|
 |
- Search
| Intest Res > Epub ahead of print |
|
Abstract
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Funding Source
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of Interest
Li Wai Suen CFD has served as a speaker for DiaSorin, has received educational support from Pfizer, and has received research funding from the Robert C Bulley Charitable Foundation and the St Vincent’s Hospital Melbourne Research Endowment Fund. And he is supported by a NHMRC Postgraduate scholarship. Choy MC has received research funding from Janssen and Gandel Philanthropy. De Cruz P has served as a consultant, an advisory board member, or a speaker for AbbVie, Baxter, Ferring, Janssen, Celltrion, Emerge Health, Shire, and Takeda. And he is supported by an NHMRC Emerging Leader 2 Fellowship and has received research support from AbbVie, Ferring, Shire, Janssen, Pfizer, and Takeda.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Li Wai Suen CFD, De Cruz P. Data curation; Formal analysis: Li Wai Suen CFD, De Cruz P. Investigation; Methodology; Project administration: Li Wai Suen CFD, De Cruz P. Software: Li Wai Suen CFD. Supervision: De Cruz P. Visualization: Li Wai Suen CFD. Writing - original draft: Li Wai Suen CFD, De Cruz P. Writing - review & editing: Li Wai Suen CFD, Choy MC, De Cruz P. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Fig. 1.
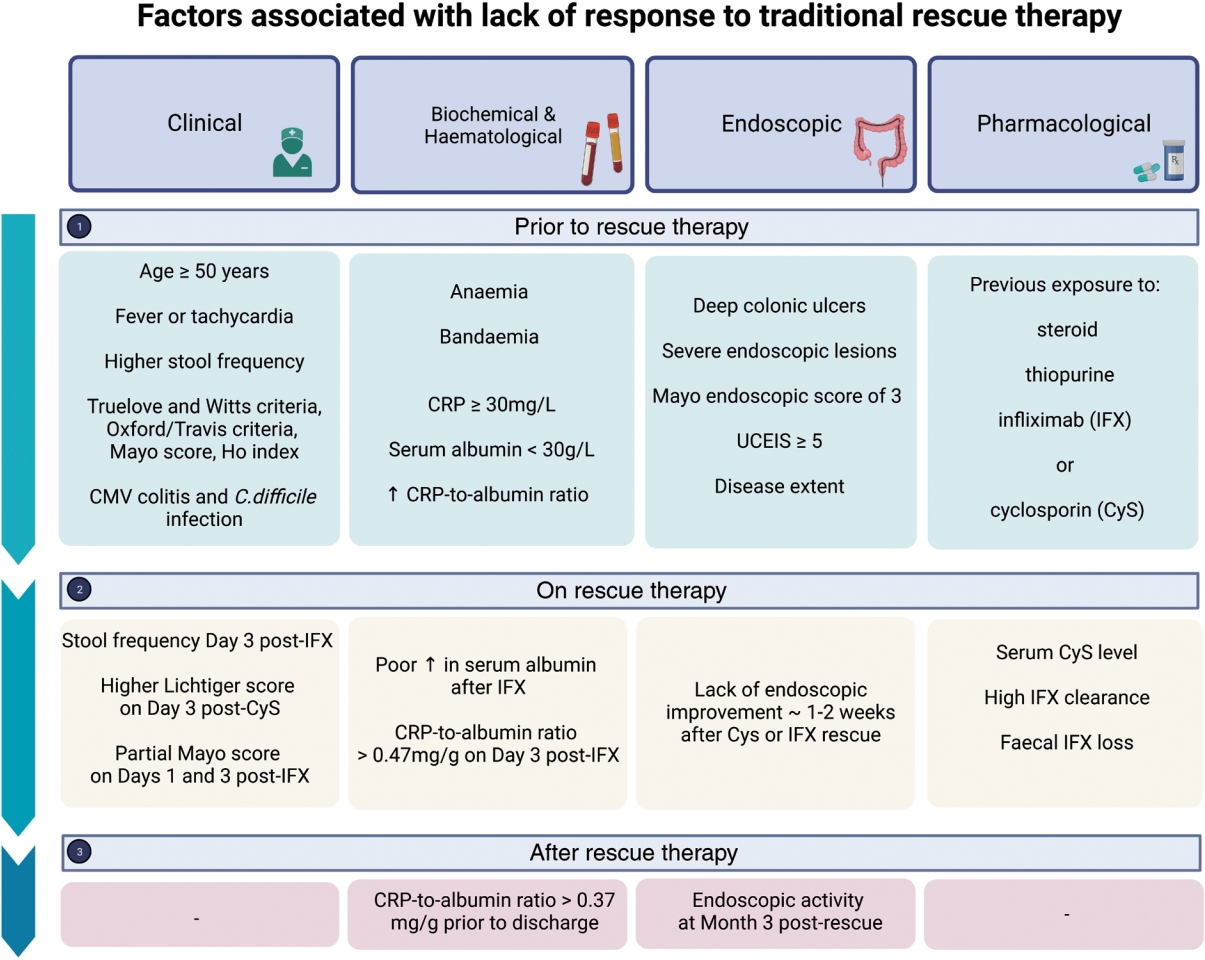
Fig. 2.
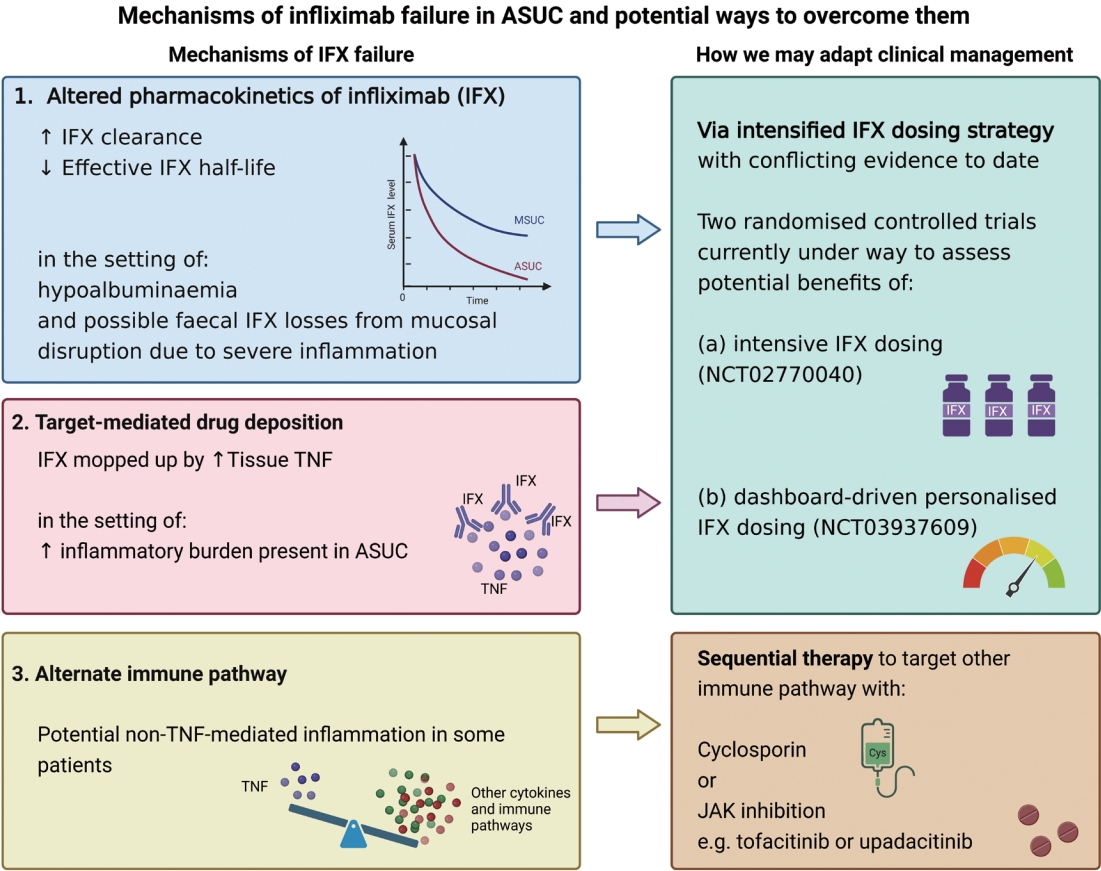
Table 1.
| Use of tofacitinib | Author (year) | No. | Study design | Patient profile | Intervention with tofacitinib | Exposure to advanced therapy prior to tofacitinib | Follow-up | Main results/salient findings: | Colectomy rate | Major AEs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sequential | Bercier (2020) [58] | 1 | Case report | ASUC after 2nd IFX induction dose for severely active UC. Received IFX rescue prior to tofacitinib | Tofacitinib 10 mg BD for 5 day; Escalated to 10 mg TDS at day 7 due to partial response; Dose decreased to 10 mg BD at follow-up 12 day later | IFX outpatient induction+IFX rescue therapy for ASUC for current admission | 30 day | Patient in clinical remission at day 30 | 0% | Nil |
| Sequential | Chen (2020) [59] | 1 | Case report | ASUC, refractory to IFX rescue | Tofacitinib 10 mg BD | Previous secukinumab for psoriatic arthritis | 4 wk | Patient in endoscopic and histological remission at 4 wk | 0% | Nil |
| IFX as rescue therapy for ASUC | ||||||||||
| Sequential | Griller (2019) [60] | 1 | Case report | Hospitalized patient with UC, with severe inflammation at endoscopy, after vedolizumab and IFX failure | Tofacitinib 10 mg BD | Vedolizumab, IFX | 8 mo | Patient in endoscopic remission and colectomy-free at 8 mo | 0% | Nil |
| Sequential | Khan (2022) [61] | 1 | Case report | ASUC, refractory to IV steroids and IFX rescue | Tofacitinib 10 mg TDS (duration of TDS dosing not stated) | IFX prior to admission and as rescue during same admission Also received IV ganciclovir for CMV colitis | 3 mo | Patient in clinical and biochemical remission at 3 mo. MES of 1 at 3 mo | 0% | Nil |
| Sequential | Yang (2021) [62] | 1 | Case report | ASUC, refractory to IV steroids and single dose IFX rescue Commenced sequential therapy with combination tofacitinib and cyclosporin | Tofacitinib 10 mg BD, in combination with IV cyclosporin 3 mg/kg daily | IFX | 1 yr | Clinical response after 10 day of combination therapy | 0% | Nil |
| At 1 mo, changed to oral cyclosporin 150 mg BD+tofacitinib 5 mg BD | Endoscopic healing with scars noted at 6 mo | |||||||||
| At 6 mo, tofacitinib decreased to 5 mg BD and mesalazine 1.5 g BD commenced | ||||||||||
| At 1 yr, tofacitinib ceased | ||||||||||
| Bio-experienced | Berinstein (2019) [10] | 4 | Case series | ASUC in 4 patients with features of severe disease, at high risk of failing medical therapy | 3 patients: IV methylprednisolone 60 mg daily+tofacitinib 10 mg TDS for 9 doses | 2 patients: IFX and/or adalimumab | 2-18 mo | 3 out of 4 patients achieved clinical remission | 50% | No major AE. 1 patient: rashtherapy changed |
| 2 patients were anti-TNF experienced and 1 was on chronic steroids | 1 patient: budesonide+tofacitinib 10 mg TDS for 9 doses | 2 out of 4 patients required colectomy (1 due to medically refractory disease to tofacitinib; 1 due to dysplasia) | ||||||||
| Bio-experienced | Berinstein (2021) [45] | 40 | Retrospective case-control study | ASUC patients who were biologicexperienced and were commenced on tofacitinib as an inpatient | Standard (tofacitinib 10 mg BD for the length of hospitalization) or highintensity tofacitinib (10 mg TDS for 9 doses followed by 10 mg BD) | IFX: 85%; Adalimumab: 40%; Golimumab: 5%; Vedolizumab 52.5%; Ustekinumab: 2.5% | 90 day | 90-day colectomy rate of 15.0% (6/40) in tofacitinib group compared to 20.4% (23/113) in control group | 15% | Similar rates of infection, venous thromboembolic events and cardiovascular events in tofacitinib group and controls |
| All patients also received IV corticosteroids | At 90 day follow-up, tofacitinib group had a decreased risk of colectomy compared to controls (HR=0.28, P=0.018) | |||||||||
| 40 cases; 113 controls | Subgroup analysis suggest that benefit might be confined to intensified tofacitinib dosing group | |||||||||
| Bio-experienced | Kotwani (2020) [66] | 4 | Case series | ASUC, with previous biologic experience and refractory to IV steroids. Mayo activity index ≥ 10 at presentation | Tofacitinib 10 mg BD; Dose increased to 15 mg BD in 1 patient | All previously exposed to IFX and vedolizumab | 5-14 mo | All 4 patients experienced clinical improvement and were discharged on tofacitinib | 0% at 30 and 90 day | Nil |
| 1 patient also previously exposed to adalimumab | At follow-up, 2 patients in steroid-free remission and 2 had endoscopically active disease | |||||||||
| Of the latter 2 patients, 1 was referred for surgery due to colonic biopsies being indefinite for dysplasia | ||||||||||
| Bio-experienced | Santos (2022) [67] | 2 | Case series | ASUC, with previous biologic experience and previous history of ASUC, refractory to IV steroids | Tofacitinib 10 mg BD; Maintenance dose of 5 mg BD in 1 patient | Both patients previously failed anti-TNF, vedolizumab and tacrolimus | 11-14 mo | Both patients in clinical and endoscopic remission at wk 16 | 0% | Nil |
| Bio-experienced | Sedano (2021) [68] | 1 | Case report | ASUC, with previous biologic experience; active disease despite tofacitinib 10 mg BD and refractory to IV steroids | Tofacitinib 30 mg daily for 48 hr, then 10 mg BD | IFX 10 mg/kg 4-weekly | 50 day | Endoscopic and histological remission at day 50 | 0% | Nil |
| Mixed | Jena (2021) [63] | 4 | Case series | ASUC, refractory to IV steroids | Tofacitinib 10 mg BD | IFX: 2/4 patients | 15 day to 1 mo | Clinical improvement in 3 patients, however 1 of them subsequently died of COVID-19 infection or pulmonary embolism | 25% | 1 death from COVID-19 infection or pulmonary embolism |
| 3 patients also failed rescue therapy with either IFX or cyclosporin during same admission | Cyclosporin: 1/4 patients | Colectomy: 1 patient due to failure to respond to tofacitinib | ||||||||
| Mixed | Constant (2022) [64] | 11 | Case series/Retrospective cohort study | Pediatric patients, hospitalized with flare of UC-steroid and biologic refractory | 3/11: tofacitinib TDS; 8/11: tofacitinib BD | 10/11 patients had prior exposure to anti-TNF, 3 of which also failed vedolizumab previously | Median 182 day | Colectomy: | 45% | Nil |
| 5 patients also received combination antibiotic salvage | 1 patient was biologic naive at time of presentation failed to respond to IFX rescue therapy for the current admission | 3/11 patients at day 90 | ||||||||
| 1 patient received tacrolimus | 5/11 patients over median 182 day follow-up | |||||||||
| Mixed | Uzzan (2021) [44] | 55 | Multicenter cohort study-Retrospective and Prospective | Patients hospitalized with UC flare | Tofacitinib induction regimen not specified. At wk 6, the 43 patients still on tofacitinib were all on 10 mg BD | IFX: 49 (89.1%); Cyclosporin: 19 (34.5%); Vedolizumab (69.1%); Ustekinumab (10.9%) | Median 6.5 mo (IQR, 3-12.3) | Wk 6-clinical response 60%, clinical remission 45.5%, clinical steroid-free remission 37.5% | 27.3% | 4 severe AE, including 2 cases of Herpes Zoster (age > 60 yr). 1 death post-colectomy, believed unrelated to tofacitinib |
| 75% of patients had Lichtiger score ≥ 10 | ||||||||||
| 66% of patients were on IV steroids at time of tofacitinib initiation | ||||||||||
| Only 10 patients received rescue therapy before tofacitinib for the current flare: 2 (3.6%) IFX, 8 (14.5%) cyclosporin | Wk 14-clinical response 41.8%, clinical remission 34.5%, clinical steroid-free remission 32.7% | |||||||||
| Not all patients met Lichtiger or Truelove and Witts criteria for ASUC | ||||||||||
| Mixed | Eqbal (2023) [46] | 11 | Case series/Retrospective cohort study | ASUC, refractory to 3 day of IV steroids | Tofacitinib 10 mg TDS for 14 day, then 10 mg BD | IFX: 11/11 patients | 12 mo | Clinical response at 6 and 12 mo: 9/11 patients | 18% | 1 transient hepatitisimproved after tofacitinib dose was decreased |
| 5 patients were previously anti-TNF naive and failed IFX rescue for the current admission | Of these, 5/11 patients had IFX rescue therapy for current admission | Colectomy: 2/11 patients | ||||||||
| 6 patients had a history of primary non-response to IFX induction within the preceding 3 mo | 6/11 patients had primary non- response to outpatient IFX induction in the preceding 3 mo | |||||||||
| 3/6 patients in the latter group also had previous vedolizumab exposure | ||||||||||
| Mixed | Gilmore (2022) [42] | 5 | Case series | ASUC, receiving tofacitinib immediately after IFX failure | Tofacitinib 10 mg TDS for up to 14 day, then 10 mg BD for 8 wk, then 5 mg BD maintenance | IFX: 5/5 patients | 90 day | Clinical response during inpatient stay: 4 out of 5 patients 1 failed to respond and required inpatient colectomy | 20% | Nil |
| 2 patients were biologic naïve at admission and received IFX rescue | 1 patient also previously exposed to vedolizumab | |||||||||
| 3 patients were admitted with ASUC within 7 day of completed IFX induction | 90-day outcomes: 4 responders remained colectomy-free 2 patients in combined clinical and endoscopic remission | |||||||||
| Mixed | Honap (2020) [48] | 7 | Case series | UC patients with previous biologic experience and severe colitis (MES 3) receiving inpatient tofacitinib after IV hydrocortisone failure | Tofacitinib regimen not specified | Anti-TNF (IFX, golimumab, adalimumab): 7/7 patients | 2-52 wk | 2 inpatient colectomies; 2 colectomies after initial response; 3 patients still on tofacitinib at wk 26 | 57% | 1 CMV colitis |
| 5/7 patients met Truelove and Witts criteria for ASUC | Most patients failed more than one line of therapy: Vedolizumab: 4/7 patients; Ustekinumab: 1/7 patients; Cyclosporin: 1/7 patients | |||||||||
| Only 1 patient received IFX rescue the same admission | ||||||||||
| Mixed | Naganuma (2023) [69] | 9 | Prospective cohort study | ASUC patients who received tofacitinib following initial treatment with IFX, tacrolimus, apheresis or cyclosporin during the same admission | Tofacitinib regimen not specified | As per “Patient profile” column | 28 day | Clinical remission: 5 out of 9 patients at day 28 | 44% | 1 CMV reactivation |
| 4 patients had IFX rescue and 3 patients had tacrolimus rescue | History of experience to biologics prior to admission not stated | Colectomy: 4 out of 9 patients at day 28 | ||||||||
| 1 patient received adalimumab and 1 patient received plasmapheresis prior to tofacitinib | ||||||||||
| Mixed | Rutka (2020) [65] | 3 | Case series | ASUC, biologic-experienced patients with inadequate response to IV steroids | Tofacitinib 10 mg BD | All patients had previously failed at least 2 biologics prior to presentation | 90 day | Clinical response at 8 wk: 3/3 patients | 0% | Nil |
| Clinical remission at 8 wk: 2/3 patients | ||||||||||
| 2 patients received IV cyclosporin or IFX rescue for the current admission prior to tofacitinib | IFX: 3/3 patients; adalimumab: 2/3 patients; vedolizumab: 2/3 patients; cyclosporin: 1/3 patients | Colectomy at 30 and 90 day: 0/3 patients | ||||||||
| Mixed | Xiao (2022) [47] | 8 | Case series/Retrospective cohort study | Patients with ASUC, defined as UC requiring hospitalization and IV steroids | Tofacitinib 10 mg BD, or 10 mg TDS followed by 10 mg BD, at physician’s discretion | 3 patients started anti-TNF during current admission | 6 mo | Clinical response in 5/8 patients during index hospitalization | 37.5% | Nil |
| All patients failed or were intolerant to anti-TNF therapy and started tofacitinib as inpatient | 5 patients received anti-TNF prior to hospitalization (3 anti-TNF+ vedolizumab; 2: anti-TNF+vedolizumab+ustekinumab) | Clinical remission: all clinical responders (5/5) at 30 and 90 day. However, only 3/5 responders were still in clinical remission at 6 mo | ||||||||
| 3 patients who were IFX-naive received IFX rescue during the same admission | ||||||||||
| 5 patients received anti-TNF prior to the current hospitalization | Colectomy: 3/8 patients by 6 mo |
Studies have been classified as follows: (1) “Sequential” studies where patients received tofacitinib as true sequential therapy after failure of IFX or cyclosporin rescue therapy during the same admission; (2) “Bio-experienced” studies where patients received tofacitinib as inpatient following prior treatment with 1 or more biologic agent, but IFX or cyclosporin rescue was not administered during the same admission that tofacitinib was commenced; (3) “Mixed” studies combining patients from the 2 former group.
ASUC, acute severe ulcerative colitis; AE, adverse events; IFX, infliximab; UC, ulcerative colitis; BD, twice a day; TDS, three times a day; CMV, cytomegalovirus; MES, Mayo endoscopic score; IV, intravenous; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; HR, hazard ratio.
Table 2.
| Use of tofacitinib | Author (year) | No. | Study design | Patient profile | Intervention with tofacitinib | Exposure to advanced therapy prior to tofacitinib | Follow-up | Main results/salient findings: | Response rate | Colectomy rate | Major adverse events |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bio-naïve patients | Komeda (2023) [93] | 8 | Case series/retrospective cohort study | Biologic-naïve patients with ASUC who were refractory to IV steroids and received tofacitinib as first-line rescue therapy | Tofacitinib 20 mg/day | Nil | Date of discharge from hospital | 6 out of 8 patients responded to tofacitinib rescue Time to clinical response: 2-5 day | 75% | 12.5% However note that 1 patient responded to IFX after tofacitinib failure | Herpes zoster in 1 patient-treated with antiviral therapy while tofacitinib was continued |
| 2 patients did not respond to tofacitinib | |||||||||||
| Of the 2 tofacitinib nonresponders, 1 patient achieved clinical remission with IFX while 1 patient did not respond to IFX and required colectomy | |||||||||||
| Predominantly bio-naïve patients | Malakar (2023) [94] | 8a | Case series/retrospective cohort study | Patients with ASUC, all biologic-naïve except for 1, refractory to IV hydrocortisone and received first-line tofacitinib rescue therapy | Tofacitinib 10 mg BD | All biologicnaïve except for 1 patient experienced to IFX and vedolizumab | 10 day to 16 mo (median: 6 mo) | 7 out of 8 patients responded to tofacitinib | 88% | 13% | 2 deaths: 1 patient died of sepsis after colectomy, 1 patient died of bacterial pneumonia |
| Time to clinical response: 3 to 5 day | |||||||||||
| Colectomy: 1 out of 8 patients. The colectomy occurred in a bio-naïve patient |