 |
 |
- Search
| Intest Res > Volume 22(1); 2024 > Article |
|
Abstract
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a multifactorial disease, which is thought to be an interplay between genetic, environment, microbiota, and immune-mediated factors. Dysbiosis in the gut microbial composition, caused by antibiotics and diet, is closely related to the initiation and progression of IBD. Differences in gut microbiota composition between IBD patients and healthy individuals have been found, with reduced biodiversity of commensal microbes and colonization of opportunistic microbes in IBD patients. Gut microbiota can, therefore, potentially be used for diagnosing and prognosticating IBD, and predicting its treatment response. Currently, there are no curative therapies for IBD. Microbiota-based interventions, including probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation, have been recognized as promising therapeutic strategies. Clinical studies and studies done in animal models have provided sufficient evidence that microbiota-based interventions may improve inflammation, the remission rate, and microscopic aspects of IBD. Further studies are required to better understand the mechanisms of action of such interventions. This will help in enhancing their effectiveness and developing personalized therapies. The present review summarizes the relationship between gut microbiota and IBD immunopathogenesis. It also discusses the use of gut microbiota as a noninvasive biomarker and potential therapeutic option.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is characterized by chronic and relapsing inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract [1]. It encompasses 2 main clinical entities, Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). Though CD and UC show similar clinical symptoms, they vary in their anatomical distribution, which can occur anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract for CD but only in the colon and rectum for UC [2]. Depending on symptoms and disease severity, UC and CD are classified into mild, moderate, and severe [3]. IBD affects about 6.8 million people globally [4]. The incidence of IBD has been rising in developing countries [4,5], whereas a stabilizing trend has been observed in high-prevalence developed countries in Europe and North America [6]. Individuals with IBD are at greater risk of developing colorectal cancer (CRC), called colitis-associated cancer, than normal individuals [7-9]. The risk of developing CRC is about 20% and 2.5% to 4.5% for patients with UC [10] and CD [11], respectively. Colitis stimulates carcinogenesis by inducing the expansion of genotoxic bacteria [12], Patients with IBD show a significant clinical heterogeneity, which makes the right treatment for each patient difficult [13,14].
The human gastrointestinal tract contains a diverse assembly of microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, protozoa, and viruses [15]. It has been estimated that there are approximately 40 trillion microorganisms that constitute the human gut microbiota [16]. The gut microbiota possesses approximately 150-fold more genes than the human genes [17]. The gut microbiota and humans show a symbiotic relationship, and the composition of the human gut microbiota is closely linked to health and disease [18,19]. Many factors influence the composition of gut microbiota, including the delivery (C-section or normal), diet, age, race, environmental factors, use of antibiotics, or population geography [20-28]. The gut microbiota constantly crosstalk with each other and the host cells and maintain the homeostasis of the intestinal environment.
More than 99% of the bacteria in the human intestine belong to the 4 major phyla: Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, and Proteobacteria [29,30]. Nearly 90% of bacterial phyla in the colon are represented by Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria, while 40% of the bacterial phyla in the small intestine are represented by Firmicutes [26,31]. The composition and diversity of gut microbiota vary along the gastrointestinal tract and between mucosal surfaces and the lumen [32-35]. It has been found that the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio is a critical parameter for gut health [36]. Various studies have found that a change in the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio is associated with IBD [37-41].
Pathogenic and symbiotic microbiota can coexist in a healthy human gut. Any disturbance can alter the normal interactions between microbiota and the host, potentially affecting the susceptibility to IBD [33]. Such disturbance or change in microbiota, commonly referred to as “dysbiosis,” is involved in the pathophysiology of gastrointestinal diseases such as IBD and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) [42-44]. A significant reduction in the complexity of the gut microbial ecosystem and alterations in a few specific taxa have been observed in patients with IBD [45]. The association of gut microbiota with IBD is strengthened by the fact that when germ-free mice are inoculated with IBD microbiota, they develop severe colitis [46,47]. However, it remains unclear whether dysbiosis of the gut microbiota is a cause or a consequence of IBD. An increase in microbial species capable of tolerating oxidative stress indicates that dysbiosis in IBD is caused by inflammation [48]. Though the precise etiopathology of the disease remains to be elucidated, one of the hypotheses suggests that an inappropriate immune response to the intestinal microbiota in genetically predisposed individuals can lead to IBD [49]. Over 200 IBD-associated susceptible genes have been identified, some of which are involved in host innate or adaptive immune responses to gut microbiota [3,50-52]. This indicates that gut microbiota play an essential role in the pathogenesis of IBD [53].
This review discusses the relationship between the gut microbiota and the onset and progression of IBD and their potential role in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of IBD.
Various molecular techniques have been employed to study the human gut microbiota. These techniques have their own biases and limitations, and no known molecular technique is able to capture all of the microorganisms that inhabit the human gut. Moreover, as mentioned earlier, individual gut microbiota is affected by numerous factors, and comparing microbiota from different individuals is not often conclusive. However, it is still possible to reach a consensus by comparing different studies conducted using different techniques and experimental settings. By comparing cases and controls, we can identify recurring patterns of trends that provide a comprehensive understanding of the gut microbiota. Collectively they can contribute to a more robuse and reliable consensus regarding the characteristics of the gut microbiota in diseases.
Studies have shown that alterations in the gut microbiota, often called dysbiosis, are associated with IBD [54,55]. Burgeoning evidence suggests that a reduction in fecal microbial diversity is an indicator of IBD. A decline in Firmicutes and Bacteriodetes [42,43,53,56-58] and an increase in Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria have been observed in IBD [54,58,59]. Specific genera, such as Bacteroides, Eubacterium, Faecalibacterium, and Ruminococcus, are reduced in fecal samples of patients with CD [60]. Nemoto et al. [61] observed that patients with UC showed a decline in Bacteroides and Clostridium XIVab. In another study, Fuentes et al. [62] found that patients with UC had fewer Clostridium and increased Bacteriodetes, whereas Khalil et al. [63] found that sulfate-reducing bacteria were dominant in UC but were fewer in healthy subjects. A multicenter study by Gevers et al. [64] reported an increase in the members of Pasteurellaceae, Veillonellaceae, and Enterobacteriaceae and a decrease in the members of Clostridioides, Bacteroidales, and Erysipelotrichales in CD patients. Members of the family Enterobacteriaceae express lipopolysaccharide that can trigger strong inflammatory responses, contributing to IBD [65,66]. Studies have also found decreased abundance of Clostridium lavalense, Ruminococcus torques, Blautia faecis, and Roseburia inulinivorans in patients with CD [67,68]. Takahashi et al. [68] reported a decrease in Faecalibacterium, Eubacterium, Bacteroides, and Ruminococcus and an increase in Actinomyces and Bifidobacterium in CD patients.
In addition to changes in bacterial diversity, changes in archaeal [55,69-71], and viral diversity [72] have also been reported in IBD. Interkingdom crosstalk between the bacteriome and mycobiome has been implicated in CD.73
A change in the human bacteriome has been found in IBD (Table 1), due to their greater abundance than other kingdoms of microbes in the gut. The bacteria found to be associated with IBD include Escherichia coli, Bacteroides fragilis, Ruminococcus gnavus, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, and Roseburia (Fig. 1).
E. coli is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic bacterium and a normal inhabitant of the human gut. The gut microbiota of patients with IBD show an increased abundance of adherentinvasive E. coli (AIEC) [74-77]. AIEC can adhere to and cross the intestinal mucosa of IBD patients, induce inflammation, and increase the permeability of the intestinal epithelium [78,79]. Mancini et al. [80] found that AIEC could disrupt epithelial mitochondrial networks and influence gut permeability by affecting gene expression. AIEC can survive and replicate in macrophages, resulting in the secretion of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and, thus, inflammation [81,82]. A high abundance of E. coli has been linked to inflammation in patients with IBD [83].
B. fragilis is a commensal Gram-negative anaerobic bacterium. It is an opportunistic pathogen with pro-inflammatory properties [84] and contributes to IBD [85]. Strains of B. fragilis that express a zinc-dependent metalloprotease, called B. fragilis toxin (BFT or fragilysin), are known as enterotoxigenic B. fragilis (ETBF) [86,87]. The strains that lack BFT are called nontoxigenic B. fragilis (NTBF). ETBF is responsible for diarrhea in children [88] and IBD [89,90]. BFT directly affects signaling pathways such as Wnt, NF-κB, STAT3, and MAPK pathways, leading to the production of pro-inflammatory mediators [91-95]. ETBF activates the Stat3 transcription factor, increases Th17 and T regulatory cells (Treg), and promotes mucosal permeability [96,97]. ETBF also induces reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and DNA damage by inducing the expression of spermine oxidase in colonocytes [98]. Kordahi et al. [99] found a correlation between B. fragilis and the levels of inflammatory cytokines. Contrary to ETBF, NTBF can induce the anti-inflammatory effects of Treg and direct the development of CD4+ T cells [100,101].
R. gnavus is a strict anaerobic Gram-positive bacterium and a part of the normal intestinal flora in humans. An increased abundance of R. gnavus is associated with IBD [57,102-104]. Hall et al. [103] found that R. gnavus could reach an abundance of 69% in patients with severe CD. R. gnavus produces complex glucorhamnan polysaccharide, which can induce the secretion of inflammatory cytokines, like TNF-α, by dendritic cells [104].
F. prausnitzii is one of the most important butyrate-producing bacteria found in the gastrointestinal tract [105,106], which has drawn much attention in recent years. A decrease in F. prausnitzii has been reported in IBD [67,107-114]. Varela et al. [115] found that UC patients had insufficient colonization of F. prausnitzii, and the maintenance of clinical remission required F. prausnitzii colonization. They also found that the abundance of F. prausnitzii was correlated with a relapse of ileal CD after surgery. F. prausnitzii mediates anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway in intestinal epithelial cells [111] and by producing butyrate, which maintains a balance of Th17/Treg cells [107,116]. F. prausnitzii also stimulates the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-10, and inhibits the production of inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-12 and interferon-γ [107].
Roseburia is a genus of anaerobic, Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria known for butyrate production in the human colon. Several studies have confirmed that a decrease in Roseburia is associated with IBD [109,113,117-119]. Roseburia intestinalis can convert acetate to butyrate and has anti-inflammatory effects [118]. The patients with high genetic risk for IBD have significantly reduced Roseburia spp [117]. Other bacteria, such as Enterococcus faecium, Citrobacter rodentium, and Mycobacterium, can promote cytokine expression and inflammation in the colon, inducing IBD [120-122]. Fusobacterium is also found to be abundant in the colonic mucosa of UC patients [123]. Fusobacterium nucleatum is a pro-inflammatory bacterium that activates epithelial TLR4, resulting in inflammation [124,125].
Archaea are single-celled prokaryotes like bacteria but are closer to eukaryotes at the genetic level. Like bacteria, they also inhabit various locations of the human body [126-129]. The most dominant archaea in the human gut are methanogens, particularly Methaonbrevibacter and Methanosphaera [126]. Studies have found that a decrease in methanogens like Methanobrevibacter smit-hii is associated with IBD [69-70]. M. smithii plays a role in digestive health by directing Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron-mediated fermentation of dietary fructans to acetate [130]. Contrary to M. smithii, studies have found that the abundance of Methanosphaera stadtmanae increases up to 3-fold in IBD patients [131,132]. M. stadtmanae stimulates pro-inflammatory cytokine production by dendritic cells [132]. In addition to methanogens, halophilic archaea may also be involved in the etiology of IBD [133]. Contrary to these results, Chehoud et al. [134] reported that there were no alterations in the archaeome associated with IBD. Nevertheless, their role in the onset and progression of IBD is still debatable [127], probably due to a lack of sufficient studies.
Fungi represent just 0.1% of the total microbial community in the gut [135]. Alterations in the mycobiome are also associated with IBD. Studies have found reduced fungal diversity and dysbiosis in patients with IBD [55,71,73,136]. Sokol et al. [55] found an increased Basidiomycota/Ascomycota ratio in patients with IBD. Other studies have reported an increase in Candida, Malasseziales, and Filobasidiaceae and a decrease in Saccharomyces, Penicillium, and Kluyveromyces [137,138]. Candida is a pathogenic fungus and has gathered much attention in recent years. Several studies have reported an increased abundance of Candida in IBD patients [73,134,139,140]. Studies have also reported the involvement of Candida in causing severe colitis in a mouse model [141,142]. Mounting evidence suggests that colonization by Candida albicans enhances inflammation by increasing IL-17 and IL-23 production [143-145].
Contrary to Candida, decreased abundance of Saccharomyces cerevisae is reported in patients with IBD [55,139]. Limon et al. [151]. S. cerevisae may prevent IBD by preventing AIEC from adhering to the inflamed intestinal mucosa [146] and inhibiting aspartyl proteases-2 and 6 from C. albicans, preventing its transformation into an invasive hyphal form [147]. Saccharomyces boulardii may also have a preventive role in IBD owing to its anti-inflammatory effects and protection against intestinal pathogens [148,149]. Increased abundances of Malassezia have been reported in patients with IBD [55,150,151]. Limon et al. [151] found that Malassezia restricta was enriched in the mucosa of patients with CD. Many Malassezia strains can synthesize indole compounds that act on the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) [152-154] and also regulate the production of inflammatory mediators [155].
The human gut virome includes mostly bacteriophages and eukaryotic viruses [156,157]. Alterations in the gut virome have also been reported in IBD [72,158-160]. IBD is also associated with the loss of the core phagome and increased abundance of temperate phages [160]. However, contrary to bacterial diversity, increased virome diversity has been reported in IBD patients [72,159,161,162], indicating the role of gut virome in bacterial dysbiosis [162]. In particular, the abundance of bacteriophages of the family Caudovirales was found to increase in patients with UC and CD [72,159,161,162]. Caudovirales may contribute to IBD by decreasing bacterial richness.
Studies have also found significantly increased phage populations in the gut biopsies of patients with IBD compared to controls [163,164]. Duerkop et al. [165] reported that bacteriophages Caudovirales and Podoviridae were enriched in a mouse model of colitis. Similarly, Seth et al. [166] found that increased viral diversity was correlated with gut dysbiosis and levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in mouse models. Gogokhia et al. [167] found that an increase in bacteriophage abundance aggravated colitis in germ-free mice. Pérez-Brocal et al. [168] reported that bacteriophages that infect Alteromonadales and Clostridiales were enriched in IBD. In another study, Cornuault et al. [169] found a high proportion of F. prausnitzii temperate phages in IBD patients, which results in the depletion of F. prausnitzii. Contrary to the above studies, Galtier et al. [170] found that bacteriophages could significantly reduce the abundance of AIEC in a mouse model of dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis. Similarly, Yang et al. [171] found that enteric viruses could ameliorate gut inflammation by stimulating interferon-β production. In addition to bacteriophages, eukaryotic viruses may also trigger intestinal inflammation and contribute to IBD pathogenesis [158,159,164,172]. Studies have found an increased abundance of the eukaryotic viruses Pneumoviridae [159] and Hepadnaviridae [173] in UC patients and Herpesviridae in IBD patients [164]. Cadwell et al. [174] found that in mice with a risk gene for CD, Atg16L1HM, norovirus could induce intestinal pathologies. In a similar study, Bolsega et al. [175] found that murine norovirus could induce colitis in an Il10-deficient mouse model of IBD in a microbiota-dependent manner.
The current methods of assessing IBD activity include measuring inflammation using biomarkers from plasma and feces, such as C-reactive protein and fecal calprotectin, which are not IBD-specific. Other methods, such as colonoscopy, can precisely predict IBD but have limited clinical application due to their invasiveness and risk of intestinal perforation. The use of gut microbiota as a diagnostic tool for IBD can reduce the frequency of such invasive procedures. Stool samples can be used to generate data through 16S rRNA sequencing, metagenomic sequencing, or metabolomic profiling. The presence or absence of specific gut microbiota can also help predict treatment response in IBD [176]. The use of microbial biomarkers for IBD diagnosis is a promising method that needs to be utilized in clinical practice.
Lopez-Siles et al. [177] confirmed that F. prausnitzii was a specific indicator of IBD. They also reported that the patients with IBD had a lower abundance of F. prausnitzii than IBS patients and healthy controls. Combining F. prausnitzii with E. coli could even distinguish colonic CD from extensive colitis. Prosberg et al. [178] also found that the patients with active CD and UC had a lower abundance of F. prausnitzii than those in remission. These studies confirm that F. prausnitzii may be a reliable biomarker for IBD. A significant decrease in Bifidobacterium has also been reported in IBD patients [179-182]. Contrary to this, other studies have found an increased abundance of Bifidobacterium in IBD patients compared to controls [68,183,184]. Further research is required in this direction to know the precise role of Bifidobacterium in IBD pathogenesis.
Using gut microbiota, it is even possible to distinguish healthy individuals from UC or CD patients with an accuracy of 93.2% and 89.5%, respectively [59]. Fukuda and Fujita [185] used TRFLP of feces samples for operational taxonomic unit (OTU) discriminant analysis. They could distinguish between patients with active UC and other groups, which include individuals with mild inflammation in the large intestine, no inflammation, consanguineous-healthy individuals, and non-consanguineous healthy individuals. He et al. [186] reported a higher abundance of Klebsiella, Enterococcus, and Haemophilus in patients with active UC and a higher abundance of Roseburia, Lachnospira, Blautia, and Faecalibacterium in patients in remission. They also reported that decreased abundance of F. prausnitzii was related to a higher risk of recurrence in ileal CD. A combination of multiple microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, and fungi, may serve as a more accurate and reliable biomarker to distinguish between individuals with UC, CD, and IBS from healthy individuals.
Gut microbiota can also be used as a biomarker for predicting the clinical relapse of IBD. A high abundance of Streptococcus has been reported in patients with postoperative recurrence [187]. Screening preoperative stool samples for Streptococcus may be a predictive marker of disease recurrence.
The gut microbial metabolites include metabolites produced de novo by the gut microbes, metabolites produced by the host and modified by the gut microbes, and by-products of microbial interactions with dietary components. Metabolomics has been used to distinguish between IBD patients and healthy subjects [119,188-190]. Metabolites, particularly short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), bile acids, and tryptophan metabolites, are found to be involved in IBD pathogenesis (Fig. 2). Various studies have confirmed reductions in the levels of medium-chain fatty acids and SCFAs [119,189,191,192], dysregulation of bile acid metabolism [113,193], and changes in the levels of amino acids [193,194] in the feces samples of IBD patients. Other studies have reported alterations in tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) intermediates [195,196], hippurate [197], and amino acid metabolism [198] in patients with IBD.
Differences in the diversity and abundance of intestinal metabolites are seen in patients with IBD compared to control, with increased levels of primary bile acids, sphingolipids, and amino acids and decreased levels of indoles, long-chain fatty acids, cholesterol, and tetrapyrroles in IBD patients [119].
Studies have indicated that anti-inflammatory microbial metabolites are decreased [119,199], while pro-inflammatory microbial metabolites are enriched [118] in IBD patients compared to healthy subjects. Morgan et al. [200] reported that 12% of metabolic pathways significantly differed between IBD patients and healthy controls. They also found that the genes for the metabolism of butanoate and propanoate were decreased in CD patients.
SCFAs, such as acetate, propionate, and butyrate, are produced by the anaerobic fermentation of non-digestible carbohydrates by gut microbes [201-203]. Acetate accounts for nearly 50% to 70%, propionate for 10% to 20%, and butyrate for 20% to 30%. Acetate is produced by a variety of gut microbes [204], propionate is mainly produced by Bacteroidetes, Negativicutes, and Lachnospiraceae [201,205], while butyrate is mostly produced by Eubacterium, Clostridium, and Fusobacterium [206]. SCFAs are important players in regulating intestinal barrier integrity and reducing intestinal inflammation [109,207]. SCFAs regulate colonic Treg and show anti-inflammatory effects [208]. Butyrate and propionate can downregulate pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6 and IL-12 [209,210]. Butyrate and propionate can also alter the chromatin state by inhibiting histone deacetylases [211]. Furusawa et al. [212] found that butyrate upregulated histone H3 acetylation of the Foxp3 gene and promoted CD4+ T cell differentiation into Treg. Many studies have confirmed lower levels of SCFAs in the feces of IBD patients compared to healthy controls [109,113,213-215]. However, other studies have found a non-significant reduction in SCFAs in IBD [188,189]. Contrary to the levels of other SCFAs, lactate levels are elevated in both UC and CD [119,216,217].
SCFAs affect cellular functions by interacting with G protein-coupled receptors expressed in human colon epithelial cells [218]. Orphan G protein-coupled receptor (GPR43) interacts with acetate, propionate, and butyrate [219]. The binding of SCFAs with GPR43 reduces inflammation [100]. Loss of GPR43 results in refractory colitis in the DSS mice model [100]. Butyrate binds and activates GPR109A [220,221]. The interaction of butyrate with GPR109A reduces inflammation by promoting the differentiation of Treg, suppressing the induction of inflammatory cytokine, IL-6, and secreting anti-inflammatory cytokine, IL-10, by TH1 cells, and also activates macrophages and CD+ T cells [208,212,222,223]. SCFAs regulate intestinal homeostasis by stimulating the production of antimicrobial peptides and intestinal IgA [224,225]. They promote epithelial homeostasis through the production of IL-18 [226]. They also inhibit NF-κB expression and secretion of TNF-α [227]. They also have anti-proliferative effects [228] and a protective role in animal models of colitis [208] and colitis-induced CRC [221].
Butyrate is the major energy source for colonic epithelial cells and inhibits epithelial stem cells [229]. It modulates mitochondrial function, increasing oxygen consumption of colonic epithelial cells [230-233], which decreases oxygen concentration in the intestinal tract, increasing the number of obligate anaerobic bacteria, including butyrate-producing Firmicutes [234]. IBD is characterized by the loss of butyrate-producing bacterial species, such as F. prausnitzii, Roseburia hominis, and Clostridium cluster IV and XIVa, as is evident by a reduction in fecal butyrate levels in IBD patients [68,107,109,183]. Administration of butyrate by enema in UC has been found to be beneficial [235]. Therefore, decreased concentrations of SCFA-producing bacteria and SCFAs may be involved in chronic intestinal inflammation and the pathophysiology of IBD.
Bile acids play an essential role in the emulsification and absorption of fats and the elimination of cholesterol. They are a type of steroid acid found in bile and synthesized from cholesterol by the liver. Primary bile acids, such as cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid, are synthesized in the host liver and are metabolized to secondary bile acids, such as deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid by anaerobic microorganisms, particularly clostridial species, in the colon [238]. Many gut microbes can produce unique bile acids by conjugating amino acids to cholic acid [239]. Bile acids exert many metabolic effects by binding to various receptors, including the farnesoid X receptor (FXR), pregnane X receptor (PXR), transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor 5 (TGR5), vitamin D receptor, and androstane receptor [240].
A bidirectional relationship exists between bile acids and the microbiota. Gut microbiota can deconjugate amino acid residues from primary bile acids using the enzyme bile salt hydrolases [241]. Labbé et al. [242] analyzed metagenomics samples from the Human Microbiome Project and MetaHit. They found a reduction in the clusters of bile salt hydrolase (bsh) genes associated with Firmicutes in IBD. Bile acids have strong antimicrobial properties [243] and may change gut microbiota composition and density. They may have direct antimicrobial effects on bacteria such as Bifidobacterium breve and Lactobacillus salivarius [243]. The indirect antimicrobial effects of bile acids include stimulating the production of antimicrobial peptides from the host and activation of FXR [244-246]. Bile acids are crucial in the development of colonic RORγ+ Treg in mice, suggesting their anti-inflammatory effects [247].
Various studies have reported altered bile acid profiles in fecal samples of IBD patients [119,193,248-250]. Bile acid synthesis is regulated by the FXR. Once activated, FXR can reduce bile acid synthesis and uptake by downregulating gene expression in enterocytes [251]. FXR activation also exerts anti-inflammatory effects and is protective in chemically induced colitis [252,253]. Concomitant with this finding, studies have shown a significant reduction in FXR expression in CD patients [252,254].
Tryptophan is an essential aromatic amino acid. Alterations in the concentration of tryptophan and its metabolites and changes in the activity of associated enzymes have been reported in IBD [255]. Dietary tryptophan is metabolized by 3 metabolic pathways: the kynurenine pathway, serotonin pathway, and indole pathway. The indole pathway is the microbial pathway used by the gut microbes to metabolize indole, while the kynurenine and serotonin pathways are the endogenous pathways. The majority of dietary tryptophan is metabolized by the kynurenine pathway [256]. The microbial pathway can convert tryptophan into various bioactive indole derivatives, such as indole propionic acid, indole acetic acid, indole acrylic acid, indole 3-aldehyde, and tryptamine. These indole metabolites can act as agonists for the AhR, an important transcription factor that regulates T cell immunity, cytokine expression, and anti-inflammatory effects through IL-22 [257-261]. Concomitant with these findings, Monteleone et al. [262] reported that the inflamed mucosa of CD patients had reduced expression of AhR. Lactobacillus strains that can activate AhR have been shown to reduce the severity of DSS-induced colitis [263]. Indole metabolites can also activate PXR, which promotes intestinal barrier function in a mouse model of CRC [264]. Indole propionic acid inhibits TNF production by binding to PXR [258]. Reduced levels of indole propionic acid have been found in the serum of UC patients [265]. Other indole metabolites, such as indole acrylic acid, are also reduced in patients with IBD [258,266]. Wlodarska et al. [266] found that Peptostreptococcus russellii, a mucin-utilizing bacterium, could metabolize tryptophan to indole acrylic acid thus could reduce susceptibility to colitis. A critical study by Nikolaus et al. [255] identified a crucial link between tryptophan metabolism and IBD in a large clinical cohort of 535 patients. This study found an inverse relationship between tryptophan levels and IBD. A similar study found that a deficiency of dietary tryptophan could worsen colitis in mouse models [267].
Succinate is a TCA intermediate produced by both the host and the microbiota [268]. Succinate metabolism has gathered much attention in recent years due to its potential link with IBD. Succinate acts as a key pro-inflammatory signal, and its levels are increased in CD [269,270]. Similarly, the levels of fecal succinate have also been found to be increased in UC and CD patients [216]. Concomitant with these findings, both UC and CD patients have reduced abundances of succinate-utilizing Phascolarctobacterium compared to healthy individuals [200].
Although a complete cure for IBD is unknown, the current treatment regimen is adopted to reduce inflammation, promote clinical remission, and prevent disease relapse [271-273]. The human gut microbiota is being recognized as a potential therapeutic solution for IBD [274]. Studies have demonstrated that probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics effectively modulate the gut microbiota [275-277]. Though promising results have been obtained, much research is needed to establish the efficacy of these treatment options. Clinical trials have shed some light on manipulating gut microbiota through probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) for IBD treatment (Tables 2 and 3).
Probiotics are defined as live microorganisms that provide multiple health benefits when administered in adequate amounts [278]. Probiotics deliver many health benefits, modify the gut microflora composition, enhance the intestinal mucosal barrier function, prevent the colonization of pathogenic microbes, and modulate the local and systemic immune responses [279-285]. Accumulating evidence has also revealed that probiotics influence gut microbiota. Since IBD has been linked to dysbiosis of the gut microflora, restoring the normal gut microflora through probiotics is one of the recommended therapeutic options for IBD. Probiotics may prevent IBD by reducing intestinal inflammation [286], downregulating inflammation pathways [287], and producing SCFAs [212]. Studies have found that probiotic therapy can suppress the NF-κB signaling pathway [288,289] and decrease inflammatory cytokines [290].
The most important probiotics for IBD treatment are Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, and yeasts [291]. Other probiotics, such as Clostridium butyricum have also been shown to be effective in suppressing inflammation in experimental colitis and are therefore considered for IBD treatment [292]. Although no gold standard regarding effective probiotic doses exists, most commercially available probiotics contain one to 10 billion CFU per dose [290,293]. S. boulardii, Escherichia coli Nissle 1917, and B. breve strain Yakult have shown effectiveness similar to 5-aminosalicylic acid (mesalamine) in maintaining clinical remission in UC patients [294-296]. European Crohn’s and Colitis Organization guidelines mention E. coli Nissle 1917 as an effective alternative to mesalamine in the maintenance of remission in UC patients [297]. Lactobacillus reuteri ATCC 55730, when combined with mesalamine, showed a better clinical response and remission rate in children with UC [298]. Jin et al. [299] found that Lactobacillus plantarum could restore gut barrier function and reduce intestinal inflammation in a mouse model of DSS-induced colitis.
Various probiotic cocktails have been used for IBD treatment. The probiotic VSL#3 is a mixture of 8 bacterial strains: Lactobacillus acidophilus, L. plantarum, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus delbrueckii subspecies bulgaricus, B. breve, Bifidobacterium longum, Bifidobacterium infantis, and Streptococcus salivarius subspecies thermophiles [300]. Studies have found the effectiveness of VSL#3 in inducing remission in patients with mild-to-moderately active UC [301,302]. VSL#3 can also reduce inflammation in pouchitis [303,304]. Studies on a mouse model have shown that VSL#3 effectively reduces ileitis [305] and 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-induced colitis [306]. Fedorak et al. [290] reported that VSL#3 could reduce endoscopic recurrence after surgery for CD. Miele et al. [307] showed that combining VSL#3 with 5-aminosalicylic acid (mesalamine) and steroids could significantly improve the remission rate in children with UC. Huynh et al. [308] also showed that combining VSL#3 with standard therapy could improve histological scores in children with UC. A meta-analysis by Mardini and Grigorian [309] suggested that VSL#3 in combination with standard therapy was more effective than standard therapy for UC.
Administration of a cocktail of L. acidophilus, L. plantarum, Bifidobacterium lactis, and B. breve has been shown to enhance the production of intestinal mucus and goblet cells in mice [310]. Another cocktail mixture of L. plantarum, L. acidophilus, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, and E. faecium can increase wound healing and enhance the integrity of tight junctions of epithelial cells [311]. Chen et al. [312] reported that the probiotic mixture of B. infantis, L. acidophilus, and Enterococcus faecalis with or without Bacillus cereus could restore the relative abundance of Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Bacteroides, and Akkermansia in a mouse model of DSS-induced chronic colitis. In UC patients, a mixture of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium significantly increases the population of Proteobacteria and reduces Gramnegative rods [313].
When combined with mesalazine S. boulardii, a yeast, can reduce the recurrence rates in CD patients [314]. S. boulardii can also reduce intestinal permeability, increase plasma levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokine, IL-10 and increase intestinal IgA secretion [315]. S. boulardii has also been shown to prevent relapses in patients with CD [316]. Contrary to these studies, Bourreille et al. [317] reported that S. boulardii did not demonstrate any significant efficacy in IBD compared to control individuals.
Next-generation probiotics (NGPs) include human gut commensals that produce some beneficial metabolites [291]. Currently, their use is limited by difficulties in isolation, characterization, cultivation, and formulation. One of the potential NGPs is F. prausnitzii, which has anti-inflammatory properties [318,319]. Several animal experiments have confirmed the therapeutic potential of F. prausnitzii in UC.318,320-322 C. butyricum MIYAIRI, a butyrate-producing bacterium, is effective in preventing pouchitis and alterations of the microbiota in UC patients [83]. Recently, Ma et al. [323] found that C. butyricum MIYAIRI-II could alleviate colitis-related parameters in a mouse model of DSS-induced colitis. NGPs also include genetically engineered probiotic strains. Recently, Zhou et al. [324] genetically engineered E. coli Nissle 1917 to overexpress catalase and superoxide dismutase for treating intestinal inflammation. They found that genetically engineered E. coli Nissle 1917 could effectively alleviate inflammation and repair epithelial barriers in the colon of a mouse model of IBD. They also found that genetically engineered E. coli Nissle 1917 improved the abundance of microbes that maintain intestinal homeostasis, such as Lachnospiraceae and Odoribacter. Many non-conventional probiotics, including Akkermansia muciniphila [325,326], Companilactobacillus crustorum [327], Pediococcus pentosaceus [328,329], Lactiplantibacillus plantarum [330], B. thetaiotaomicron [331], and Christensenella minuta [332], have shown promise in animal studies. More extensive clinical cohort studies are required to evaluate their efficacy in humans.
However, Cochran systematic reviews have concluded that there is no evidence to suggest that probiotics are beneficial for the induction or maintenance of remission in CD [333,334]. Zhang et al. [335], in a systematic review, also concluded that there was no evidence to support the use of probiotics in CD. Studies have also shown that L. rhamnosus GG has no additional benefit over placebo in treating CD [336-338]. Marteau et al. [339] reported that Lactobacillus johnsonii and E. coli Nissle had no significant benefit in maintaining IBD remission. Mallon et al. [340] found that combining S. boulardii and VSL#3 did not significantly improve the remission rates of UC. Matthes et al. [341] reported that the rectal administration of E. coli Nissle for UC had no additional benefits over placebo. Petersen et al. [342] reported that using E. coli Nissle in probiotic therapy had a lower rate of clinical remission in UC. In a randomized controlled trial, Matsuoka et al. [343] reported that probiotics were not effective in maintaining remission in UC.
Prebiotics are food components that are selectively fermented by the gut microflora and help maintain healthy gut microbiota by stimulating the growth of beneficial bacteria [344]. Prebiotics mostly include fructooligosaccharides (FOS), galactooligosaccharides (GOS), and other oligosaccharides, such as pectin [277]. Prebiotics have shown some promise in IBD therapeutics, but some studies have shown contrary results. Prebiotics, such as inulin, have been shown to induce the growth of SCFA-producing bacteria, including Lactobacillus, F. prausnitzii, and Bifidobacterium [345-348]. Inulin has also been shown to improve histological lesions in patients with pouchitis [349]. FOS and GOS can improve the levels of F. prausnitzii [350]. FOS-enriched inulin supplementation can elevate the levels of butyrate [351,352]. FOS are known to increase the population of endogenous microflora, particularly Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium [353]. FOS are fermented by the gut microbes to produce SCFAs, which exert anti-inflammatory effects [68,354]. Contrary to this, Benjamin et al. [355] reported that the use of FOS in patients with active CD did not improve the remission rate. Casellas et al. [356] found that oligofructose-enriched inulin did not influence the remission rate in patients with UC but could reduce fecal calprotectin levels. The use of prebiotics in IBD treatment is limited by a few studies that are not sufficiently conclusive. More elaborate studies are required to show the efficacy and therapeutic effects of prebiotics for IBD treatment.
Preparations containing both prebiotics and probiotics are called synbiotics [357,358]. Clinical studies [275,357,359,360] and animal studies [361-365] have suggested that synbiotics are effective therapeutic options for IBD. However, contrary results have been obtained in other clinical intervention studies with IBD patients [366-368], raising doubts about their effectiveness.
FMT is an emerging biotherapeutic procedure that aims to restore gut microbial ecology by transplanting intestinal microbiota from healthy donors to ameliorate various gastrointestinal disorders [369,370]. FMT enhances the production of SCFAs and restores immune dysregulation [371-373]. FMT has proven successful in treating recurrent Clostridioides difficile infections resistant to antibiotic treatment [374-377].
FMT has gathered much attention recently as a new therapeutic option for IBD (Table 3). Studies have found that FMT is effective in inducing remission in UC patients [373,378-381]. Tian et al. [382] found that after FMT, there was a significant enrichment of Bacteroides, Proteus, and Prevotella and a decline in Klebsiella and Streptococcus. A meta-analysis by Colman and Rubin [383] showed a remission rate of 36.2% in IBD patients who received FMT. They also showed a higher remission rate in CD patients than in UC patients. In a randomized controlled trial by Moayyedi et al. [378], FMT induced clinical remission in patients with active UC. In another randomized placebo-controlled trial for UC by Paramsothy et al. [379], the remission rate of multidonorintensive FMT was higher than placebo. Similar results were obtained by Costello et al. [373] Contrary to these findings, a randomized controlled trial by Rossen et al. [384] failed to find any significant effect of FMT in patients with UC. In a pilot study, Sood et al. [381] concluded that FMT may be one of the therapeutic options for clinical remission in UC patients. Sokol et al. [385] carried out a pilot randomized controlled study to find the effects of FMT in CD patients showing clinical remission with systemic corticosteroids. In this study, the beneficial effects of FMT were evaluated using several clinically relevant endpoints, such as C-reactive protein level and CD Endoscopic Index of Severity. Kunde et al. [386] found significant improvement in 9 children with UC who received FMT via enema. Cui et al. [387] showed that FMT improved clinical outcomes in 57% of patients with steroid-dependent UC. A meta-analysis on FMT for IBD by Paramsothy et al. [372] showed a clinical remission rate of 50.5%. A meta-analysis by Caldeira et al. [388] reported that FMT had a complete remission rate of 37% for IBD patients.
However, various clinical studies conducted to examine the effect of FMT on IBD have obtained inconsistent results, raising doubts about its effectiveness. Available data suggest that the efficacy of FMT in treating IBD is not predictable [389]. Angelberger et al. [390] reported that only one UC patient showed some improvement after 12 weeks of FMT. Similarly, Suskind et al. [391] failed to find any significant improvement in 4 children who received a single FMT through a nasogastric tube. Such discrepant results in clinical trials may reflect the heterogeneity in disease biology, donor selection, FMT regimen, and individual response to the treatment.
The safety and questionable efficacy of FMT have precluded its wider use for IBD treatment. FMT is also associated with certain risks, further limiting its use as a therapeutic option [16]. The success rate of FMT in IBD treatment can be enhanced by standardizing various parameters, such as donor selection, route and mode of administration, and optimal dose and frequency of infusions.
The human gut is a complex ecosystem with a continuous crosstalk between microbes and host cells. A growing body of evidence has indicated a close association between alterations in gut microbiota and the pathophysiology of IBD. Furthermore, the microbial metabolites may also affect the progression of IBD. Since different studies provide inconsistent, even contradictory results, further studies must be carried out to reach a consensus. Advances in next-generation sequencing technology have enabled deep insights into the complex microbial communities inhabiting the human gut and have helped identify and compare the normal gut microbiota with the altered microbiota in IBD. Also, metabolomics has helped identify altered microbial metabolites in IBD patients. Further research describing the role of the gut microbiota in maintaining gut barrier function and the immune system is essential to understand IBD pathophysiology. The findings from such studies must be translated into clinical practice.
There is no known cure for IBD. The current treatment options help induce clinical remission by reducing inflammation. Though still in its infancy, targeted microbiota manipulation using probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and FMT is one of the potential armamentariums in IBD. Although promising results have been shown for many probiotics, including VSL#3 and E. coli Nissle 1917, clinical trials with larger cohorts must be carried out to reach conclusive evidence. NGPs, including engineered microbes, may provide a new direction for IBD treatment. Another microbiota-based intervention, FMT, has gathered much attention as a new therapeutic option for IBD, but its efficacy remains questionable. Standardization of various parameters will surely help increase its effectiveness and success rate in IBD. Future research should be directed towards utilizing gut microbiota for developing less invasive diagnostic tools for IBD and microbiota replacement as a potential therapeutic for IBD treatment.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Funding Source
The authors would like to acknowledge the NTU Start Up Grant (021337-00001), Wang Lee Wah Memorial Fund, and Singapore Ministry of Education (MOE) Tier 1 Academic Research Fund (RG37/22) for support of this work.
Author Contribution
Conceptualization: Pandey H, Wong SH, Lal D. Resources: Pandey H, Jain D, Tang DWT, Wong SH, Lal D. Diagrams: Tang DWT. Supervision: Lal D, Wong SH. Writing-original draft: Pandey H, Jain D, Tang DWT, Wong SH, Lal D. Writing-review & editing: Pandey H, Jain D, Tang DWT, Wong SH, Lal D. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Fig. 1.
Microbes involved in inflammatory bowel disease and their molecular mechanisms. Figure created with BioRender. B. fragilis, Bacteroides fragilis; E. faecium, Enterococcus faecium; E. coli, Escherichia coli; F. nucleatum, Fusobacterium nucleatum; F. prausnitzii, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii; M. stadtmanae, Methanosphaera stadtmanae; R. gnavus, Ruminococcus gnavus; TLR4, Toll-like receptor 4; BFT, B. fragilis toxin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; ETBF, enterotoxigenic B. fragilis; AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; IL, interleukin; PLC, phospholipase C; DAG, diacylglycerol; PKC, protein kinase C.

Fig. 2.
Microbial metabolites implicated in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and their molecular mechanisms. Figure created with BioRender. SCFA, short-chain fatty acid; PXR, pregnane X receptor; AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; IL, interleukin; Treg, T regulatory; GPCRs, G protein-coupled receptors; CD, Crohn’s disease; UC, ulcerative colitis; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; TGR5, transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor 5.
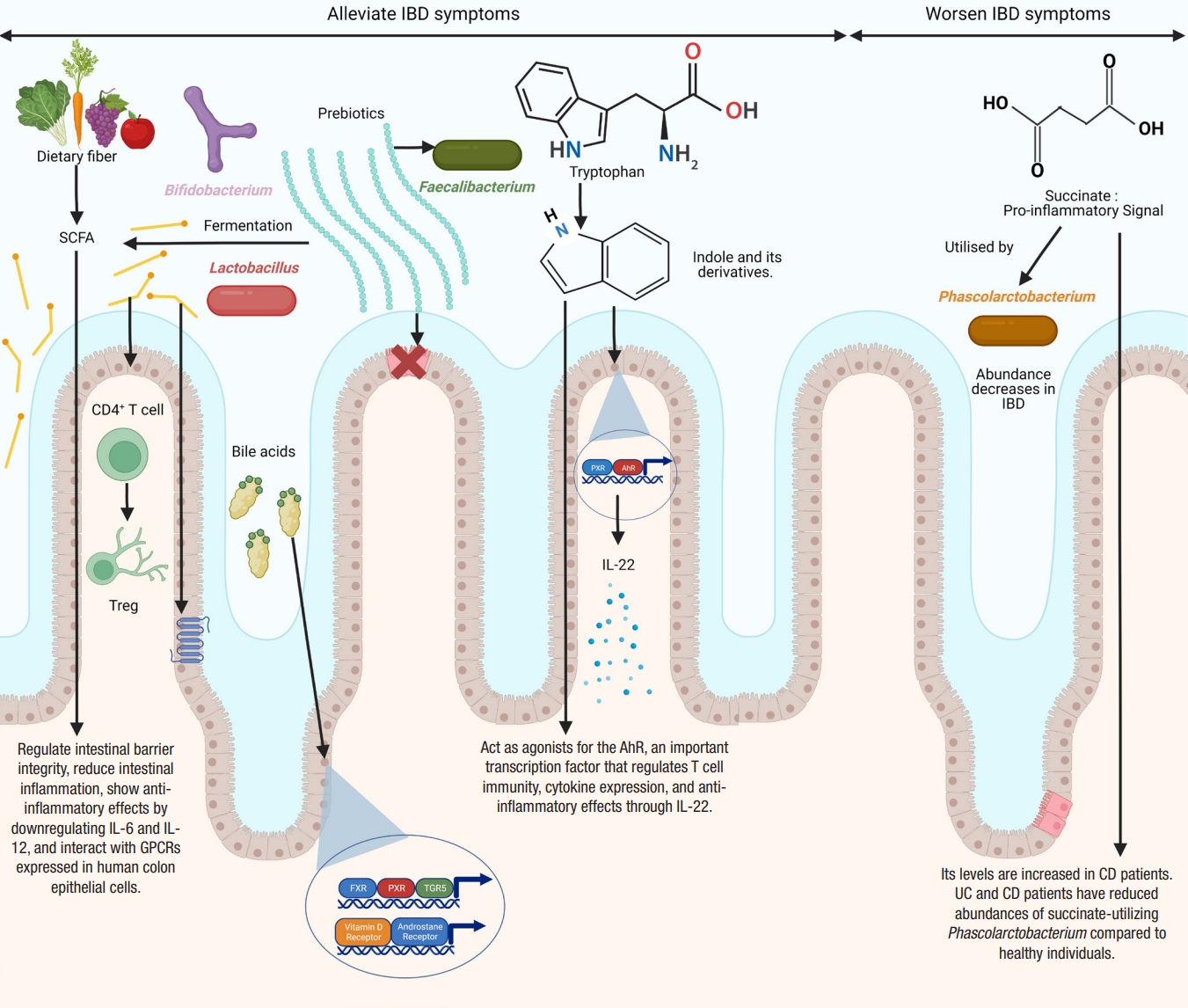
Table 1.
Putative IBD-Associated Gut Microbes and Potential Mechanism
Table 2.
Completed Clinical Trials on the Effects of Probiotics, Prebiotics and Synbiotics on Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Table 3.
Completed Clinical Trials on FMT in IBD
REFERENCES
1. Borowitz SM. The epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease: clues to pathogenesis? Front Pediatr 2022;10:1103713.



2. Kovarik JJ, Tillinger W, Hofer J, et al. Impaired anti-inflammatory efficacy of n-butyrate in patients with IBD. Eur J Clin Invest 2011;41:291-298.


3. Dmochowska N, Wardill HR, Hughes PA. Advances in imaging specific mediators of inflammatory bowel disease. Int J Mol Sci 2018;19:2471.



4. GBD 2017 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Collaborators. The global, regional, and national burden of inflammatory bowel disease in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020;5:17-30.

5. Ramos GP, Papadakis KA. Mechanisms of disease: inflammatory bowel diseases. Mayo Clin Proc 2019;94:155-165.



6. Ng SC, Shi HY, Hamidi N, et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet 2017;390:2769-2778.


7. Danese S, Malesci A, Vetrano S. Colitis-associated cancer: the dark side of inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2011;60:1609-1610.


8. Beaugerie L, Itzkowitz SH. Cancers complicating inflammatory bowel disease. N Engl J Med 2015;372:1441-1452.


9. Loddo I, Romano C. Inflammatory bowel disease: genetics, epigenetics, and pathogenesis. Front Immunol 2015;6:551.



11. Canavan C, Abrams KR, Mayberry J. Meta-analysis: colorectal and small bowel cancer risk in patients with Crohn’s disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2006;23:1097-1104.


12. Arthur JC, Perez-Chanona E, Mühlbauer M, et al. Intestinal inflammation targets cancer-inducing activity of the microbiota. Science 2012;338:120-123.



13. Torres J, Mehandru S, Colombel JF, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Crohn’s disease. Lancet 2017;389:1741-1755.


14. Ungaro R, Mehandru S, Allen PB, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Colombel JF. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet 2017;389:1756-1770.


15. Rowan-Nash AD, Korry BJ, Mylonakis E, Belenky P. Cross-domain and viral interactions in the microbiome. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2019;83:e00044-18.




16. Pandey H, Tang DW, Wong SH, Lal D. Gut microbiota in colorectal cancer: biological role and therapeutic opportunities. Cancers (Basel) 2023;15:866.



17. Bäckhed F. Programming of host metabolism by the gut microbiota. Ann Nutr Metab 2011;58 Suppl 2:44-52.

18. Round JL, Mazmanian SK. The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2009;9:313-323.




19. Sommer F, Anderson JM, Bharti R, Raes J, Rosenstiel P. The resilience of the intestinal microbiota influences health and disease. Nat Rev Microbiol 2017;15:630-638.



20. Dethlefsen L, Eckburg PB, Bik EM, Relman DA. Assembly of the human intestinal microbiota. Trends Ecol Evol 2006;21:517-523.


21. Turnbaugh PJ, Bäckhed F, Fulton L, Gordon JI. Diet-induced obesity is linked to marked but reversible alterations in the mouse distal gut microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2008;3:213-223.



23. Collado MC, Delgado S, Maldonado A, Rodríguez JM. Assessment of the bacterial diversity of breast milk of healthy women by quantitative real-time PCR. Lett Appl Microbiol 2009;48:523-528.


24. Biasucci G, Rubini M, Riboni S, Morelli L, Bessi E, Retetangos C. Mode of delivery affects the bacterial community in the newborn gut. Early Hum Dev 2010;86 Suppl 1:13-15.


25. Yatsunenko T, Rey FE, Manary MJ, et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2012;486:222-227.




26. Faith JJ, Guruge JL, Charbonneau M, et al. The long-term stability of the human gut microbiota. Science 2013;341:1237439.



27. David LA, Materna AC, Friedman J, et al. Host lifestyle affects human microbiota on daily timescales. Genome Biol 2014;15:R89.



28. Rothschild D, Weissbrod O, Barkan E, et al. Environment dominates over host genetics in shaping human gut microbiota. Nature 2018;555:210-215.

29. Andoh A. Physiological role of gut microbiota for maintaining human health. Digestion 2016;93:176-181.



30. Nishida A, Inoue R, Inatomi O, Bamba S, Naito Y, Andoh A. Gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin J Gastroenterol 2018;11:1-10.



31. Peterson DA, Frank DN, Pace NR, Gordon JI. Metagenomic approaches for defining the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases. Cell Host Microbe 2008;3:417-427.



32. Li G, Yang M, Zhou K, et al. Diversity of duodenal and rectal microbiota in biopsy tissues and luminal contents in healthy volunteers. J Microbiol Biotechnol 2015;25:1136-1145.


34. Carstens A, Roos A, Andreasson A, et al. Differential clustering of fecal and mucosa-associated microbiota in ‘healthy’ individuals. J Dig Dis 2018;19:745-752.



35. Rajilic-Stojanovic M, Figueiredo C, Smet A, et al. Systematic review: gastric microbiota in health and disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2020;51:582-602.



36. Corr SC, Hill C, Gahan CG. Understanding the mechanisms by which probiotics inhibit gastrointestinal pathogens. Adv Food Nutr Res 2009;56:1-15.

37. Podolsky DK. The current future understanding of inflammatory bowel disease. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2002;16:933-943.


38. Swidsinski A, Ladhoff A, Pernthaler A, et al. Mucosal flora in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 2002;122:44-54.


39. Andoh A, Kuzuoka H, Tsujikawa T, et al. Multicenter analysis of fecal microbiota profiles in Japanese patients with Crohn’s disease. J Gastroenterol 2012;47:1298-1307.



40. Kabeerdoss J, Jayakanthan P, Pugazhendhi S, Ramakrishna BS. Alterations of mucosal microbiota in the colon of patients with inflammatory bowel disease revealed by real time polymerase chain reaction amplification of 16S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. Indian J Med Res 2015;142:23-32.



41. Stojanov S, Berlec A, Štrukelj B. The influence of probiotics on the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio in the treatment of obesity and inflammatory bowel disease. Microorganisms 2020;8:1715.



42. Kamada N, Seo SU, Chen GY, Núñez G. Role of the gut microbiota in immunity and inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2013;13:321-335.



44. Brown EM, Kenny DJ, Xavier RJ. Gut microbiota regulation of T cells during inflammation and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol 2019;37:599-624.


45. Ott SJ, Musfeldt M, Wenderoth DF, et al. Reduction in diversity of the colonic mucosa associated bacterial microflora in patients with active inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2004;53:685-693.



46. DeGruttola AK, Low D, Mizoguchi A, Mizoguchi E. Current understanding of dysbiosis in disease in human and animal models. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2016;22:1137-1150.



47. Singh VP, Proctor SD, Willing BP. Koch’s postulates, microbial dysbiosis and inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Microbiol Infect 2016;22:594-599.


48. Ni J, Wu GD, Albenberg L, Tomov VT. Gut microbiota and IBD: causation or correlation? Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;14:573-584.




49. Sartor RB. Mechanisms of disease: pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006;3:390-407.



50. Bringiotti R, Ierardi E, Lovero R, Losurdo G, Di Leo A, Principi M. Intestinal microbiota: the explosive mixture at the origin of inflammatory bowel disease? World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2014;5:550-559.



51. Liu JZ, van Sommeren S, Huang H, et al. Association analyses identify 38 susceptibility loci for inflammatory bowel disease and highlight shared genetic risk across populations. Nat Genet 2015;47:979-986.




52. Su HJ, Chiu YT, Chiu CT, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease and its treatment in 2018: global and Taiwanese status updates. J Formos Med Assoc 2019;118:1083-1092.


53. Manichanh C, Borruel N, Casellas F, Guarner F. The gut microbiota in IBD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;9:599-608.



54. Matsuoka K, Kanai T. The gut microbiota and inflammatory bowel disease. Semin Immunopathol 2015;37:47-55.




56. Gophna U, Sommerfeld K, Gophna S, Doolittle WF, Veldhuyzen van Zanten SJ. Differences between tissue-associated intestinal microfloras of patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. J Clin Microbiol 2006;44:4136-4141.




57. Frank DN, St Amand AL, Feldman RA, Boedeker EC, Harpaz N, Pace NR. Molecular-phylogenetic characterization of microbial community imbalances in human inflammatory bowel diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007;104:13780-13785.



58. Xu J, Chen N, Wu Z, et al. 5-aminosalicylic acid alters the gut bacterial microbiota in patients with ulcerative colitis. Front Microbiol 2018;9:1274.



59. Zhou Y, Xu ZZ, He Y, et al. Gut microbiota offers universal biomarkers across ethnicity in inflammatory bowel disease diagnosis and infliximab response prediction. mSystems 2018;3:e00188-17.




60. Yu Y, Yang W, Li Y, Cong Y. Enteroendocrine cells: sensing gut microbiota and regulating inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2020;26:11-20.




61. Nemoto H, Kataoka K, Ishikawa H, et al. Reduced diversity and imbalance of fecal microbiota in patients with ulcerative colitis. Dig Dis Sci 2012;57:2955-2964.



62. Fuentes S, Rossen NG, van der Spek MJ, et al. Microbial shifts and signatures of long-term remission in ulcerative colitis after faecal microbiota transplantation. ISME J 2017;11:1877-1889.




63. Khalil NA, Walton GE, Gibson GR, Tuohy KM, Andrews SC. In vitro batch cultures of gut microbiota from healthy and ulcerative colitis (UC) subjects suggest that sulphate-reducing bacteria levels are raised in UC and by a protein-rich diet. Int J Food Sci Nutr 2014;65:79-88.


64. Gevers D, Kugathasan S, Denson LA, et al. The treatment-naive microbiome in new-onset Crohn’s disease. Cell Host Microbe 2014;15:382-392.



65. Zhu W, Winter MG, Byndloss MX, et al. Precision editing of the gut microbiota ameliorates colitis. Nature 2018;553:208-211.




66. Thomann AK, Mak JW, Zhang JW, et al. Review article: bugs, inflammation and mood-a microbiota-based approach to psychiatric symptoms in inflammatory bowel diseases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2020;52:247-266.



67. Fujimoto T, Imaeda H, Takahashi K, et al. Decreased abundance of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in the gut microbiota of Crohn’s disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013;28:613-619.

68. Takahashi K, Nishida A, Fujimoto T, et al. Reduced abundance of butyrate-producing bacteria species in the fecal microbial community in Crohn’s disease. Digestion 2016;93:59-65.



69. Scanlan PD, Marchesi JR. Micro-eukaryotic diversity of the human distal gut microbiota: qualitative assessment using culture-dependent and -independent analysis of faeces. ISME J 2008;2:1183-1193.



70. Ghavami SB, Rostami E, Sephay AA, et al. Alterations of the human gut Methanobrevibacter smithii as a biomarker for inflammatory bowel diseases. Microb Pathog 2018;117:285-289.


71. Qiu X, Ma J, Jiao C, et al. Alterations in the mucosa-associated fungal microbiota in patients with ulcerative colitis. Oncotarget 2017;8:107577-107588.



72. Fernandes MA, Verstraete SG, Phan TG, et al. Enteric virome and bacterial microbiota in children with ulcerative colitis and crohn disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2019;68:30-36.



73. Hoarau G, Mukherjee PK, Gower-Rousseau C, et al. Bacteriome and mycobiome interactions underscore microbial dysbiosis in familial Crohn’s disease. mBio 2016;7:e01250-16.




74. Barnich N, Darfeuille-Michaud A. Adherent-invasive Escherichia coli and Crohn’s disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2007;23:16-20.


75. Mukhopadhya I, Hansen R, El-Omar EM, Hold GL. IBD: what role do Proteobacteria play? Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;9:219-230.



76. Cammarota G, Ianiro G, Cianci R, Bibbò S, Gasbarrini A, Currò D. The involvement of gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis: potential for therapy. Pharmacol Ther 2015;149:191-212.


77. Palmela C, Chevarin C, Xu Z, et al. Adherent-invasive Escherichia coli in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2018;67:574-587.


78. Barnich N, Carvalho FA, Glasser AL, et al. CEACAM6 acts as a receptor for adherent-invasive E. coli, supporting ileal mucosa colonization in Crohn disease. J Clin Invest 2007;117:1566-1574.



79. Ahmed I, Roy BC, Khan SA, Septer S, Umar S. Microbiome, metabolome and inflammatory bowel disease. Microorganisms 2016;4:20.



80. Mancini NL, Rajeev S, Jayme TS, et al. Crohn’s disease pathobiont adherent-invasive E. coli disrupts epithelial mitochondrial networks with implications for gut permeability. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;11:551-571.



81. Martinez-Medina M, Garcia-Gil LJ. Escherichia coli in chronic inflammatory bowel diseases: an update on adherent invasive Escherichia coli pathogenicity. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2014;5:213-227.



82. Chervy M, Barnich N, Denizot J. Adherent-invasive E. coli: update on the lifestyle of a troublemaker in Crohn’s disease. Int J Mol Sci 2020;21:3734.



83. Yasueda A, Mizushima T, Nezu R, et al. The effect of Clostridium butyricum MIYAIRI on the prevention of pouchitis and alteration of the microbiota profile in patients with ulcerative colitis. Surg Today 2016;46:939-949.



84. Sears CL, Geis AL, Housseau F. Bacteroides fragilis subverts mucosal biology: from symbiont to colon carcinogenesis. J Clin Invest 2014;124:4166-4172.



85. Lukiw WJ. Bacteroides fragilis lipopolysaccharide and inflammatory signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Microbiol 2016;7:1544.



86. Huang JY, Lee SM, Mazmanian SK. The human commensal Bacteroides fragilis binds intestinal mucin. Anaerobe 2011;17:137-141.



87. Boleij A, Hechenbleikner EM, Goodwin AC, et al. The Bacteroides fragilis toxin gene is prevalent in the colon mucosa of colorectal cancer patients. Clin Infect Dis 2015;60:208-215.



88. Sears CL. Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis: a rogue among symbiotes. Clin Microbiol Rev 2009;22:349-369.




89. Zamani S, Hesam Shariati S, Zali MR, et al. Detection of enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis in patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut Pathog 2017;9:53.




90. Tan H, Zhao J, Zhang H, Zhai Q, Chen W. Novel strains of Bacteroides fragilis and Bacteroides ovatus alleviate the LPS-induced inflammation in mice. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2019;103:2353-2365.



91. Wu S, Morin PJ, Maouyo D, Sears CL. Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin induces c-Myc expression and cellular proliferation. Gastroenterology 2003;124:392-400.


92. Toprak NU, Yagci A, Gulluoglu BM, et al. A possible role of Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin in the aetiology of colorectal cancer. Clin Microbiol Infect 2006;12:782-786.


93. Rabizadeh S, Rhee KJ, Wu S, et al. Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis: a potential instigator of colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2007;13:1475-1483.



94. Grivennikov S, Karin E, Terzic J, et al. IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of intestinal epithelial cells and development of colitis-associated cancer. Cancer Cell 2009;15:103-113.



95. Housseau F, Sears CL. Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis (ETBF)-mediated colitis in Min (Apc+/-) mice: a human commensal-based murine model of colon carcinogenesis. Cell Cycle 2010;9:3-5.



96. Geis AL, Fan H, Wu X, et al. Regulatory T-cell response to enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis colonization triggers IL17-dependent colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Discov 2015;5:1098-1109.




97. Chung L, Orberg ET, Geis AL, et al. Bacteroides fragilis toxin coordinates a pro-carcinogenic inflammatory cascade via targeting of colonic epithelial cells. Cell Host Microbe 2018;23:421.



98. Goodwin AC, Destefano Shields CE, et al. Polyamine catabolism contributes to enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis-induced colon tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011;108:15354-15359.



99. Kordahi MC, Stanaway IB, Avril M, et al. Genomic and functional characterization of a mucosal symbiont involved in early-stage colorectal cancer. Cell Host Microbe 2021;29:1589-1598.e6.



100. Maslowski KM, Vieira AT, Ng A, et al. Regulation of inflammatory responses by gut microbiota and chemoattractant receptor GPR43. Nature 2009;461:1282-1286.




101. Round JL, Lee SM, Li J, et al. The Toll-like receptor 2 pathway establishes colonization by a commensal of the human microbiota. Science 2011;332:974-977.



102. Verma R, Verma AK, Ahuja V, Paul J. Real-time analysis of mucosal flora in patients with inflammatory bowel disease in India. J Clin Microbiol 2010;48:4279-4282.




103. Hall AB, Yassour M, Sauk J, et al. A novel Ruminococcus gnavus clade enriched in inflammatory bowel disease patients. Genome Med 2017;9:103.




104. Henke MT, Kenny DJ, Cassilly CD, Vlamakis H, Xavier RJ, Clardy J. Ruminococcus gnavus, a member of the human gut microbiome associated with Crohn’s disease, produces an inflammatory polysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019;116:12672-12677.



105. Duncan SH, Hold GL, Harmsen HJ, Stewart CS, Flint HJ. Growth requirements and fermentation products of Fusobacterium prausnitzii, and a proposal to reclassify it as Faecalibacterium prausnitzii gen. nov., comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2002;52:2141-2146.


106. Mentella MC, Scaldaferri F, Pizzoferrato M, Gasbarrini A, Miggiano GA. Nutrition, IBD and gut microbiota: a review. Nutrients 2020;12:944.



107. Sokol H, Pigneur B, Watterlot L, et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is an anti-inflammatory commensal bacterium identified by gut microbiota analysis of Crohn disease patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008;105:16731-16736.



108. Vermeiren J, Van den Abbeele P, Laukens D, et al. Decreased colonization of fecal Clostridium coccoides/Eubacterium rectale species from ulcerative colitis patients in an in vitro dynamic gut model with mucin environment. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 2012;79:685-696.


109. Machiels K, Joossens M, Sabino J, et al. A decrease of the butyrate-producing species Roseburia hominis and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii defines dysbiosis in patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut 2014;63:1275-1283.


110. Lopez-Siles M, Martinez-Medina M, Abellà C, et al. Mucosaassociated Faecalibacterium prausnitzii phylotype richness is reduced in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Appl Environ Microbiol 2015;81:7582-7592.




111. Quévrain E, Maubert MA, Michon C, et al. Identification of an anti-inflammatory protein from Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, a commensal bacterium deficient in Crohn’s disease. Gut 2016;65:415-425.



112. Heidarian F, Alebouyeh M, Shahrokh S, Balaii H, Zali MR. Altered fecal bacterial composition correlates with disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease and the extent of IL8 induction. Curr Res Transl Med 2019;67:41-50.


113. Lloyd-Price J, Arze C, Ananthakrishnan AN, et al. Multi-omics of the gut microbial ecosystem in inflammatory bowel diseases. Nature 2019;569:655-662.




114. Pittayanon R, Lau JT, Leontiadis GI, et al. Differences in gut microbiota in patients with vs without inflammatory bowel diseases: a systematic review. Gastroenterology 2020 158:930-946.e1.


115. Varela E, Manichanh C, Gallart M, et al. Colonisation by Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and maintenance of clinical remission in patients with ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2013;38:151-161.


116. Zhou L, Zhang M, Wang Y, et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii produces butyrate to maintain Th17/Treg balance and to ameliorate colorectal colitis by inhibiting histone deacetylase 1. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2018;24:1926-1940.


117. Imhann F, Vich Vila A, Bonder MJ, et al. Interplay of host genetics and gut microbiota underlying the onset and clinical presentation of inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2018;67:108-119.



118. Vich Vila A, Imhann F, Collij V, et al. Gut microbiota composition and functional changes in inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome. Sci Transl Med 2018;10:eaap8914.

119. Franzosa EA, Sirota-Madi A, Avila-Pacheco J, et al. Gut microbiome structure and metabolic activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Microbiol 2019;4:293-305.




120. Ryz NR, Patterson SJ, Zhang Y, et al. Active vitamin D (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3) increases host susceptibility to Citrobacter rodentium by suppressing mucosal Th17 responses. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2012;303:G1299-G1311.



121. Nazareth N, Magro F, Machado E, et al. Prevalence of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis and Escherichia coli in blood samples from patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Med Microbiol Immunol 2015;204:681-692.



122. Seishima J, Iida N, Kitamura K, et al. Gut-derived Enterococcus faecium from ulcerative colitis patients promotes colitis in a genetically susceptible mouse host. Genome Biol 2019;20:252.




123. Ohkusa T, Yoshida T, Sato N, Watanabe S, Tajiri H, Okayasu I. Commensal bacteria can enter colonic epithelial cells and induce proinflammatory cytokine secretion: a possible pathogenic mechanism of ulcerative colitis. J Med Microbiol 2009;58:535-545.



124. Bashir A, Miskeen AY, Hazari YM, Asrafuzzaman S, Fazili KM. Fusobacterium nucleatum, inflammation, and immunity: the fire within human gut. Tumour Biol 2016;37:2805-2810.



125. Engevik M, Danhof H, Britton R, Versalovic J. Elucidating the role of Fusobacterium nucleatum in intestinal inflammation. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2020;26:S29.
126. Lurie-Weinberger MN, Gophna U. Archaea in and on the human body: health implications and future directions. PLoS Pathog 2015;11:e1004833.



127. Nkamga VD, Henrissat B, Drancourt M. Archaea: essential inhabitants of the human digestive microbiota. Human Microbiome J 2017;3:1-8.

128. Pausan MR, Csorba C, Singer G, et al. Exploring the archaeome: detection of archaeal signatures in the human body. Front Microbiol 2019;10:2796.



129. Kim JY, Whon TW, Lim MY, et al. The human gut archaeome: identification of diverse haloarchaea in Korean subjects. Microbiome 2020;8:114.




130. Samuel BS, Gordon JI. A humanized gnotobiotic mouse model of host-archaeal-bacterial mutualism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006;103:10011-10016.



131. Blais Lecours P, Marsolais D, Cormier Y, et al. Increased prevalence of Methanosphaera stadtmanae in inflammatory bowel diseases. PLoS One 2014;9:e87734.



132. Bang C, Weidenbach K, Gutsmann T, Heine H, Schmitz RA. The intestinal archaea Methanosphaera stadtmanae and Methanobrevibacter smithii activate human dendritic cells. PLoS One 2014;9:e99411.



133. Oxley AP, Lanfranconi MP, Würdemann D, et al. Halophilic archaea in the human intestinal mucosa. Environ Microbiol 2010;12:2398-2410.


134. Chehoud C, Albenberg LG, Judge C, et al. Fungal signature in the gut microbiota of pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2015;21:1948-1956.



135. Qin J, Li R, Raes J, et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010;464:59-65.


136. Lewis JD, Chen EZ, Baldassano RN, et al. Inflammation, antibiotics, and diet as environmental stressors of the gut microbiome in pediatric Crohn’s disease. Cell Host Microbe 2015;18:489-500.



137. Hallen-Adams HE, Suhr MJ. Fungi in the healthy human gastrointestinal tract. Virulence 2017;8:352-358.



138. Jones L, Kumar J, Mistry A, et al. The transformative possibilities of the microbiota and mycobiota for health, disease, aging, and technological innovation. Biomedicines 2019;7:24.



139. Liguori G, Lamas B, Richard ML, et al. Fungal dysbiosis in mucosa-associated microbiota of Crohn’s disease patients. J Crohns Colitis 2016;10:296-305.



140. Lam S, Zuo T, Ho M, Chan FK, Chan PK, Ng SC. Review article: fungal alterations in inflammatory bowel diseases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2019;50:1159-1171.



141. Iliev ID, Funari VA, Taylor KD, et al. Interactions between commensal fungi and the C-type lectin receptor Dectin-1 influence colitis. Science 2012;336:1314-1317.



142. Wang T, Pan D, Zhou Z, et al. Dectin-3 deficiency promotes colitis development due to impaired antifungal innate immune responses in the gut. PLoS Pathog 2016;12:e1005662.



143. Zelante T, De Luca A, Bonifazi P, et al. IL-23 and the Th17 pathway promote inflammation and impair antifungal immune resistance. Eur J Immunol 2007;37:2695-2706.


144. Conti HR, Shen F, Nayyar N, et al. Th17 cells and IL-17 receptor signaling are essential for mucosal host defense against oral candidiasis. J Exp Med 2009;206:299-311.


145. Saunus JM, Wagner SA, Matias MA, Hu Y, Zaini ZM, Farah CS. Early activation of the interleukin-23-17 axis in a murine model of oropharyngeal candidiasis. Mol Oral Microbiol 2010;25:343-356.


146. Tiago FC, Porto BA, Ribeiro NS, et al. Effect of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain UFMG A-905 in experimental model of inflammatory bowel disease. Benef Microbes 2015;6:807-815.


147. Pericolini E, Gabrielli E, Ballet N, et al. Therapeutic activity of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae-based probiotic and inactivated whole yeast on vaginal candidiasis. Virulence 2017;8:74-90.




148. Guslandi M, Giollo P, Testoni PA. A pilot trial of Saccharomyces boulardii in ulcerative colitis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2003;15:697-698.


149. Thomas S, Metzke D, Schmitz J, Dörffel Y, Baumgart DC. Anti-inflammatory effects of Saccharomyces boulardii mediated by myeloid dendritic cells from patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2011;301:G1083-G1092.


150. Kellermayer R, Mir SA, Nagy-Szakal D, et al. Microbiota separation and C-reactive protein elevation in treatment-naïve pediatric granulomatous Crohn disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2012;55:243-250.



151. Limon JJ, Tang J, Li D, et al. Malassezia is associated with Crohn’s disease and exacerbates colitis in mouse models. Cell Host Microbe 2019;25:377-388.e6.



152. Magiatis P, Pappas P, Gaitanis G, et al. Malassezia yeasts produce a collection of exceptionally potent activators of the Ah (dioxin) receptor detected in diseased human skin. J Invest Dermatol 2013;133:2023-2030.



153. Wheeler ML, Limon JJ, Underhill DM. Immunity to commensal fungi: detente and disease. Annu Rev Pathol 2017;12:359-385.



154. Spatz M, Richard ML. Overview of the potential role of Malassezia in gut health and disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2020;10:201.



155. Swanson HI. Cytochrome P450 expression in human keratinocytes: an aryl hydrocarbon receptor perspective. Chem Biol Interact 2004;149:69-79.


156. Minot S, Bryson A, Chehoud C, Wu GD, Lewis JD, Bushman FD. Rapid evolution of the human gut virome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013;110:12450-12455.



157. Shkoporov AN, Clooney AG, Sutton TD, et al. The human gut virome is highly diverse, stable, and individual specific. Cell Host Microbe 2019;26:527-541.


158. Ungaro F, Massimino L, D’Alessio S, Danese S. The gut virome in inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis: from metagenomics to novel therapeutic approaches. United European Gastroenterol J 2019;7:999-1007.




159. Zuo T, Lu XJ, Zhang Y, et al. Gut mucosal virome alterations in ulcerative colitis. Gut 2019;68:1169-1179.



160. Clooney AG, Sutton TD, Shkoporov AN, et al. Whole-virome analysis sheds light on viral dark matter in inflammatory bowel disease. Cell Host Microbe 2019;26:764-778.


161. Waller AS, Yamada T, Kristensen DM, et al. Classification and quantification of bacteriophage taxa in human gut metagenomes. ISME J 2014;8:1391-1402.




162. Norman JM, Handley SA, Baldridge MT, et al. Disease-specific alterations in the enteric virome in inflammatory bowel disease. Cell 2015;160:447-460.



163. Pérez-Brocal V, García-López R, Vázquez-Castellanos JF, et al. Study of the viral and microbial communities associated with Crohn’s disease: a metagenomic approach. Clin Transl Gastroenterol 2013;4:e36.




164. Wang W, Jovel J, Halloran B, et al. Metagenomic analysis of microbiome in colon tissue from subjects with inflammatory bowel diseases reveals interplay of viruses and bacteria. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2015;21:1419-1427.



165. Duerkop BA, Kleiner M, Paez-Espino D, et al. Murine colitis reveals a disease-associated bacteriophage community. Nat Microbiol 2018;3:1023-1031.




166. Seth RK, Maqsood R, Mondal A, et al. Gut DNA virome diversity and its association with host bacteria regulate inflammatory phenotype and neuronal immunotoxicity in experimental gulf war illness. Viruses 2019;11:968.



167. Gogokhia L, Buhrke K, Bell R, et al. Expansion of bacteriophages is linked to aggravated intestinal inflammation and colitis. Cell Host Microbe 2019;25:285-299.



168. Pérez-Brocal V, García-López R, Nos P, Beltrán B, Moret I, Moya A. Metagenomic analysis of Crohn’s disease patients identifies changes in the virome and microbiome related to disease status and therapy, and detects potential interactions and biomarkers. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2015;21:2515-2532.


169. Cornuault JK, Petit MA, Mariadassou M, et al. Phages infecting Faecalibacterium prausnitzii belong to novel viral genera that help to decipher intestinal viromes. Microbiome 2018;6:65.




170. Galtier M, De Sordi L, Sivignon A, et al. bacteriophages targeting adherent invasive Escherichia coli strains as a promising new treatment for Crohn’s disease. J Crohns Colitis 2017;11:840-847.


171. Yang JY, Kim MS, Kim E, et al. Enteric viruses ameliorate gut inflammation via toll-like receptor 3 and toll-like receptor 7-mediated interferon-β production. Immunity 2016;44:889-900.


173. Ungaro F, Massimino L, Furfaro F, et al. Metagenomic analysis of intestinal mucosa revealed a specific eukaryotic gut virome signature in early-diagnosed inflammatory bowel disease. Gut Microbes 2019;10:149-158.



174. Cadwell K, Patel KK, Maloney NS, et al. Virus-plus-susceptibility gene interaction determines Crohn’s disease gene Atg16L1 phenotypes in intestine. Cell 2010;141:1135-1145.



175. Bolsega S, Basic M, Smoczek A, et al. Composition of the intestinal microbiota determines the outcome of virus-triggered colitis in mice. Front Immunol 2019;10:1708.



176. Ananthakrishnan AN, Luo C, Yajnik V, et al. Gut microbiome function predicts response to anti-integrin biologic therapy in inflammatory bowel diseases. Cell Host Microbe 2017;21:603-610.



177. Lopez-Siles M, Martinez-Medina M, Busquets D, et al. Mucosa-associated Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Escherichia coli co-abundance can distinguish irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease phenotypes. Int J Med Microbiol 2014;304:464-475.


178. Prosberg M, Bendtsen F, Vind I, Petersen AM, Gluud LL. The association between the gut microbiota and the inflammatory bowel disease activity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand J Gastroenterol 2016;51:1407-1415.


179. Duranti S, Gaiani F, Mancabelli L, et al. Elucidating the gut microbiome of ulcerative colitis: bifidobacteria as novel microbial biomarkers. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 2016;92:fiw191.


180. Gong D, Gong X, Wang L, Yu X, Dong Q. Involvement of reduced microbial diversity in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2016;2016:6951091.




181. Sartor RB, Wu GD. Roles for intestinal bacteria, viruses, and fungi in pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases and therapeutic approaches. Gastroenterology 2017;152:327-339.


182. Dong LN, Wang M, Guo J, Wang JP. Role of intestinal microbiota and metabolites in inflammatory bowel disease. Chin Med J (Engl) 2019;132:1610-1614.



183. Wang W, Chen L, Zhou R, et al. Increased proportions of Bifidobacterium and the Lactobacillus group and loss of butyrate-producing bacteria in inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Microbiol 2014;52:398-406.




184. Nishino K, Nishida A, Inoue R, et al. Analysis of endoscopic brush samples identified mucosa-associated dysbiosis in inflammatory bowel disease. J Gastroenterol 2018;53:95-106.



185. Fukuda K, Fujita Y. Determination of the discriminant score of intestinal microbiota as a biomarker of disease activity in patients with ulcerative colitis. BMC Gastroenterol 2014;14:49.




186. He XX, Li YH, Yan PG, et al. Relationship between clinical features and intestinal microbiota in Chinese patients with ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2021;27:4722-4737.



187. Pascal V, Pozuelo M, Borruel N, et al. A microbial signature for Crohn’s disease. Gut 2017;66:813-822.



188. Le Gall G, Noor SO, Ridgway K, et al. Metabolomics of fecal extracts detects altered metabolic activity of gut microbiota in ulcerative colitis and irritable bowel syndrome. J Proteome Res 2011;10:4208-4218.


189. De Preter V, Machiels K, Joossens M, et al. Faecal metabolite profiling identifies medium-chain fatty acids as discriminating compounds in IBD. Gut 2015;64:447-458.


190. Santoru ML, Piras C, Murgia A, et al. Cross sectional evaluation of the gut-microbiome metabolome axis in an Italian cohort of IBD patients. Sci Rep 2017;7:9523.




191. Marchesi JR, Holmes E, Khan F, et al. Rapid and noninvasive metabonomic characterization of inflammatory bowel disease. J Proteome Res 2007;6:546-551.


192. Bjerrum JT, Wang Y, Hao F, et al. Metabonomics of human fecal extracts characterize ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease and healthy individuals. Metabolomics 2015;11:122-133.




193. Jacobs JP, Goudarzi M, Singh N, et al. A disease-associated microbial and metabolomics state in relatives of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease patients. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;2:750-766.



194. Kolho KL, Pessia A, Jaakkola T, de Vos WM, Velagapudi V. Faecal and serum metabolomics in paediatric inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis 2017;11:321-334.


195. Ooi M, Nishiumi S, Yoshie T, et al. GC/MS-based profiling of amino acids and TCA cycle-related molecules in ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Res 2011;60:831-840.



196. Stephens NS, Siffledeen J, Su X, Murdoch TB, Fedorak RN, Slupsky CM. Urinary NMR metabolomic profiles discriminate inflammatory bowel disease from healthy. J Crohns Colitis 2013;7:e42-e48.


197. Williams HR, Cox IJ, Walker DG, et al. Differences in gut microbial metabolism are responsible for reduced hippurate synthesis in Crohn’s disease. BMC Gastroenterol 2010;10:108.




198. Hisamatsu T, Okamoto S, Hashimoto M, et al. Novel, objective, multivariate biomarkers composed of plasma amino acid profiles for the diagnosis and assessment of inflammatory bowel disease. PLoS One 2012;7:e31131.



199. Postler TS, Ghosh S. Understanding the holobiont: how microbial metabolites affect human health and shape the immune system. Cell Metab 2017;26:110-130.



200. Morgan XC, Tickle TL, Sokol H, et al. Dysfunction of the intestinal microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease and treatment. Genome Biol 2012;13:R79.



201. Louis P, Hold GL, Flint HJ. The gut microbiota, bacterial metabolites and colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Microbiol 2014;12:661-672.



202. Dalile B, Van Oudenhove L, Vervliet B, Verbeke K. The role of short-chain fatty acids in microbiota-gut-brain communication. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019;16:461-478.



203. Liu P, Wang Y, Yang G, et al. The role of short-chain fatty acids in intestinal barrier function, inflammation, oxidative stress, and colonic carcinogenesis. Pharmacol Res 2021;165:105420.


204. Flint HJ, Scott KP, Louis P, Duncan SH. The role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;9:577-589.



205. Louis P, Flint HJ. Formation of propionate and butyrate by the human colonic microbiota. Environ Microbiol 2017;19:29-41.



206. Jang YS, Im JA, Choi SY, Lee JI, Lee SY. Metabolic engineering of Clostridium acetobutylicum for butyric acid production with high butyric acid selectivity. Metab Eng 2014;23:165-174.


207. Deleu S, Machiels K, Raes J, Verbeke K, Vermeire S. Short chain fatty acids and its producing organisms: an overlooked therapy for IBD? EBioMedicine 2021;66:103293.



208. Smith PM, Howitt MR, Panikov N, et al. The microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, regulate colonic Treg cell homeostasis. Science 2013;341:569-573.



209. Chang PV, Hao L, Offermanns S, Medzhitov R. The microbial metabolite butyrate regulates intestinal macrophage function via histone deacetylase inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014;111:2247-2252.



210. Krautkramer KA, Kreznar JH, Romano KA, et al. Diet-microbiota interactions mediate global epigenetic programming in multiple host tissues. Mol Cell 2016;64:982-992.



211. Hinnebusch BF, Meng S, Wu JT, Archer SY, Hodin RA. The effects of short-chain fatty acids on human colon cancer cell phenotype are associated with histone hyperacetylation. J Nutr 2002;132:1012-1017.


212. Furusawa Y, Obata Y, Fukuda S, et al. Commensal microbederived butyrate induces the differentiation of colonic regulatory T cells. Nature 2013;504:446-450.



213. Takaishi H, Matsuki T, Nakazawa A, et al. Imbalance in intestinal microflora constitution could be involved in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Int J Med Microbiol 2008;298:463-472.


214. Huda-Faujan N, Abdulamir AS, Fatimah AB, et al. The impact of the level of the intestinal short chain fatty acids in inflammatory bowel disease patients versus healthy subjects. Open Biochem J 2010;4:53-58.



215. Facchin S, Vitulo N, Calgaro M, et al. Microbiota changes induced by microencapsulated sodium butyrate in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2020;32:e13914.




216. Vernia P, Gnaedinger A, Hauck W, Breuer RI. Organic anions and the diarrhea of inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci 1988;33:1353-1358.



217. Hove H, Mortensen PB. Influence of intestinal inflammation (IBD) and small and large bowel length on fecal short-chain fatty acids and lactate. Dig Dis Sci 1995;40:1372-1380.



218. Ang Z, Ding JL. GPR41 and GPR43 in obesity and inflammation:protective or causative? Front Immunol 2016;7:28.



219. Brown AJ, Goldsworthy SM, Barnes AA, et al. The orphan G protein-coupled receptors GPR41 and GPR43 are activated by propionate and other short chain carboxylic acids. J Biol Chem 2003;278:11312-11319.


220. Thangaraju M, Cresci GA, Liu K, et al. GPR109A is a G-protein-coupled receptor for the bacterial fermentation product butyrate and functions as a tumor suppressor in colon. Cancer Res 2009;69:2826-2832.




221. Singh N, Gurav A, Sivaprakasam S, et al. Activation of Gpr109a, receptor for niacin and the commensal metabolite butyrate, suppresses colonic inflammation and carcinogenesis. Immunity 2014;40:128-139.



222. Arpaia N, Campbell C, Fan X, et al. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature 2013;504:451-455.




223. Sun M, Wu W, Liu Z, Cong Y. Microbiota metabolite short chain fatty acids, GPCR, and inflammatory bowel diseases. J Gastroenterol 2017;52:1-8.




224. Zhao Y, Chen F, Wu W, et al. GPR43 mediates microbiota metabolite SCFA regulation of antimicrobial peptide expression in intestinal epithelial cells via activation of mTOR and STAT3. Mucosal Immunol 2018;11:752-762.




225. Tominaga K, Tsuchiya A, Mizusawa T, et al. Evaluation of intestinal microbiota, short-chain fatty acids, and immunoglobulin a in diversion colitis. Biochem Biophys Rep 2021;25:100892.



226. Macia L, Tan J, Vieira AT, et al. Metabolite-sensing receptors GPR43 and GPR109A facilitate dietary fibre-induced gut homeostasis through regulation of the inflammasome. Nat Commun 2015;6:6734.



227. Usami M, Kishimoto K, Ohata A, et al. Butyrate and trichostatin A attenuate nuclear factor kappaB activation and tumor necrosis factor alpha secretion and increase prostaglandin E2 secretion in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Nutr Res 2008;28:321-328.

229. Kaiko GE, Ryu SH, Koues OI, et al. The colonic crypt protects stem cells from microbiota-derived metabolites. Cell 2016;165:1708-1720.



230. Sartor RB. Gut microbiota: diet promotes dysbiosis and colitis in susceptible hosts. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;9:561-562.



231. El Kaoutari A, Armougom F, Gordon JI, Raoult D, Henrissat B. The abundance and variety of carbohydrate-active enzymes in the human gut microbiota. Nat Rev Microbiol 2013;11:497-504.



232. Daïen CI, Pinget GV, Tan JK, Macia L. Detrimental impact of microbiota-accessible carbohydrate-deprived diet on gut and immune homeostasis: an overview. Front Immunol 2017;8:548.


233. Tingirikari JM. Microbiota-accessible pectic poly- and oligosaccharides in gut health. Food Funct 2018;9:5059-5073.


234. Kelly CJ, Zheng L, Campbell EL, et al. Crosstalk between microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids and intestinal epithelial HIF augments tissue barrier function. Cell Host Microbe 2015;17:662-671.



235. Vernia P, Marcheggiano A, Caprilli R, et al. Short-chain fatty acid topical treatment in distal ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1995;9:309-313.


236. Garner CE, Smith S, de Lacy Costello B, et al. Volatile organic compounds from feces and their potential for diagnosis of gastrointestinal disease. FASEB J 2007;21:1675-1688.



237. Mañé J, Pedrosa E, Lorén V, et al. Partial replacement of dietary (n-6) fatty acids with medium-chain triglycerides decreases the incidence of spontaneous colitis in interleukin-10-deficient mice. J Nutr 2009;139:603-610.


238. Ridlon JM, Kang DJ, Hylemon PB, Bajaj JS. Bile acids and the gut microbiome. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2014;30:332-338.



239. Quinn RA, Melnik AV, Vrbanac A, et al. Global chemical effects of the microbiome include new bile-acid conjugations. Nature 2020;579:123-129.




240. Wang YD, Chen WD, Yu D, Forman BM, Huang W. The G-protein-coupled bile acid receptor, Gpbar1 (TGR5), negatively regulates hepatic inflammatory response through antagonizing nuclear factor κ light-chain enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) in mice. Hepatology 2011;54:1421-1432.




241. Jones BV, Begley M, Hill C, Gahan CG, Marchesi JR. Functional and comparative metagenomic analysis of bile salt hydrolase activity in the human gut microbiome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008;105:13580-13585.



242. Labbé A, Ganopolsky JG, Martoni CJ, Prakash S, Jones ML. Bacterial bile metabolising gene abundance in Crohn’s, ulcerative colitis and type 2 diabetes metagenomes. PLoS One 2014;9:e115175.



243. Kurdi P, Kawanishi K, Mizutani K, Yokota A. Mechanism of growth inhibition by free bile acids in lactobacilli and bifidobacteria. J Bacteriol 2006;188:1979-1986.




244. Inagaki T, Moschetta A, Lee YK, et al. Regulation of antibacterial defense in the small intestine by the nuclear bile acid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006;103:3920-3925.



245. Termén S, Tollin M, Rodriguez E, et al. PU.1 and bacterial metabolites regulate the human gene CAMP encoding antimicrobial peptide LL-37 in colon epithelial cells. Mol Immunol 2008;45:3947-3955.


246. D’Aldebert E, Biyeyeme Bi Mve MJ, Mergey M, et al. Bile salts control the antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin through nuclear receptors in the human biliary epithelium. Gastroenterology 2009;136:1435-1443.


247. Song X, Sun X, Oh SF, et al. Microbial bile acid metabolites modulate gut RORγ+ regulatory T cell homeostasis. Nature 2020;577:410-415.




248. Jansson J, Willing B, Lucio M, et al. Metabolomics reveals metabolic biomarkers of Crohn’s disease. PLoS One 2009;4:e6386.



249. Torres J, Palmela C, Brito H, et al. The gut microbiota, bile acids and their correlation in primary sclerosing cholangitis associated with inflammatory bowel disease. United European Gastroenterol J 2018;6:112-122.




250. Sinha SR, Haileselassie Y, Nguyen LP, et al. Dysbiosis-induced secondary bile acid deficiency promotes intestinal inflammation. Cell Host Microbe 2020;27:659-670.



251. Sun L, Cai J, Gonzalez FJ. The role of farnesoid X receptor in metabolic diseases, and gastrointestinal and liver cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;18:335-347.



252. Vavassori P, Mencarelli A, Renga B, Distrutti E, Fiorucci S. The bile acid receptor FXR is a modulator of intestinal innate immunity. J Immunol 2009;183:6251-6261.



253. Gadaleta RM, van Erpecum KJ, Oldenburg B, et al. Farnesoid X receptor activation inhibits inflammation and preserves the intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2011;60:463-472.


254. Wilson A, Almousa A, Teft WA, Kim RB. Attenuation of bile acid-mediated FXR and PXR activation in patients with Crohn’s disease. Sci Rep 2020;10:1866.




255. Nikolaus S, Schulte B, Al-Massad N, et al. Increased tryptophan metabolism is associated with activity of inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology 2017;153:1504-1516.


256. Cervenka I, Agudelo LZ, Ruas JL. Kynurenines: tryptophan’s metabolites in exercise, inflammation, and mental health. Science 2017;357:eaaf9794.


257. Zenewicz LA, Yancopoulos GD, Valenzuela DM, Murphy AJ, Stevens S, Flavell RA. Innate and adaptive interleukin-22 protects mice from inflammatory bowel disease. Immunity 2008;29:947-957.



258. Venkatesh M, Mukherjee S, Wang H, et al. Symbiotic bacterial metabolites regulate gastrointestinal barrier function via the xenobiotic sensor PXR and Toll-like receptor 4. Immunity 2014;41:296-310.



259. Agus A, Planchais J, Sokol H. Gut microbiota regulation of tryptophan metabolism in health and disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018;23:716-724.


260. Roager HM, Licht TR. Microbial tryptophan catabolites in health and disease. Nat Commun 2018;9:3294.




261. Li X, Zhang ZH, Zabed HM, Yun J, Zhang G, Qi X. An insight into the roles of dietary tryptophan and its metabolites in intestinal inflammation and inflammatory bowel disease. Mol Nutr Food Res 2021;65:e2000461.



262. Monteleone I, Rizzo A, Sarra M, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-induced signals up-regulate IL-22 production and inhibit inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology 2011;141:237-248.


263. Takamura T, Harama D, Fukumoto S, et al. Lactobacillus bulgaricus OLL1181 activates the aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathway and inhibits colitis. Immunol Cell Biol 2011;89:817-822.




264. Ga1rg A, Zhao A, Erickson SL, et al. Pregnane X receptor activation attenuates inflammation-associated intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction by inhibiting cytokine-induced myosin light-chain kinase expression and c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1/2 activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2016;359:91-101.



265. Alexeev EE, Lanis JM, Kao DJ, et al. Microbiota-derived indole metabolites promote human and murine intestinal homeostasis through regulation of interleukin-10 receptor. Am J Pathol 2018;188:1183-1194.



266. Wlodarska M, Luo C, Kolde R, et al. Indoleacrylic acid produced by commensal peptostreptococcus species suppresses inflammation. Cell Host Microbe 2017;22:25-37.



267. Hashimoto T, Perlot T, Rehman A, et al. ACE2 links amino acid malnutrition to microbial ecology and intestinal inflammation. Nature 2012;487:477-481.




268. De Vadder F, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Zitoun C, Duchampt A, Bäckhed F, Mithieux G. Microbiota-produced succinate improves glucose homeostasis via intestinal gluconeogenesis. Cell Metab 2016;24:151-157.


269. Mills EL, Kelly B, Logan A, et al. Succinate dehydrogenase supports metabolic repurposing of mitochondria to drive inflammatory macrophages. Cell 2016;167:457-470.



270. Macias-Ceja DC, Ortiz-Masiá D, Salvador P, et al. Succinate receptor mediates intestinal inflammation and fibrosis. Mucosal Immunol 2019;12:178-187.



271. Casén C, Vebø HC, Sekelja M, et al. Deviations in human gut microbiota: a novel diagnostic test for determining dysbiosis in patients with IBS or IBD. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2015;42:71-83.



272. Zimmermann P, Curtis N. The effect of antibiotics on the composition of the intestinal microbiota: a systematic review. J Infect 2019;79:471-489.


273. Hazel K, O’Connor A. Emerging treatments for inflammatory bowel disease. Ther Adv Chronic Dis 2020;11:2040622319899297.




274. Hoffmann TW, Pham HP, Bridonneau C, et al. Microorganisms linked to inflammatory bowel disease-associated dysbiosis differentially impact host physiology in gnotobiotic mice. ISME J 2016;10:460-477.




275. Kamarlı Altun H, Akal Yıldız E, Akın M. Effects of synbiotic therapy in mild-to-moderately active ulcerative colitis: a randomized placebo-controlled study. Turk J Gastroenterol 2019;30:313-320.



276. Amoroso C, Perillo F, Strati F, Fantini MC, Caprioli F, Facciotti F. The role of gut microbiota biomodulators on mucosal immunity and intestinal inflammation. Cells 2020;9:1234.



277. Naseer M, Poola S, Ali S, Samiullah S, Tahan V. Prebiotics and probiotics in inflammatory bowel disease: where are we now and where are we going? Curr Clin Pharmacol 2020;15:216-233.


278. Hill C, Guarner F, Reid G, et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014;11:506-514.



279. Neish AS, Gewirtz AT, Zeng H, et al. Prokaryotic regulation of epithelial responses by inhibition of IkappaB-alpha ubiquitination. Science 2000;289:1560-1563.


280. Kamada N, Kim YG, Sham HP, et al. Regulated virulence controls the ability of a pathogen to compete with the gut microbiota. Science 2012;336:1325-1329.



281. Balakrishnan M, Floch MH. Prebiotics, probiotics and digestive health. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2012;15:580-585.


282. Mackowiak PA. Recycling Metchnikoff: probiotics, the intestinal microbiome and the quest for long life. Front Public Health 2013;1:52.



283. Tojo R, Suárez A, Clemente MG, et al. Intestinal microbiota in health and disease: role of bifidobacteria in gut homeostasis. World J Gastroenterol 2014;20:15163-15176.



284. Mills JP, Rao K, Young VB. Probiotics for prevention of Clostridium difficile infection. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2018;34:3-10.



285. Piewngam P, Zheng Y, Nguyen TH, et al. Pathogen elimination by probiotic Bacillus via signalling interference. Nature 2018;562:532-537.




286. Raman M, Ambalam P, Kondepudi KK, et al. Potential of probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics for management of colorectal cancer. Gut Microbes 2013;4:181-192.



287. Saber R, Zadeh M, Pakanati KC, Bere P, Klaenhammer T, Mohamadzadeh M. Lipoteichoic acid-deficient Lactobacillus acidophilus regulates downstream signals. Immunotherapy 2011;3:337-347.


288. Tamaki H, Nakase H, Inoue S, et al. Efficacy of probiotic treatment with Bifidobacterium longum 536 for induction of remission in active ulcerative colitis: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled multicenter trial. Dig Endosc 2016;28:67-74.



289. Xia Y, Chen Y, Wang G, et al. Lactobacillus plantarum AR113 alleviates DSS-induced colitis by regulating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-kB pathway and gut microbiota composition. J Funct Foods 2020;67:103854.
290. Fedorak RN, Feagan BG, Hotte N, et al. The probiotic VSL#3 has anti-inflammatory effects and could reduce endoscopic recurrence after surgery for Crohn’s disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;13:928-935.


291. O’Toole PW, Marchesi JR, Hill C. Next-generation probiotics: the spectrum from probiotics to live biotherapeutics. Nat Microbiol 2017;2:17057.

292. Hayashi A, Sato T, Kamada N, et al. A single strain of Clostridium butyricum induces intestinal IL-10-producing macrophages to suppress acute experimental colitis in mice. Cell Host Microbe 2013;13:711-722.


293. Yoshimatsu Y, Yamada A, Furukawa R, et al. Effectiveness of probiotic therapy for the prevention of relapse in patients with inactive ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2015;21:5985-5994.



294. Kruis W, Schütz E, Fric P, Fixa B, Judmaier G, Stolte M. Double-blind comparison of an oral Escherichia coli preparation and mesalazine in maintaining remission of ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1997;11:853-858.



295. Kruis W, Fric P, Pokrotnieks J, et al. Maintaining remission of ulcerative colitis with the probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 is as effective as with standard mesalazine. Gut 2004;53:1617-1623.



296. Shanahan F, Collins SM. Pharmabiotic manipulation of the microbiota in gastrointestinal disorders, from rationale to reality. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2010;39:721-726.


297. Harbord M, Eliakim R, Bettenworth D, et al. Third European evidence-based consensus on diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis. Part 2: current management. J Crohns Colitis 2017;11:769-784.



298. Oliva S, Di Nardo G, Ferrari F, et al. Randomised clinical trial: the effectiveness of Lactobacillus reuteri ATCC 55730 rectal enema in children with active distal ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2012;35:327-334.


299. Jin J, Wu S, Xie Y, Liu H, Gao X, Zhang H. Live and heat-killed cells of Lactobacillus plantarum Zhang-LL ease symptoms of chronic ulcerative colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium in rats. J Funct Foods 2020;71:103994.

300. Cheng FS, Pan D, Chang B, Jiang M, Sang LX. Probiotic mixture VSL#3: an overview of basic and clinical studies in chronic diseases. World J Clin Cases 2020;8:1361-1384.



301. Sood A, Midha V, Makharia GK, et al. The probiotic preparation, VSL#3 induces remission in patients with mild-to-moderately active ulcerative colitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009;7:1202-1209.


302. Tursi A, Brandimarte G, Papa A, et al. Treatment of relapsing mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis with the probiotic VSL#3 as adjunctive to a standard pharmaceutical treatment: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Am J Gastroenterol 2010;105:2218-2227.


303. Gionchetti P, Rizzello F, Venturi A, et al. Oral bacteriotherapy as maintenance treatment in patients with chronic pouchitis: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterology 2000;119:305-309.


304. Shen J, Zuo ZX, Mao AP. Effect of probiotics on inducing remission and maintaining therapy in ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, and pouchitis: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2014;20:21-35.

305. Pagnini C, Saeed R, Bamias G, Arseneau KO, Pizarro TT, Cominelli F. Probiotics promote gut health through stimulation of epithelial innate immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010;107:454-459.



306. Mencarelli A, Distrutti E, Renga B, et al. Probiotics modulate intestinal expression of nuclear receptor and provide counter-regulatory signals to inflammation-driven adipose tissue activation. PLoS One 2011;6:e22978.



307. Miele E, Pascarella F, Giannetti E, Quaglietta L, Baldassano RN, Staiano A. Effect of a probiotic preparation (VSL#3) on induction and maintenance of remission in children with ulcerative colitis. Am J Gastroenterol 2009;104:437-443.


308. Huynh HQ, deBruyn J, Guan L, et al. Probiotic preparation VSL#3 induces remission in children with mild to moderate acute ulcerative colitis: a pilot study. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2009;15:760-768.


309. Mardini HE, Grigorian AY. Probiotic mix VSL#3 is effective adjunctive therapy for mild to moderately active ulcerative colitis: a meta-analysis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2014;20:1562-1567.

310. Toumi R, Abdelouhab K, Rafa H, et al. Beneficial role of the probiotic mixture Ultrabiotique on maintaining the integrity of intestinal mucosal barrier in DSS-induced experimental colitis. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 2013;35:403-409.


311. Ghyselinck J, Verstrepen L, Moens F, et al. A 4-strain probiotic supplement influences gut microbiota composition and gut wall function in patients with ulcerative colitis. Int J Pharm 2020;587:119648.


312. Chen Y, Zhang L, Hong G, et al. Probiotic mixtures with aerobic constituent promoted the recovery of multi-barriers in DSS-induced chronic colitis. Life Sci 2020;240:117089.


313. Pilarczyk-Zurek M, Zwolinska-Wcislo M, Mach T, et al. Influence of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium combination on the gut microbiota, clinical course, and local gut inflammation in patients with ulcerative colitis: a preliminary, single-center, open-label study. J Prob Health 2017;5:163.
314. Guslandi M, Mezzi G, Sorghi M, Testoni PA. Saccharomyces boulardii in maintenance treatment of Crohn’s disease. Dig Dis Sci 2000;45:1462-1464.

315. Generoso SV, Viana ML, Santos RG, et al. Protection against increased intestinal permeability and bacterial translocation induced by intestinal obstruction in mice treated with viable and heat-killed Saccharomyces boulardii. Eur J Nutr 2011;50:261-269.



316. Kelesidis T, Pothoulakis C. Efficacy and safety of the probiotic Saccharomyces boulardii for the prevention and therapy of gastrointestinal disorders. Therap Adv Gastroenterol 2012;5:111-125.




317. Bourreille A, Cadiot G, Le Dreau G, et al. Saccharomyces boulardii does not prevent relapse of Crohn’s disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013;11:982-987.


318. Martín R, Chain F, Miquel S, et al. The commensal bacterium Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is protective in DNBS-induced chronic moderate and severe colitis models. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2014;20:417-430.


319. Martín R, Miquel S, Benevides L, et al. Functional characterization of novel Faecalibacterium prausnitzii strains isolated from healthy volunteers: a step forward in the use of f. prausnitzii as a next-generation probiotic. Front Microbiol 2017;8:1226.


320. Carlsson AH, Yakymenko O, Olivier I, et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii supernatant improves intestinal barrier function in mice DSS colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol 2013;48:1136-1144.


321. Martín R, Miquel S, Chain F, et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii prevents physiological damages in a chronic low-grade inflammation murine model. BMC Microbiol 2015;15:67.


322. Zhou Y, Xu H, Xu J, et al. F. prausnitzii and its supernatant increase SCFAs-producing bacteria to restore gut dysbiosis in TNBS-induced colitis. AMB Express 2021;11:33.




323. Ma L, Shen Q, Lyu W, et al. Clostridium butyricum and its derived extracellular vesicles modulate gut homeostasis and ameliorate acute experimental colitis. Microbiol Spectr 2022;10:e0136822.




324. Zhou J, Li M, Chen Q, et al. Programmable probiotics modulate inflammation and gut microbiota for inflammatory bowel disease treatment after effective oral delivery. Nat Commun 2022;13:3432.




325. Bian X, Wu W, Yang L, et al. Administration of Akkermansia muciniphila ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice. Front Microbiol 2019;10:2259.



326. Liu Q, Lu W, Tian F, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila exerts strain-specific effects on DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2021;11:698914.



327. Wang T, Shi C, Wang S, et al. Protective effects of Companilactobacillus crustorum MN047 against dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis: a fecal microbiota transplantation study. J Agric Food Chem 2022;70:1547-1561.


328. Bian X, Yang L, Wu W, et al. Pediococcus pentosaceus LI05 alleviates DSS-induced colitis by modulating immunological profiles, the gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acid levels in a mouse model. Microb Biotechnol 2020;13:1228-1244.




329. Dong F, Xiao F, Li X, et al. Pediococcus pentosaceus CECT 8330 protects DSS-induced colitis and regulates the intestinal microbiota and immune responses in mice. J Transl Med 2022;20:33.




330. Huang YY, Wu YP, Jia XZ, et al. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum DMDL 9010 alleviates dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis and behavioral disorders by facilitating microbiotagut-brain axis balance. Food Funct 2022;13:411-424.


331. Delday M, Mulder I, Logan ET, Grant G. Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron ameliorates colon inflammation in preclinical models of Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2019;25:85-96.


332. Kropp C, Le Corf K, Relizani K, et al. The Keystone commensal bacterium Christensenella minuta DSM 22607 displays anti-inflammatory properties both in vitro and in vivo. Sci Rep 2021;11:11494.




333. Rolfe VE, Fortun PJ, Hawkey CJ, Bath-Hextall F. Probiotics for maintenance of remission in Crohn’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006;(4):CD004826.

334. Limketkai BN, Akobeng AK, Gordon M, Adepoju AA. Probiotics for induction of remission in Crohn’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2020;(7):CD006634.


335. Zhang XF, Guan XX, Tang YJ, et al. Clinical effects and gut microbiota changes of using probiotics, prebiotics or synbiotics in inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Nutr 2021;60:2855-2875.



336. Schultz M, Timmer A, Herfarth HH, Sartor RB, Vanderhoof JA, Rath HC. Lactobacillus GG in inducing and maintaining remission of Crohn’s disease. BMC Gastroenterol 2004;4:5.




337. Bousvaros A, Guandalini S, Baldassano RN, et al. A randomized, double-blind trial of Lactobacillus GG versus placebo in addition to standard maintenance therapy for children with Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2005;11:833-839.


338. Fujimori S, Tatsuguchi A, Gudis K, et al. High dose probiotic and prebiotic cotherapy for remission induction of active Crohn’s disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;22:1199-1204.


339. Marteau P, Lémann M, Seksik P, et al. Ineffectiveness of Lactobacillus johnsonii LA1 for prophylaxis of postoperative recurrence in Crohn’s disease: a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled GETAID trial. Gut 2006;55:842-847.



340. Mallon P, McKay D, Kirk S, Gardiner K. Probiotics for induction of remission in ulcerative colitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2007;(4):CD005573.

341. Matthes H, Krummenerl T, Giensch M, Wolff C, Schulze J. Clinical trial: probiotic treatment of acute distal ulcerative colitis with rectally administered Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (EcN). BMC Complement Altern Med 2010;10:13.




342. Petersen AM, Mirsepasi H, Halkjær SI, Mortensen EM, Nordgaard-Lassen I, Krogfelt KA. Ciprofloxacin and probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle add-on treatment in active ulcerative colitis: a double-blind randomized placebo controlled clinical trial. J Crohns Colitis 2014;8:1498-1505.


343. Matsuoka K, Uemura Y, Kanai T, et al. Efficacy of Bifidobacterium breve fermented milk in maintaining remission of ulcerative colitis. Dig Dis Sci 2018;63:1910-1919.




344. Pandey KR, Naik SR, Vakil BV. Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics: a review. J Food Sci Technol 2015;52:7577-7587.




345. Ramirez-Farias C, Slezak K, Fuller Z, Duncan A, Holtrop G, Louis P. Effect of inulin on the human gut microbiota: stimulation of Bifidobacterium adolescentis and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii. Br J Nutr 2009;101:541-550.


346. Vandeputte D, Falony G, Vieira-Silva S, et al. Prebiotic inulintype fructans induce specific changes in the human gut microbiota. Gut 2017;66:1968-1974.



347. Akram W, Garud N, Joshi R. Role of inulin as prebiotics on inflammatory bowel disease. Drug Discov Ther 2019;13:1-8.


348. Hiel S, Bindels LB, Pachikian BD, et al. Effects of a diet based on inulin-rich vegetables on gut health and nutritional behavior in healthy humans. Am J Clin Nutr 2019;109:1683-1695.




349. Welters CF, Heineman E, Thunnissen FB, van den Bogaard AE, Soeters PB, Baeten CG. Effect of dietary inulin supplementation on inflammation of pouch mucosa in patients with an ileal pouch-anal anastomosis. Dis Colon Rectum 2002;45:621-627.


350. Rivière A, Selak M, Lantin D, Leroy F, De Vuyst L. Bifidobacteria and butyrate-producing colon bacteria: importance and strategies for their stimulation in the human gut. Front Microbiol 2016;7:979.


351. De Preter V, Vanhoutte T, Huys G, et al. Effects of Lactobacillus casei Shirota, Bifidobacterium breve, and oligofructoseenriched inulin on colonic nitrogen-protein metabolism in healthy humans. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2007;292:G358-G368.


352. Morse AL, Dlusskaya EA, Valcheva R, Haynes KM, Gänzle MG, Dieleman LA. T2041 Prebiotic mixture of inulin plus oligofructose is effective adjunct therapy for treatment of mild to moderate ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 2010;138(5 Suppl 1):S-619.

353. Azpiroz F, Dubray C, Bernalier-Donadille A, et al. Effects of scFOS on the composition of fecal microbiota and anxiety in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: a randomized, double blind, placebo controlled study. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2017;29:e12911.
354. Zha Z, Lv Y, Tang H, et al. An orally administered butyratereleasing xylan derivative reduces inflammation in dextran sulphate sodium-induced murine colitis. Int J Biol Macromol 2020;156:1217-1233.


355. Benjamin JL, Hedin CR, Koutsoumpas A, et al. Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of fructo-oligosaccharides in active Crohn’s disease. Gut 2011;60:923-929.


356. Casellas F, Borruel N, Torrejón A, et al. Oral oligofructose-enriched inulin supplementation in acute ulcerative colitis is well tolerated and associated with lowered faecal calprotectin. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2007;25:1061-1067.


357. Rogha M, Esfahani MZ, Zargarzadeh AH. The efficacy of a synbiotic containing Bacillus coagulans in treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench 2014;7:156-163.


358. Darb Emamie A, Rajabpour M, Ghanavati R, et al. The effects of probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics on the reduction of IBD complications, a periodic review during 2009-2020. J Appl Microbiol 2021;130:1823-1838.



359. Steed H, Macfarlane GT, Blackett KL, et al. Clinical trial: the microbiological and immunological effects of synbiotic consumption: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study in active Crohn’s disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2010;32:872-883.


360. Ishikawa H, Matsumoto S, Ohashi Y, et al. Beneficial effects of probiotic bifidobacterium and galacto-oligosaccharide in patients with ulcerative colitis: a randomized controlled study. Digestion 2011;84:128-133.



361. Ivanovska TP, Mladenovska K, Zhivikj Z, et al. Synbiotic loaded chitosan-Ca-alginate microparticles reduces inflammation in the TNBS model of rat colitis. Int J Pharm 2017;527:126-134.


362. Kaur R, Gulati M, Singh SK. Role of synbiotics in polysaccharide assisted colon targeted microspheres of mesalamine for the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Int J Biol Macromol 2017;95:438-450.


363. Son SJ, Koh JH, Park MR, et al. Effect of the Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain GG and tagatose as a synbiotic combination in a dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis murine model. J Dairy Sci 2019;102:2844-2853.


364. Seong G, Lee S, Min YW, et al. Effect of a synbiotic containing Lactobacillus paracasei and Opuntia humifusa on a murine model of irritable bowel syndrome. Nutrients 2020;12:3205.



365. Dos Santos Cruz BC, da Silva Duarte V, Giacomini A, et al. Synbiotic VSL#3 and yacon-based product modulate the intestinal microbiota and prevent the development of pre-neoplastic lesions in a colorectal carcinogenesis model. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2020;104:8837-8857.



366. Cappello C, Tremolaterra F, Pascariello A, Ciacci C, Iovino P. A randomised clinical trial (RCT) of a symbiotic mixture in patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): effects on symptoms, colonic transit and quality of life. Int J Colorectal Dis 2013;28:349-358.



367. Shavakhi A, Minakari M, Farzamnia S, et al. The effects of multi-strain probiotic compound on symptoms and qualityof-life in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Adv Biomed Res 2014;3:140.



368. Bogovič Matijašić B, Obermajer T, Lipoglavšek L, et al. Effects of synbiotic fermented milk containing Lactobacillus acidophilus La-5 and Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis BB-12 on the fecal microbiota of adults with irritable bowel syndrome: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Dairy Sci 2016;99:5008-5021.


369. Brandt LJ, Borody TJ, Campbell J. Endoscopic fecal microbiota transplantation: “first-line” treatment for severe Clostridium difficile infection? J Clin Gastroenterol 2011;45:655-657.

370. Smits LP, Bouter KE, de Vos WM, Borody TJ, Nieuwdorp M. Therapeutic potential of fecal microbiota transplantation. Gastroenterology 2013;145:946-953.


371. Park J, Kim M, Kang SG, et al. Short-chain fatty acids induce both effector and regulatory T cells by suppression of histone deacetylases and regulation of the mTOR-S6K pathway. Mucosal Immunol 2015;8:80-93.




372. Paramsothy S, Paramsothy R, Rubin DT, et al. Faecal microbiota transplantation for inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Crohns Colitis 2017;11:1180-1199.


373. Costello SP, Hughes PA, Waters O, et al. Effect of fecal microbiota transplantation on 8-week remission in patients with ulcerative colitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2019;321:156-164.



374. van Nood E, Vrieze A, Nieuwdorp M, et al. Duodenal infusion of donor feces for recurrent Clostridium difficile. N Engl J Med 2013;368:407-415.


375. Austin M, Mellow M, Tierney WM. Fecal microbiota transplantation in the treatment of Clostridium difficile infections. Am J Med 2014;127:479-483.


376. Kelly CR, Ihunnah C, Fischer M, et al. Fecal microbiota transplant for treatment of Clostridium difficile infection in immunocompromised patients. Am J Gastroenterol 2014;109:1065-1071.




377. Cammarota G, Masucci L, Ianiro G, et al. Randomised clinical trial: faecal microbiota transplantation by colonoscopy vs. vancomycin for the treatment of recurrent Clostridium difficile infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2015;41:835-843.


378. Moayyedi P, Surette MG, Kim PT, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation induces remission in patients with active ulcerative colitis in a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology 2015;149:102-109.


379. Paramsothy S, Kamm MA, Kaakoush NO, et al. Multidonor intensive faecal microbiota transplantation for active ulcerative colitis: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2017;389:1218-1228.


380. Nusbaum DJ, Sun F, Ren J, et al. Gut microbial and metabolomic profiles after fecal microbiota transplantation in pediatric ulcerative colitis patients. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 2018;94:fiy133.



381. Sood A, Mahajan R, Singh A, et al. Role of faecal microbiota transplantation for maintenance of remission in patients with ulcerative colitis: a pilot study. J Crohns Colitis 2019;13:1311-1317.


382. Tian Y, Zhou Y, Huang S, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation for ulcerative colitis: a prospective clinical study. BMC Gastroenterol 2019;19:116.




383. Colman RJ, Rubin DT. Fecal microbiota transplantation as therapy for inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Crohns Colitis 2014;8:1569-1581.




384. Rossen NG, Fuentes S, van der Spek MJ, et al. Findings from a randomized controlled trial of fecal transplantation for patients with ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 2015;149:110-118.


385. Sokol H, Landman C, Seksik P, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation to maintain remission in Crohn’s disease: a pilot randomized controlled study. Microbiome 2020;8:12.




386. Kunde S, Pham A, Bonczyk S, et al. Safety, tolerability, and clinical response after fecal transplantation in children and young adults with ulcerative colitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2013;56:597-601.


387. Cui B, Li P, Xu L, et al. Step-up fecal microbiota transplantation strategy: a pilot study for steroid-dependent ulcerative colitis. J Transl Med 2015;13:298.



388. Caldeira LF, Borba HH, Tonin FS, Wiens A, Fernandez-Llimos F, Pontarolo R. Fecal microbiota transplantation in inflammatory bowel disease patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2020;15:e0238910.



389. Borody TJ, Paramsothy S, Agrawal G. Fecal microbiota transplantation: indications, methods, evidence, and future directions. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2013;15:337.













