Crohn’s disease (CD) is a chronic, idiopathic inflammatory disorder of the intestinal tract without cure. The disease burden of CD has increased worldwide, including in Asian countries, in spite of the development of medical therapies for CD in these countries [
1]. Fistula formation is a common complication of CD that occurred in approximately 17% to 50% of patients [
2]. Fistulizing CD is classified into abdominal and perianal fistula depending on its location, and the management varies for each fistula type [
3]. In case of entero-enteric or entero-colic fistula, which is the most common type of abdominal fistula in CD, surgery is not usually required unless there are symptoms or complications from abscess or stricture formation. Enteric and colo-duodenal fistula (ECDF) is a very rare type of abdominal fistula, and surgical intervention is necessary but challenging [
4,
5]. Since the proximal transverse colonic posterior side and descending duodenal anterior side are anatomically closely related, ECDF mainly occurs at this location [
4]. However, ECDF could also occur in other segments, most commonly anastomotic sites such as ileocolic anastomosis following right hemi-colectomy (RHC) or the ileum following ileocecal resection for management of CD [
5]. Usually, ECDF originates from diseased small and large intestines, not the duodenum [
4]. The common symptoms of ECDF are abdominal pain, diarrhea, and weight loss [
4,
6]. However, these symptoms are difficult to distinguish from the symptoms of active CD, which makes early detection of ECDF difficult [
6]. The high intraluminal pressure found in the large intestine than in the duodenum in ECDF, colonic contents can flow back to the duodenum, but pylorus acts as a barrier to the reflux of the contents. Therefore, fecal vomiting is a pathognomonic symptom but very rare, occurring in only 0.5% to 2% of the cases [
6]. Further, ECDF is diagnosed by clinical manifestation, radiologic images, endoscopy, and intraoperative findings. Among them, contrast radiography is the most sensitive diagnostic tool, and barium enema is more susceptible than barium meal [
4]. Further, surgery is the most common ECDF treatment; no case has been reported to be cured with medical treatment, including with infliximab, which exhibits good effects on perianal fistulizing CD. In addition, surgery after failed biologic treatment increases postoperative complications in patients with CD [
7]. For these reasons, surgical treatment for ECDF is preferred even in the biologic era. However, since ECDF cases are rare, and surgery is not easy, the appropriate diagnostic approach and treatment for ECDF are controversial. Also, outcomes and long-term follow-up data of ECDF are not known. Therefore, we sought to investigate the clinical features of ECDF in patients with CD in Korea.
We investigated all the CD patients with ECDF in a large tertiary hospital (Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea) between January 1999 and December 2021 using medical records. The data of patients including clinical characteristics such as age, gender, laboratory examination, previous operative history, preoperative medical treatment, clinical manifestation, diagnostic methods, operative findings, postoperative pathology, and hospital course were reviewed. The Institutional Review Board of Asan Medical Center (IRB No. 2022-0080) approved this study and waived the requirement for informed consent due to its observational nature. Subsequently, ECDF was confirmed by radiology using cross-sectional imaging or upper gastrointestinal series (UGIS), endoscopy, or intraoperative findings. Follow-up data were collected from clinical visit data that were accessible until death or December 2021. In the descriptive analysis, categorical variables are expressed as numbers with percentages. Continuous variables are expressed as medians with ranges. The paired t-test was used to evaluate the significance of the changes over time (preoperative vs. 6 months after surgery) in serum albumin and body mass index. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 24.0 for Windows (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
A total of 26 patients with CD were identified to have ECDF during the study period. The baseline features of patients are presented in
Table 1. The mean age was 31.5 years (range, 19-62 years), and 19 patients (73.1%) were male. The median duration of CD in patients was 120.5 months. All patients had abdominal pain, and the second most common symptom was weight loss (n = 8, 30.8%). No patient had fecal vomiting, which is a pathognomonic symptom. Further, 16 patients had a history of previous surgeries: RHC (n = 11, 42.3%), ileocecal resection (n = 2, 7.7%), small bowel resection and anastomosis (n = 1, 3.8%), and appendectomy (n = 2, 7.7%). The most common site of ECDF origin was the ileocolic anastomosis site (n = 12, 46.2%), followed by the ascending colon (n = 9, 34.6%).
The 14 patients (53.8%) were administered biologics before surgical treatment of ECDF. Medical treatment before and after surgery was described in
Table 1.
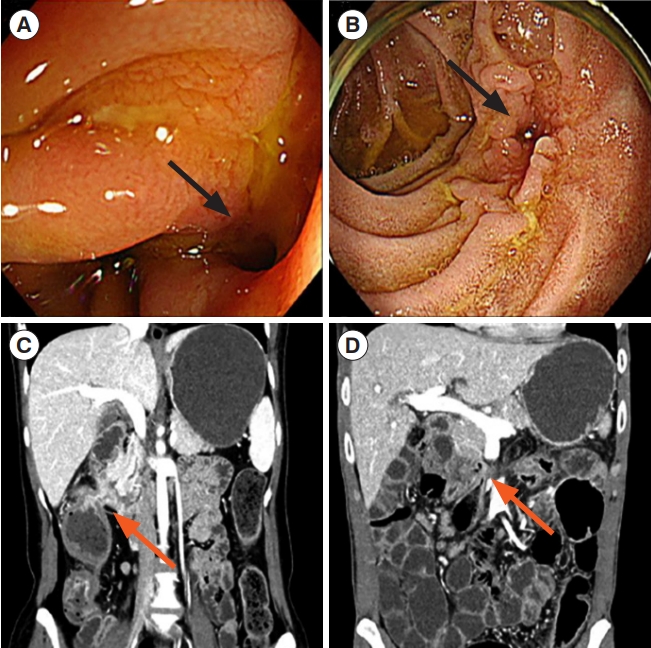
Preoperative diagnosis of ECDF was performed in 13 (50.0%) out of 26 patients. Of them, 12 patients (46.2%) were diagnosed using computed tomography (
Fig. 1), 8 (30.8%) using esophagogastroduodenoscopy (
Fig. 1), and 1 using UGIS; 8 patients were diagnosed using more than 2 techniques. In 13 patients (50%), ECDF was not obvious in radiology including cross-sectional imaging or UGIS, esophagogastroduodenoscopy and colonoscopy. These 13 patients exhibited symptoms; required surgery for obstruction, abscess, and fistulas at another site; and were confirmed to have ECDF intraoperatively. Further, 23 patients (88.5%) underwent duodenal primary repair and 2 patients (7.7%) had duodenal wedge resection (
Table 1). In 1 patient, methylene-blue injection test indicated a negative result, but the fistula could not be excluded during surgery. Therefore, glue was applied to the serosal surface in this case. After surgery, the health of most patients (n = 25, 96.2%) improved, and hence, they were discharged. However, one patient expired because of peritonitis caused by uncontrolled ECDF. The fistula in this patient could not be resolved even after 3 additional surgeries, and the patient died of multidrug-resistant bacteremia and fungal infection. During the follow-up for a median of 85.5 months, no recurrence of ECDF was identified. In addition, serum albumin and body mass index of patients were improved postoperatively (
P<0.001) (
Supplementary Fig. 1).
To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to report the clinical features and outcomes of ECDF in Korean patients with CD. Our study indicated that most patients with ECDF improved with surgical treatment and underwent primary repair without complicated surgeries such as pyloric exclusion or pancreaticoduodenectomy. The clinical symptoms of ECDF, such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, malnutrition, and weight loss, in the present study were comparable with those in the previous reports [
4,
6]. The diagnosis of ECDF is usually made using contrast radiography, and barium enema has the highest sensitivity [
6], which was reported to be 54% to 95% [
6]. In the present study, evaluation of the diagnostic value of barium enema was not possible because no patient was tested using this modality. In this study, half of the patients could be intraoperatively diagnosed with ECDF. Also, since the symptoms of ECDF are difficult to distinguish from the active symptoms of CD, appropriate clinical consideration is important to preoperatively diagnose ECDF. In previous study, Freund et al. [
8] reported only 4 patients (23.5%) were preoperatively diagnosed, despite all patients having underwent extensive preoperative imaging and endoscopy. In our study, ECDF origin was the most common in the ileocolic anastomosis site (n = 12, 46.2%), followed by ascending colon (n = 9, 34.6%). As previous studies indicated, ileocolic anastomosis was the most common location for ECDF [
6]. This is because the anastomotic site after RHC is in contact with the duodenum.
In the present study, most patients underwent duodenal primary repair and wedge resection of duodenum, and the surgical outcome of ECDF was successful; however, 1 patient who received primary repair died of sepsis. If the fistula is not large and surrounding inflammation is not severe, primary repair is possible without pyloric exclusion or pancreaticoduodenectomy. Therefore, as mentioned above, early diagnosis through appropriate clinical consideration can prevent complex surgeries. Self-limited cases without surgery are rare in ECDF patients with CD [
4]. Bressler and Sands [
9] demonstrated that the spontaneous healing rate is only 6% to 13%. Recently, the number of CD patients with fistula who are under medical treatment has increased due to development of immunosuppressive agents and biologics. A meta-analysis indicated a favorable effect of these medications [
10]. Another study indicated that infliximab was effective in the induction and maintenance therapy for CD. However, this efficacy was limited to external fistula and perianal fistula [
11]. So far, no study has presented an effective medical treatment for ECDF. Therefore, ECDF is considered an absolute indication for surgical treatment. Surgical intervention in fistulizing CD patients is effective and safe. Taken together, surgical treatment for ECDF will remain an optimal choice even in the biologic era.
Our study had several limitations. First, this is a retrospective study with a small number of patients. Since there was no control group, the effect of surgical treatment could not be compared with that of the medical treatment. However, the clinical features and outcomes of the 26 cases from a single institution hold significance because ECDF incidence is rare. Second, barium study was not performed in most patients. Usually, radiologic barium study is the most sensitive diagnostic tool to detect ECDF [
4,
6]. However, barium study has rarely been performed in our institution since the development of imaging modalities such as computed tomography enterography or magnetic resonance enterography in patients with CD. Third, although ECDF recurrence was not observed in the present study, accurately evaluating the recurrence rate is challenging owing to the short follow-up period.
In conclusion, accurate diagnosis based on clinical suspicion along with timely surgery seems to be an optimal approach for managing ECDF in CD patients. We believe that well-designed studies with a high patient count and long follow-up periods are mandatory for effective results.