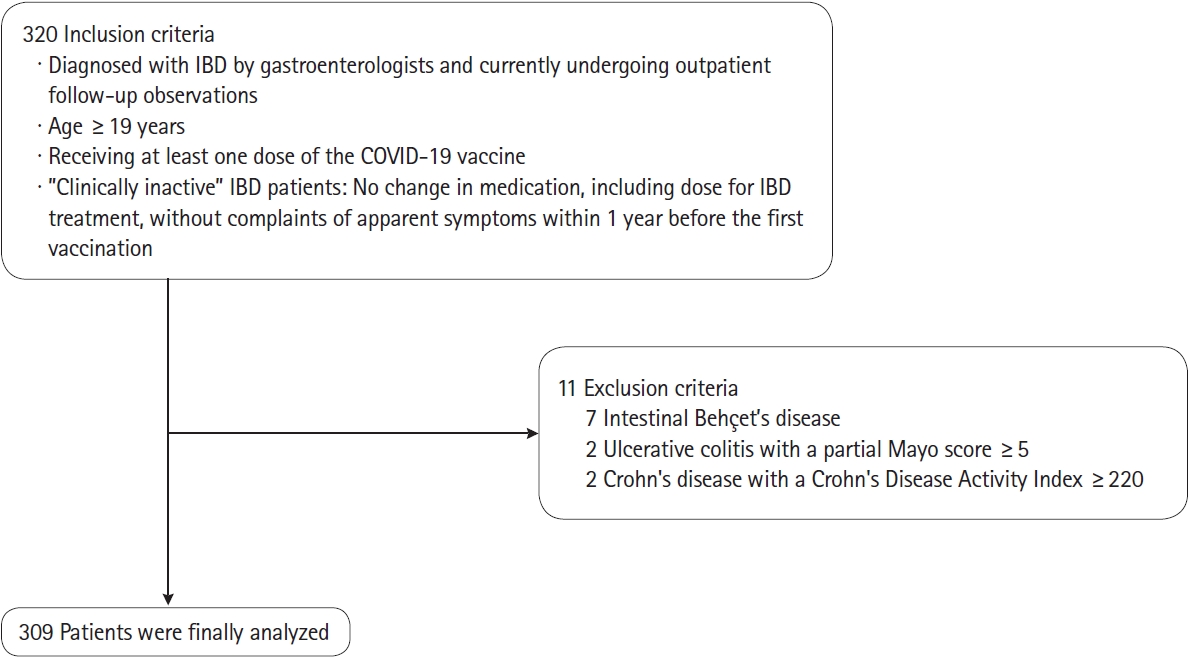
|
 |
- Search
| Intest Res > Epub ahead of print |
|
Abstract
Background/Aims
Methods
Results
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Funding Source
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of Interest
Park YE, Park J, and Cheon JH are editorial board members of the journal but were not involved in the peer reviewer selection, evaluation, or decision process of this article. No other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Park YE, Kang SB, Park SH, Park SJ. Data curation: Ji JH, Shin SH, Park YE, Kang SB. Formal analysis: Ji JH, Shin SH. Investigation: Ji JH, Shin SH, Park YE, Kang SB, Park SH, Park SJ. Methodology: Ji JH, Park SJ. Project administration: Kang SB, Park SH, Park SJ. Resources: Kang SB, Park SH, Park SJ. Software: Ji JH, Park SJ. Supervision: Kang SB, Park SH, Park SJ. Validation: Park YE, Park J, Park JJ, Cheon JH, Kim TI, Kang SB, Park SH, Park SJ. Visualization: Ji JH. Writing - original draft: Ji JH. Writing - review & editing: Ji JH, Park SJ. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Fig. 2.
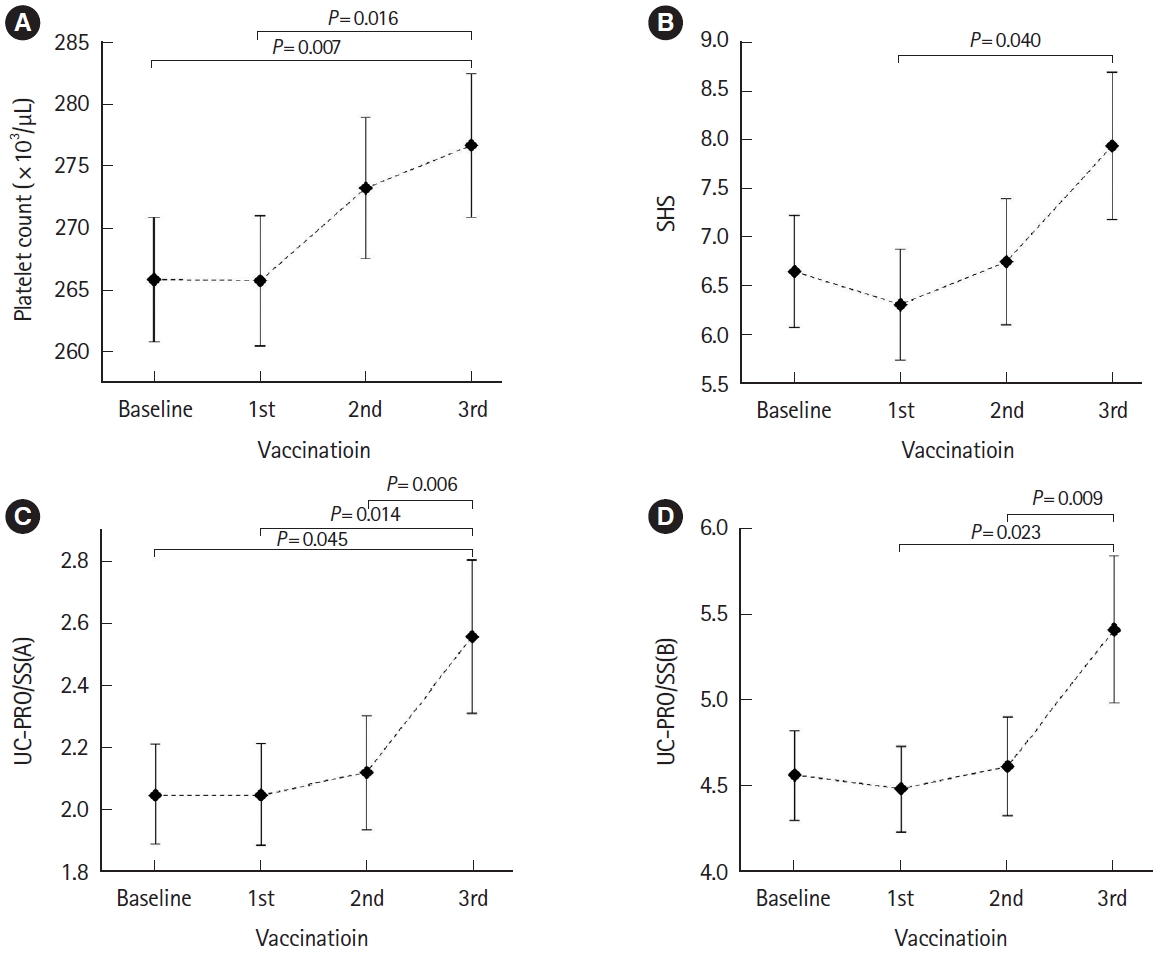
Table 1.
| Characteristic | Total (n = 309) | UC (n = 148) | CD (n = 161) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic variable | ||||
| Age (yr) | 40.80 ± 14.30 | 46.40 ± 15.31 | 35.65 ± 11.08 | < 0.001 |
| Sex | 0.082 | |||
| Male | 199 (64.4) | 88 (59.5) | 111 (68.9) | |
| Female | 110 (35.6) | 60 (40.5) | 50 (31.1) | |
| Smoking | 24 (7.8) | 13 (8.8) | 11 (6.8) | 0.522 |
| Family historya | 31 (10.0) | 17 (11.5) | 14 (8.7) | 0.415 |
| Vaccination | ||||
| 1st | 309 (100) | |||
| AstraZeneca | 49 (15.9) | 37 (25.0) | 12 (7.5) | |
| Pfizer | 198 (64.1) | 86 (58.1) | 112 (69.6) | |
| Moderna | 53 (17.2) | 22 (14.9) | 31 (19.3) | |
| Janssen | 8 (2.6) | 2 (1.3) | 6 (3.7) | |
| Novavax | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.7) | 0 | |
| 2nd | 307 (99.4) | |||
| AstraZeneca | 32 (10.4) | 26 (17.8) | 6 (3.7) | |
| Pfizer | 213 (69.4) | 96 (65.8) | 117 (72.7) | |
| Moderna | 56 (18.2) | 22 (15.1) | 34 (21.1) | |
| Janssen | 5 (1.6) | 1 (0.7) | 4 (2.5) | |
| Novavax | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.7) | 0 | |
| 3rd | 251 (81.2) | |||
| AstraZeneca | 2 (0.8) | 2 (1.6) | 0 | |
| Pfizer | 181 (72.1) | 88 (71.5) | 93 (72.7) | |
| Moderna | 67 (26.7) | 32 (26.0) | 35 (27.3) | |
| Janssen | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Novavax | 1 (0.4) | 1 (0.8) | 0 | |
| COVID-19 infection | 121 (39.2) | 54 (3.65) | 67 (41.6) | 0.356 |
| Self-imposed cessation of medication | 27 (8.8) | 10 (6.8) | 17 (10.6) | 0.252 |
| Booster vaccination | 251 (81.2) | 123 (83.1) | 128 (79.5) | 0.418 |
| Scores of PRO range | ||||
| SHS (0-40)b | 7.36 ± 7.08 | 6.65 ± 7.01 | 8.01 ± 7.10 | 0.092 |
| PRO/SS(A), IBD (0-12)c | 2.55 ± 2.25 | 2.05 ± 1.97 | 3.01 ± 2.40 | < 0.001 |
| UC-PRO/SS(B) (0-28)c | - | 4.57 ± 3.21 | - | |
| pMayo (0-9) | - | 0.94 ± 0.94 | - | |
| CD-PRO/SS(B) (0-16)c | - | - | 3.01 ± 2.40 | |
| CDAI (0-400) | - | - | 74.04 ± 52.52 | |
| Laboratory variable | ||||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.74 ± 1.71 | 13.82 ± 1.70 | 13.68 ± 1.72 | 0.529 |
| WBC count (/μL) | 6,174 ± 1,802 | 6,344 ± 1,842 | 6,043 ± 1,766 | 0.192 |
| Platelet count (× 103/μL) | 263.70 ± 71.84 | 259.95 ± 80.23 | 266.60 ± 64.77 | 0.469 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.42 ± 0.40 | 4.56 ± 0.32 | 4.31 ± 0.43 | < 0.001 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/dL) | 0.30 ± 0.78 | 0.21 ± 0.45 | 0.36 ± 0.96 | 0.125 |
| Lymphocyte count (/μL)d | 2,154 ± 1,006 | 2,781 ± 1,118 | 1,807 ± 742 | < 0.001 |
| Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratiod | 146.14 ± 82.01 | 100.24 ± 49.83 | 171.59 ± 85.40 | < 0.001 |
| Fecal calprotectin (μg/g)d | 513.19 ± 891.67 | 369.33 ± 601.81 | 622.53 ± 1,051 | 0.084 |
b SHS is a simple, 4-part visual analog scale questionnaire that is designed to assess the impact of IBD on health-related quality of life. Total SHS scores correlated with total Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire scores in both CD and UC. There was a stepwise increase in SHS scores with increasing disease activity in both CD and UC groups. Reliability was confirmed using test-retest correlations. [14,15]
c PROs signs and symptoms of ulcerative colitis and CD (UC-PRO/SS, CD-PRO/SS) were developed to standardize the quantification of gastrointestinal signs and symptoms of patients with IBD including ulcerative colitis and CD through direct reports from patient ratings. These are the first symptom measures of UC and CD to meet U.S. Food and Drug Administration PRO guidelines. [12,13]
d The following variables, due to missing values, resulted in differing counts of the total number of patients: lymphocyte count and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (total n=157, UC n=56, CD n=101), fecal calprotectin (total n=132, UC n=57, CD n=75).
UC, ulcerative colitis; CD, Crohn’s disease; COVID-19, coronavirus disease; PRO, patient-reported outcome; SHS, short health scale; PRO/SS(A), patientreported outcome signs and symptoms (abdominal symptoms); PRO/SS(B), patient-reported outcome signs and symptoms (bowel signs and symptoms); IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; pMayo, partial Mayo score; CDAI, Crohn’s Disease Activity Index; WBC, white blood cell.
Table 2.
Table 3.
| Characteristic | Patients with aggravated PROs after vaccination (n = 34)a | Patients without aggravated PROs after vaccination (n = 275) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic variable | |||
| Age (yr) | 36.00 ± 9.58 | 41.39 ± 14.68 | 0.006 |
| Age < 40 yr | 25 (73.5) | 132 (48.0) | 0.005 |
| Sex | 0.271 | ||
| Male | 19 (55.9) | 180 (65.5) | |
| Female | 15 (44.1) | 95 (34.5) | |
| Smoking | 3 (8.8) | 21 (7.6) | 0.737 |
| Family historyb | 3 (8.8) | 28 (10.2) | 0.804 |
| COVID-19 infection | 17 (50.0) | 171 (62.2) | 0.170 |
| Self-imposed cessation of medication | 3 (8.8) | 24 (8.8) | 1.000 |
| Types of diseases | 0.176 | ||
| UC | 20 (58.8) | 128 (46.5) | |
| CD | 14 (41.2) | 147 (53.5) | |
| Type of vaccines (mRNA vs. viral-vector) | |||
| 1st vaccine; mRNA | 26 (76.5) | 225 (81.8) | 0.451 |
| 2nd vaccine; mRNA | 31 (91.2) | 240 (87.3) | 0.513 |
| 3rd vaccine; mRNA | 33 (97.1) | 275 (99.3) | 0.214 |
| Booster vaccination | 25 (73.5) | 226 (82.2) | 0.223 |
| Scores of PRO range | |||
| SHS (0-40)c | 7.59 ± 6.54 | 7.33 ± 7.15 | 0.840 |
| PRO/SS(A) IBD (0-12)d | 2.21 ± 1.89 | 2.59 ± 2.29 | 0.345 |
| Laboratory variable | |||
| Hemoglobin, (g/dL) | 13.22 ± 2.32 | 13.79 ± 1.64 | 0.147 |
| WBC count (/μL) | 6,208 ± 2,246 | 6,171 ± 1,761 | 0.928 |
| Platelet count (× 103/μL) | 314.38 ± 107.32 | 259.06 ± 66.09 | 0.030 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.50 ± 0.41 | 4.40 ± 0.40 | 0.302 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/dL) | 0.22 ± 0.21 | 0.31 ± 0.82 | 0.663 |
| Lymphocyte count (/μL)e | 2,122 ± 974 | 2,157 ± 1,012 | 0.912 |
| Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratioe | 162.23 ± 63.92 | 144.93 ± 83.27 | 0.502 |
| Fecal calprotectin (μg/g)e | 918.29 ± 997.88 | 472.68 ± 874.64 | 0.099 |
b If there was a patient with IBD among the first-degree relatives, it was defined as having a family history.
c SHS is a simple, 4-part visual analog scale questionnaire that is designed to assess the impact of IBD on health-related quality of life. Total SHS scores correlated with total Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire scores in both CD and UC. There was a stepwise increase in SHS scores with increasing disease activity in both CD and UC groups. Reliability was confirmed using test-retest correlations. [14,15]
d PROs signs and symptoms of UC and CD (UC-PRO/SS, CD-PRO/SS) were developed to standardize the quantification of gastrointestinal signs and symptoms of patients with IBD including UC and CD through direct reports from patient ratings. These are the first symptom measures of UC and CD to meet U.S. Food and Drug Administration PRO guidelines. [12,13]
e The following variables, due to missing values, resulted in differing counts of the total number of patients: lymphocyte count and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (patients with aggravated PROs after vaccination n=11, patients without aggravated PROs after vaccination n=146), fecal calprotectin (patients with aggravated PROs after vaccination n=12, patients without aggravated PROs after vaccination n=120).
PRO, patient-reported outcome; COVID-19, coronavirus disease; UC, ulcerative colitis; CD, Crohn’s disease; mRNA, messenger RNA; SHS, short health scale; PRO/SS(A), patient-reported outcome signs and symptoms (abdominal symptoms); PRO/SS(B), patient-reported outcome signs and symptoms (bowel signs and symptoms); IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; WBC, white blood cells.
Table 4.
| Characteristic | Patients with aggravated PROs after vaccination (n = 20)a | Patients without aggravated PROs after vaccination (n=128) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic variable | |||
| Age (yr) | 38.05 ± 10.00 | 47.70 ± 15.60 | 0.001 |
| Age < 40 yr | 13 (65.0) | 36 (28.1) | 0.001 |
| Sex | 0.958 | ||
| Male | 12 (60.0) | 76 (59.4) | |
| Female | 8 (40.0) | 52 (40.6) | |
| Smoking | 3 (15.0) | 10 (7.8) | 0.386 |
| Family historyb | 0 | 17 (13.3) | 0.129 |
| COVID-19 infection | 8 (40.0) | 46 (35.9) | 0.726 |
| Self-imposed cessation of medication | 1 (5.0) | 9 (7.0) | 0.736 |
| Type of vaccines (mRNA vs. viral-vector) | |||
| 1st vaccine; mRNA | 15 (75.0) | 93 (72.7) | 0.826 |
| 2nd vaccine; mRNA | 19 (95.0) | 101 (78.9) | 0.124 |
| 3rd vaccine; mRNA | 19 (95.0) | 128 (98.4) | 0.355 |
| Booster vaccination | 15 (75.0) | 108 (84.4) | 0.336 |
| Scores of PRO range | |||
| SHS (0-40)c | 6.40 ± 6.75 | 6.69 ± 7.08 | 0.865 |
| UC-PRO/SS(A) (0-12)d | 1.90 ± 1.92 | 2.08 ± 1.99 | 0.709 |
| UC-PRO/SS(B) (0-28)d | 5.05 ± 3.43 | 4.50 ± 3.18 | 0.478 |
| pMayo (0-9) | 0.91 ± 0.54 | 0.95 ± 0.97 | 0.838 |
| Laboratory variable | |||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.31 ± 2.83 | 13.87 ± 1.56 | 0.551 |
| WBC count (/μL) | 6,424 ± 2,642 | 6,336 ± 1,759 | 0.886 |
| Platelet count (× 103/μL) | 335.50 ± 122.38 | 252.32 ± 71.26 | 0.001 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.62 ± 0.29 | 4.55 ± 0.32 | 0.502 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/dL) | 0.18 ± 0.18 | 0.21 ± 0.47 | 0.816 |
| Lymphocyte count (/μL)e | 2,561 ± 990 | 1,342 ± 1,362 | 0.086 |
| Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratioe | 149.78 ± 77.26 | 94.42 ± 46.03 | 0.038 |
| Fecal calprotectin (μg/g)e | 797.50 ± 1,051.31 | 299.42 ± 475.20 | 0.226 |
b If there was a patient with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) among the first-degree relatives, it was defined as having a family history.
c SHS is a simple, 4-part visual analog scale questionnaire that is designed to assess the impact of IBD on health-related quality of life. Total SHS scores correlated with total Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire scores in both CD and UC. There was a stepwise increase in SHS scores with increasing disease activity in both CD and UC groups. Reliability was confirmed using test-retest correlations. [14,15]
d PROs signs and symptoms of UC and CD (UC-PRO/SS, CD-PRO/SS) were developed to standardize the quantification of gastrointestinal signs and symptoms of patients with IBD including UC and CD through direct reports from patient ratings. These are the first symptom measures of UC and CD to meet U.S. Food and Drug Administration PRO guidelines. [12,13]
e The following variables, due to missing values, resulted in differing counts of the total number of patients: lymphocyte count and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (patients with aggravated PROs after vaccination n=4, patients without aggravated PROs after vaccination n=52), fecal calprotectin (patients with aggravated PROs after vaccination n=8, patients without aggravated PROs after vaccination n=49).
UC, ulcerative colitis; PRO, patient-reported outcome; CD, Crohn’s disease; COVID-19, coronavirus disease; mRNA, messenger RNA; SHS, short health scale; PRO/SS(A), patient-reported outcome signs and symptoms (abdominal symptoms); PRO/SS(B), patient-reported outcome signs and symptoms (bowel signs and symptoms); pMayo, partial Mayo score; WBC, white blood cells.
Table 5.
| Characteristic | Patients with aggravated PROs after vaccination (n=14)a | Patients without aggravated PROs after vaccination (n=147) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic variable | |||
| Age (yr) | 33.07 ± 8.42 | 35.90 ± 11.29 | 0.363 |
| Age < 40 yr | 12 (85.7) | 96 (65.3) | 0.147 |
| Sex | 0.133 | ||
| Male | 7 (50.0) | 43 (29.3) | |
| Female | 7 (50.0) | 104 (70.7) | |
| Smoking | 0 | 11 (7.5) | 0.601 |
| Family historyb | 3 (21.4) | 11 (7.5) | 0.107 |
| COVID-19 infection | 9 (64.3) | 58 (39.5) | 0.072 |
| Self-imposed cessation of medication | 2 (14.3) | 15 (10.2) | 0.645 |
| Type of vaccines (mRNA vs. viral-vector) | |||
| 1st vaccine; mRNA | 11 (78.6) | 132 (89.8) | 0.194 |
| 2nd vaccine; mRNA | 12 (85.7) | 139 (94.6) | 0.211 |
| 3rd vaccine; mRNA | 14 (100) | 147 (100) | |
| Booster vaccination | 4 (28.6) | 29 (19.7) | 0.488 |
| Scores of PRO range | |||
| SHS (0-40)c | 9.29 ± 6.07 | 7.88 ± 7.20 | 0.482 |
| CD-PRO/SS(A) (0-12)d | 3.57 ± 1.65 | 4.41 ± 2.42 | 0.554 |
| CD-PRO/SS(B) (0-16)d | 2.64 ± 1.82 | 3.04 ± 2.45 | 0.204 |
| CDAI (0-400) | 73.14 ± 50.29 | 74.11 ± 52.88 | 0.953 |
| Laboratory variable | |||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.15 ± 1.87 | 13.73 ± 1.71 | 0.283 |
| WBC count (/μL) | 6,012 ± 1,927 | 6,046 ± 1,760 | 0.951 |
| Platelet count (× 103/μL) | 295.18 ± 93.30 | 264.19 ± 61.66 | 0.128 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.40 ± 0.49 | 4.30 ± 0.43 | 0.478 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/dL) | 0.27 ± 0.23 | 0.37 ± 1.00 | 0.733 |
| Lymphocyte count (/μL) | 1,871 ± 942 | 1,802 ± 731 | 0.815 |
| Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio | 169.34 ± 60.51 | 171.76 ± 87.21 | 0.943 |
| Fecal calprotectin (μg/g) | 169.34 ± 60.51 | 171.75 ± 87.21 | 0.603 |
b If there was a patient with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) among the first-degree relatives, it was defined as having a family history.
c SHS is a simple, 4-part visual analog scale questionnaire that is designed to assess the impact of IBD on health-related quality of life. Total SHS scores correlated with total Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire scores in both CD and UC. There was a stepwise increase in SHS scores with increasing disease activity in both CD and UC groups. Reliability was confirmed using test-retest correlations. [14,15]
d PROs signs and symptoms of UC and CD (UC-PRO/SS, CD-PRO/SS) were developed to standardize the quantification of gastrointestinal signs and symptoms of patients with IBD including UC and CD through direct reports from patient ratings. These are the first symptom measures of UC and CD to meet U.S. Food and Drug Administration PRO guidelines. [12,13]
e The following variables, due to missing values, resulted in differing counts of the total number of patients: lymphocyte count and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (patients with aggravated PROs after vaccination n=7, patients without aggravated PROs after vaccination n=94), fecal calprotectin (patients with aggravated PROs after vaccination n=3, patients without aggravated PROs after vaccination n=61)
CD, Crohn’s disease; PRO, patient-reported outcome; UC, ulcerative colitis; COVID-19, coronavirus disease; mRNA, messenger RNA; SHS, short health scale; PRO/SS(A), patient-reported outcome signs and symptoms (abdominal symptoms); PRO/SS(B), patient-reported outcome signs and symptoms (bowel signs and symptoms); CDAI, Crohn’s Disease Activity Index; WBC, white blood cells.
Table 6.
PRO, patient-reported outcome; COVID-19, coronavirus disease; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; UC, ulcerative colitis; CD, Crohn’s disease; PRO/SS(A), patient-reported outcome signs and symptoms (abdominal symptoms); PRO/SS(B), patient-reported outcome signs and symptoms (bowel signs and symptoms).
Table 7.
| P-value |
Post-hoc analysis |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| P-value (Bonferroni) | Pairwise comparison | ||
| Total (n = 309) | |||
| SHSa | 0.074 | ||
| PRO/SS(A), IBDb | 0.141 | ||
| Hemoglobin | 0.820 | ||
| WBC count | 0.862 | ||
| Lymphocyte count | 0.459 | ||
| Platelet count | 0.004 | 0.007 (baseline-3rd) | Baseline vs. 3rd (265.95 vs. 276.79) |
| 0.016 (1st-3rd) | 1st vs. 3rd (265.84 vs. 276.79) | ||
| Albumin | 0.323 | ||
| C-reactive protein | 0.288 | ||
| Fecal calprotectin | 0.945 | ||
| Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio | 0.596 | ||
| UC (n = 148) | |||
| SHSa | 0.041 | 0.040 (1st-3rd) | 1st vs. 3rd (6.31 vs. 7.94) |
| UC-PRO/SS(A)b | 0.007 | 0.045 (baseline-3rd) | Baseline vs. 3rd (2.05 vs. 2.56) |
| 0.014 (1st-3rd) | 1st vs. 3rd (2.05 vs. 2.56) | ||
| UC-PRO/SS(B)b | 0.012 | 0.006 (2nd-3rd) | 2nd vs. 3rd (2.12 vs. 2.56) |
| 0.023 (1st-3rd) | 1st vs. 3rd (4.49 vs. 5.42) | ||
| 0.009 (2nd-3rd) | 2nd vs. 3rd (4.62 vs. 5.42) | ||
| pMayo | 0.051 | ||
| Hemoglobin | 0.257 | ||
| WBC count | 0.494 | ||
| Lymphocyte count | 0.951 | ||
| Platelet count | 0.113 | ||
| Albumin | 0.159 | ||
| C-reactive protein | 0.234 | ||
| Fecal calprotectin | 0.976 | ||
| Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio | 0.091 | ||
| CD (n = 161) | |||
| SHSa | 0.353 | ||
| CD-PRO/SS(A)b | 0.848 | ||
| CD-PRO/SS(B)b | 0.629 | ||
| CDAI | 0.106 | ||
| Hemoglobin | 0.981 | ||
| WBC count | 0.650 | ||
| Lymphocyte count | 0.218 | ||
| Platelet count | 0.041 | 0.052 (1st-3rd) | |
| Albumin | 0.771 | ||
| C-reactive protein | 0.181 | ||
| Fecal calprotectin | 0.792 | ||
| Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio | 0.951 | ||
a SHS is a simple, 4-part visual analog scale questionnaire that is designed to assess the impact of IBD on health-related quality of life. Total SHS scores correlated with total Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire scores in both CD and UC. There was a stepwise increase in SHS scores with increasing disease activity in both CD and UC groups. Reliability was confirmed using test-retest correlations. [14,15]
b PROs signs and symptoms of UC and CD (UC-PRO/SS, CD-PRO/SS) were developed to standardize the quantification of gastrointestinal signs and symptoms of patients with IBD including UC and CD through direct reports from patient ratings. These are the first symptom measures of UC and CD to meet U.S. Food and Drug Administration PRO guidelines. [12,13]
PRO, patient-reported outcome; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; COVID-19, coronavirus disease; SHS, short health scale; PRO/SS(A), patient-reported outcome signs and symptoms (abdominal symptoms); PRO/SS(B), patient-reported outcome signs and symptoms (bowel signs and symptoms); WBC, white blood cell; UC, ulcerative colitis; pMayo, partial Mayo score; CD, Crohn’s disease; CDAI, Crohn’s Disease Activity Index.