. J Crohns Colitis 2018;12:1-16.


7. Riault C, Diouf M, Chatelain D, et al. P692 Positive histological margins is a risk factor of recurrence after ileocaecal resection in Crohn’s disease. J Crohns Colitis 2019;13(Suppl 1):S466-S467.

8. de Buck van Overstraeten A, Eshuis EJ, Vermeire S, et al. Short- and medium-term outcomes following primary ileocaecal resection for Crohn’s disease in two specialist centres. Br J Surg 2017;104:1713-1722.



9. Kinchen J, Rajaratnam K, Kingston G, Mee A, De Silva A. P211 The presence of microscopic disease at the resection margins predicts post-surgical relapse in Crohn’s disease. J Crohns Colitis 2012;6(Suppl 1):S93-S94.

10. Malireddy K, Larson DW, Sandborn WJ, et al. Recurrence and impact of postoperative prophylaxis in laparoscopically treated primary ileocolic Crohn disease. Arch Surg 2010;145:42-47.


11. Wasmann KA, van Amesfoort J, van Montfoort ML, Koens L, Bemelman WA, Buskens CJ. The predictive value of inflammation at ileocecal resection margins for postoperative Crohn’s recurrence: a cohort study. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2020;26:1691-1699.



12. Ferrante M, de Hertogh G, Hlavaty T, et al. The value of myenteric plexitis to predict early postoperative Crohn’s disease recurrence. Gastroenterology 2006;130:1595-1606.


13. Ng SC, Lied GA, Kamm MA, Sandhu F, Guenther T, Arebi N. Predictive value and clinical significance of myenteric plexitis in Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2009;15:1499-1507.


14. Boland K, Stempak J, Weizman A, et al. P311 Microscopic inflammation and myenteric plexitis at the margin of resection do not predict endoscopic recurrence in patients with Crohn’s disease after ileocolic resection. J Crohns Colitis 2017;11(Suppl 1):S235.

15. Hammoudi N, Cazals-Hatem D, Auzolle C, et al. Association between microscopic lesions at ileal resection margin and recurrence after surgery in patients with Crohn’s disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020;18:141-149.

16. Misteli H, Koh CE, Wang LM, Mortensen NJ, George B, Guy R. Myenteric plexitis at the proximal resection margin is a predictive marker for surgical recurrence of ileocaecal Crohn’s disease. Colo-rectal Dis 2015;17:304-310.

17. Nakao S, Itabashi M, Yamamoto T, Okamoto T. Predictive value of myenteric and submucosal plexitis for postoperative Crohn’s disease recurrence. J Anus Rectum Colon 2018;1:56-64.



18. Sokol H, Polin V, Lavergne-Slove A, et al. Plexitis as a predictive factor of early postoperative clinical recurrence in Crohn’s disease. Gut 2009;58:1218-1225.


19. Milassin Á, Sejben A, Tiszlavicz L, et al. Analysis of risk factors-especially different types of plexitis-for postoperative relapse in Crohn’s disease. World J Gastrointest Surg 2017;9:167-173.



20. Bressenot A, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Histologic features predicting postoperative Crohn’s disease recurrence. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2015;21:468-475.


21. Decousus S, Boucher AL, Joubert J, et al. Myenteric plexitis is a risk factor for endoscopic and clinical postoperative recurrence after ileocolonic resection in Crohn’s disease. Dig Liver Dis 2016;48:753-758.


22. Lemmens B, de Buck van Overstraeten A, Arijs I, et al. Submucosal plexitis as a predictive factor for postoperative endoscopic recurrence in patients with Crohn’s disease undergoing a resection with ileocolonic anastomosis: results from a prospective single-centre study. J Crohns Colitis 2017;11:212-220.


23. Blaker PA, Nedjat-Shokouhi B, Thomas DM, Harris AW. P074 - Myenteric plexitis does not predict endoscopic Crohn’s disease recurrence 12 months following ileo-colonic resection in district general hospital practice. J Crohns Colitis 2009;3:S40.

24. Rahier JF, Dubuquoy L, Colombel JF, et al. Decreased lymphatic vessel density is associated with postoperative endoscopic recurrence in Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2013;19:2084-2090.


25. Cullen G, O’toole A, Keegan D, Sheahan K, Hyland JM, O’donoghue DP. Long-term clinical results of ileocecal resection for Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2007;13:1369-1373.


26. Li Y, Stocchi L, Liu X, et al. Presence of granulomas in mesenteric lymph nodes is associated with postoperative recurrence in Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2015;21:2613-2618.


27. Unger LW, Argeny S, Stift A, et al. Mesenteric granulomas independently predict long-term risk of surgical recurrence in Crohn’s disease. Colorectal Dis 2020;22:170-177.




28. Poredska K, Kunovsky L, Marek F, et al. The influence of microscopic inflammation at resection margins on early postoperative endoscopic recurrence after ileocaecal resection for Crohn’s disease. J Crohns Colitis 2020;14:361-368.



29. Denoya P, Canedo J, Berho M, et al. Granulomas in Crohn’s disease: does progression through the bowel layers affect presentation or predict recurrence? Colorectal Dis 2011;13:1142-1147.


30. Heimann TM, Miller F, Martinelli G, Szporn A, Greenstein AJ, Aufses AH Jr. Correlation of presence of granulomas with clinical and immunologic variables in Crohn’s disease. Arch Surg 1988;123:46-48.


31. Gionchetti P, Dignass A, Danese S, et al. 3rd European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn’s disease 2016: Part 2: surgical management and special situations. J Crohns Colitis 2017;11:135-149.



32. Sensi B, Siragusa L, Efrati C, et al. The role of inflammation in Crohn’s disease recurrence after surgical treatment. J Immunol Res 2020;2020:8846982.




33. Coffey JC, Byrnes KG, Walsh DJ, Cunningham RM. Update on the mesentery: structure, function, and role in disease. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022;7:96-106.


34. Zhu Y, Qian W, Huang L, et al. Role of extended mesenteric excision in postoperative recurrence of Crohn’s colitis: a single-center study. Clin Transl Gastroenterol 2021;12:e00407.



35. Ble A, Renzulli C, Cenci F, et al. The relationship between endoscopic and clinical recurrence in postoperative Crohn’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Crohns Colitis 2022;16:490-499.




36. Bachour SP, Shah RS, Lyu R, et al. Test characteristics of cross-sectional imaging and concordance with endoscopy in postoperative Crohn’s disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022;20:2327-2336.

37. Fahad H, Abu-Elmagd K, Lashner B, Fiocchi C. Recurrence of Crohn’s disease after small bowel transplantation: fact or fiction. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2020;26:21-23.



38. Hamilton AL, Kamm MA, De Cruz P, et al. Luminal microbiota related to Crohn’s disease recurrence after surgery. Gut Microbes 2020;11:1713-1728.



39. Cerrillo E, Moret I, Iborra M, et al. A nomogram combining fecal calprotectin levels and plasma cytokine profiles for individual prediction of postoperative Crohn’s disease recurrence. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2019;25:1681-1691.



40. Machiels K, Pozuelo Del Río M, Martinez-De la Torre A, et al. Early postoperative endoscopic recurrence in Crohn’s disease is characterised by distinct microbiota recolonisation. J Crohns Colitis 2020;14:1535-1546.




41. Ngollo M, Perez K, Hammoudi N, et al. Identification of gene expression profiles associated with an increased risk of postoperative recurrence in Crohn’s disease. J Crohns Colitis 2022;16:1269-1280.

42. Walshe M, Nayeri S, Ji J, et al. A role for CXCR3 ligands as biomarkers of post-operative Crohn’s disease recurrence. J Crohns Colitis 2022;16:900-910.












