|
 |
- Search
| Intest Res > Volume 21(1); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background/Aims
The fecal microbiota of Korean patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) was investigated with respect to disease phenotypes and taxonomic biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of IBD.
Methods
Fecal samples from 70 ulcerative colitis (UC) patients, 39 Crohn’s disease (CD) patients, and 100 healthy control individuals (HC) were collected. The fecal samples were amplified via polymerase chain reaction and sequenced using Illumina MiSeq. The relationships between fecal bacteria and clinical phenotypes were analyzed using the EzBioCloud database and 16S microbiome pipeline.
Results
The alpha-diversity of fecal bacteria was significantly lower in UC and CD (P<0.05) compared to that in HC. Bacterial community compositions in UC and CD were significantly different from that of HC according to Bray-Curtis dissimilarities, and there was also a difference between community composition in UC and CD (P=0.01). In UC, alpha-diversity was further decreased when the disease was more severe and the extent of disease was greater, and community composition significantly differed depending on the extent of the disease. We identified 9 biomarkers of severity and 6 biomarkers of the extent of UC. We also identified 5 biomarkers of active disease and 3 biomarkers of ileocolonic involvement in CD. Lachnospiraceae and Ruminococcus gnavus were biomarkers for better prognosis in CD.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease (CD), is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the intestinal tract characterized by relapsing abdominal pain, diarrhea, and hematochezia [1-3]. Because IBD patients experience periods of various clinical courses according to the degree of inflammation, the optimal treatment of IBD should be applied according to the severity and extent of the disease [4,5]. As a result, the main challenge most clinicians face is identifying the disease phenotype before therapeutic assessment. Determination of the disease phenotype and prognosis could help to overcome the current situation in which many IBD patients experience disease complications. Several parameters based on laboratory tests and endoscopic findings have been suggested and are used for prognosis [6,7]; however, they are invasive and have unsatisfactory predictability. More dependable biomarkers are, thus, required.
In recent years, with the development of genome sequencing methods, the role of gut microbiota has been highlighted in the pathogenesis of IBD. The gut microbiota represents a complex and dynamic microbial ecosystem in the human colon [8], and developing evidence has demonstrated that there is a distinct shift in composition of gut microbiota in IBD patients compared with healthy control individuals (HC). A lower richness and diversity of microbial species are commonly identified in IBD patients [9,10]. Compositional changes in bacterial communities have also been found from the phylum to the species level [9,11]. Recently, it has been hypothesized that specific microbial pathways control intestinal barrier function and that a dysbiosis-induced inflammatory cascade drives disease development [12-17]. Even the clinical outcomes of anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) therapy are suggested to be related to the intestinal microbiota [13].
Host-microbiota interactions provide new insights for disease assessment and treatment in IBD. However, the diagnostic and prognostic role of microbiota in IBD patients remains unclear to date. Given the entity of IBD, which presents various disease phenotypes, clinical studies have been needed to discover biomarkers associated with the disease status and course. Identifying the characteristic gut microbiota associated with the disease phenotype and prediction of clinical courses may contribute to not only the growing area of these fields of research, but also optimal treatment for IBD patients. Thus, the aim of this study was to investigate the fecal microbiota of IBD patients and their relationship to disease phenotypes. We further explored taxonomic biomarkers associated with prognosis in Korean patients with IBD.
This study involved 3 academic hospitals in Korea. The study protocol was approved by an institutional review board at each center including Chung-Ang University Hospital (IRB No. C2013183[1143]). All participants voluntarily agreed to participate in this study and gave written informed consent. A baseline assessment was performed before fecal sampling, and demographic information including age, sex, and body mass index (BMI) were collected. Patients who used drugs can affect intestinal microbial community, such as probiotics and antibiotics, within a month were excluded. Prior exposure to azathioprine/6-mercaptopurine and anti-TNF-α agents was evaluated for each participant. Previous history of disease-related operations included small bowel resection, ileocolectomy and anal fistulectomy.
The disease extensions of UC were defined as proctitis, left sided colitis, and extensive colitis, and those of CD were ileal, colonic, and ileocolonic. The severity of disease was assessed by the Mayo score [18] for UC (3-5, mild; 6-10, moderate; 11-12, severe) and the Crohn’s Disease Activity Index [19] for CD (< 150, remission; 150-219, mild; 220-449, moderate; > 450, severe). Severity was estimated at the time of fecal sampling, and the average follow-up period was 8.0 ± 1.3 years. Patients with UC and CD were divided into 2 groups based on clinical courses. A “worse prognosis group” was defined as patients who experienced biologic agents (including anti-TNF-α agents) or surgical treatment after fecal sampling. A “better prognosis group” was defined as patients who did not experience such treatments. Fecal samples of HC were collected from participants of the local community cohort studies which had conducted in the Department of Preventive Medicine, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine. Stool samples were obtained from participants without underlying disease and abdominal symptoms.
Fecal samples were collected between January 2009 and December 2012, and DNA was isolated from feces and stored at −80°C. DNA was extracted using a FastDNA SPIN kit for bacterial DNA (MP Biomedicals, Santa Ana, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. In this study, the bacterial portion of the DNA samples were characterized by amplification of the V4 variable region of the 16S rRNA gene by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) (forward primer 5´-GAGTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA-3´; reverse primer 5´-ACGGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3´). The forward and reverse primers use single nucleotide shifts of 6 different lengths to improve sequence quality. Two steps of amplification were run on the DNA samples (Supplementary Material). After each PCR reaction, products were cleaned using the HighPrep PCR clean-up kit with a DynaMag-96 side magnet. Cleaned 16S PCR products were then quantified and pooled at equimolar concentrations for sequencing. The quality and product size were assessed on a Bioanalyzer 2100 (Agilent, Palo Alto, CA, USA) using a DNA 7500 chip. Mixed amplicons were pooled and sequencing was carried out by the High-Throughput Sequencing Facility at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine.
Once taxonomic or functional profiles of samples were generated, we used a web-based analysis platform for a secondary analysis with versatile visualizations and statistical reports. The EzBioCloud 16S database and 16S microbiome pipeline (EzBioCloud 16S-based MTP app, https://www.EZbiocloud.net; ChunLab Inc., Seoul, Korea) were used for data processing, statistical analysis, and data graphing.
The information collected in the pipeline was analyzed using various statistical tools. Species richness indices were determined using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test. The Chao1 estimation and Shannon diversity index were used for the richness and evenness of samples. Permutational multivariate analysis of variance based on Bray-Curtis dissimilarities at the operational taxonomic unit level was used to determine differences in bacterial communities among groups. Biomarkers were determined using linear discriminant analysis (LDA) with effect size estimation (LefSe) with an LDA effect size > 3.0 to distinguish between (1) different disease groups, (2) disease severity and extent, and (3) prognosis groups.
A total of 209 samples from 100 HC, 70 UC patients, and 39 CD patients were enrolled. Table 1 shows the baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of all participants. HC and UC patients had no difference in age and BMI, but the mean age and BMI were significantly lower in CD patients compared to the 2 groups. One patient received biologic agents in UC and 10.3% of patients (4/39) experienced biologic agents in CD. In 35.9% of patients (14/39) had previous history of disease-related operations in CD.
Analysis of alpha diversity revealed that both richness and diversity were significantly lower in IBD patients compared with HC (Fig. 1A). The Shannon diversity index was significantly lower in UC and CD compared to HC, and significantly lower in CD compared with UC (Fig. 1B). Analysis using Bray-Curtis dissimilarities and principal co-ordinates analysis revealed significant differences in microbial communities among HC, UC, and CD (Fig. 1C).
In UC patients, alpha diversity decreased as the disease severity (Fig. 2A) and extent (Fig. 2B) deteriorated. There were significantly distinct bacterial community compositions between patients with proctitis and left sided or extensive colitis (Supplementary Fig. 1). No significant differences in alpha diversity or community composition were identified according to disease severity and extent in CD patients.
Bacterial compositions of HC were different from those of IBD patients, especially for CD. Compared to HC and patients with UC, CD patients had significantly higher abundances of the phylum Proteobacteria (7.19% and 7.68% vs. 24.06%, P<0.001) (Fig. 3A), the genus Escherichia (2.00% and 2.20% vs. 11.01%, P<0.001) (Fig. 3B), and the species Escherichia coli (2.00% and 2.20% vs. 11.02%, P<0.001) (Fig. 3C).
LefSe analysis identified 9 bacterial taxa (including the Proteus vulgaris group, the Bifidobacterium dentium group, the Clostridium clostridioforme group, and Flavonifractor plautii) that were significantly more abundant in UC patients than HC (Fig. 4A), and 14 bacterial taxa (including the Pseudomonas fragi group, the Lactobacillus gasseri group, the Streptococcus gallolyticus group, the Bifidobacterium dentium group, the Veillonella parvula group, and the Lactococcus garvieae group) that were significantly more abundant in CD patients than HC (Fig. 4B).
Taxa that could differentiate 1 group from another, in terms of disease severity and extent, were determined using LefSe. The Lactobacillus salivarius group and Clostridioides difficile group were identified as potential biomarkers for moderate to severe UC, compared to mild UC (Fig. 5A). The Lactobacillus lactis group, Intestinibacter bartlettii, the C. difficile group, the Weissella confusa group, the Anaerostipes hadrus group, Clostridium spiroforme, the Leuconostoc lactis group, and the Lactobacillus plantarum group were identified as potential biomarkers for moderate to severe UC, compared to remission status (Fig. 5B). Several taxa were found to be associated with disease extent. Bifidobacterium bifidum, I. bartlettii, F. plautii, the A. hadrus group, the Lactobacillus paracasei group, and Ruminococcus gnavus were identified as potential biomarkers for left sided or extensive colitis compared to proctitis (Fig. 5C).
The Phascolarctobacterium succinatutens group, the L. salivarius group, Lactobacillus mucosae, the Porphyromonas asaccharolytica group, and Coprococcus catus were identified as possible biomarkers for active disease status, compared to remission status (Fig. 6A). The L. gasseri group, the Bacteroides ovatus group, and the W. confusa group were identified as possible biomarkers for ileocolonic involvement, compared to small bowel involvement only (Fig. 6B).
Of the UC and CD patients, 13 and 9 belonged to worse prognosis group, respectively. In CD patients, Lachnospiraceae (Fig. 7A) and R. gnavus (Fig. 7B) were significantly more abundant in the better prognosis group compared to the worse prognosis group. We found no significantly different abundances among the better and worse prognosis groups in UC patients.
In the present study, we demonstrated the dysbiosis of fecal microbiota in IBD patients. The alpha-diversity of the fecal microbiota was significantly lower in IBD patients compared to HC. Additionally, there were significant differences in bacterial community composition among UC and CD patients and HC. In UC patients, species richness decreased as the degree of severity and extent deteriorated, and distinct compositional differences were identified according to the disease extent. We also identified several microbial taxonomic biomarkers correlating to the disease severity and extent in UC and CD patients, which may be associated with prognosis of the diseases.
This study confirmed the findings of previous studies that microbial diversity is significantly lower in IBD patients [11,20]. Additionally, we found that compared to UC patients, the microbial diversity of CD patients was significantly lower. Previous studies have conflicting results regarding microbial differences between UC and CD patients [11,21,22]. In the present study, the lower diversity in CD patients is assumed to be associated with compositional changes in the microbiota in CD. The phylum Proteobacteria, genus Escherichia, and species E. coli were significantly more abundant in CD patients compared to UC patients and HC. An increased abundance of Proteobacteria has commonly been identified in IBD patients [23,24], and previous studies have shown that this is more evident in patients with aggressive CD. A higher abundance of E. coli in CD patients has also been reported in previous literature [25,26]. Meanwhile, this was not observed in UC patients, which does not support previous studies showing a higher abundance of E. coli in UC patients, as well as CD [27-30]. Further studies on the role of E. coli in UC are needed.
We found several microbial species with significantly different abundances in IBD patients compared to HC. Few previous studies have considered compositional changes in gut microbiota at the species level [11,12,25]. However, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and R. gnavus have previously been found to be associated with IBD [31,32]. Further large-scale studies are needed to confirm the role of the species identified in this study in the pathogenesis of IBD.
In a Western cohort study, patients with active IBD had lower intestinal bacterial species richness and diversity compared with those with inactive disease status [23]. Moreover, the abundance of Firmicutes was lower in patients with active UC, and that of Proteobacteria was higher in patients with aggressive CD compared with patients with non-active and non-aggressive disease status, respectively. Pediatric patients with CD who had a higher abundance of Proteobacteria were more likely to have complicated disease behavior [32]. A meta-analysis also showed a significantly lower abundance of potentially protective taxa, such as F. prausnitzii and Bifidobacterium, in patients with active IBD compared with those in remission status [33]. In the present study, we investigated bacterial taxa at the species level to determine differences related to the degree of disease severity and extent. Two species, L. salivarius and C. difficile, were identified as biomarkers to differentiate moderate to severe disease from mild disease in UC patients. L. salivarius was also a biomarker of active CD compared with a remission status. L. salivarius strains are used as probiotics; they have anti-inflammatory effects and improve intestinal permeability [34,35]. However, their role in IBD has been controversial [36], and even if the species are the same, the function of the bacteria can be significantly different if the strain is different. Therefore, L. salivarius presented in our study might be different strain from that of L. salivarius used as probiotics. Unfortunately, however, our study did not confirm their strains. Further studies for additional confirmation are needed. Clostridioides, which includes several pathogenic taxa including C. difficile, is a cause of colitis. It is not clear whether C. difficile initiates or deteriorates the inflammatory response in the intestine, but increasing evidence has shown that the incidence of C. difficile infection is higher in IBD patients [37,38], particularly in UC patients [39]. C. difficile was also suggested as a cause of an IBD relapse in a previous retrospective study [40]. Our data showed that C. difficile is a biomarker that differentiates moderate to severe disease, not only from mild disease but also from remission status. However, more frequent exposure to antibiotics and other drugs (including immunomodulators) may be associated with a higher abundance of C. difficile in patients with moderate to severe UC [41,42].
Endoscopy plays an important role in the diagnosis and evaluation of disease status in IBD patients, particularly for the classification of the disease location. However, endoscopies are invasive and cause discomfort in patients; therefore, physicians hesitate to perform this procedure frequently. Noninvasive detection tools are required. Several serologic markers and imaging-based modalities have been investigated, but their role in assessing disease location is limited [43,44]. Assessment using intestinal microbiota has also been suggested; however, data has been limited and conflicting. One study using cohort data showed no differences in diversity or phylalevel abundance in relation to disease location [23]. However, another study showed that patients with ileocolic CD and extensive UC had higher abundances of R. gnavus compared with patients with isolated CD and UC limited to left side or proctitis, respectively [32]. They also showed that Veillonella is more abundant in patients with upper gastrointestinal CD. In the present study, B. bifidum was a biomarker for left sided or extensive UC compared with proctitis. Previous results regarding the abundance of Bifidobacterium in IBD patients have varied [45-47]. In one study, a lower abundance of mucosa-associated Bifidobacterium was found in IBD patients [30], and in a meta-analysis, a lower abundance of Bifidobacterium in patients with active IBD was found compared with those in remission [33]. However, other studies have found a higher abundance of B. bifidum in IBD patients [45,46]. As a result, the use of Bifidobacterium as a probiotic for IBD patients during the active disease status requires caution [48]. In the present study, a higher abundance of B. bifidum in fecal samples reflected more extensive disease status. The function of the bacteria can be different if the strain is different even if the species are the same, as we mentioned above. Therefore, the fact that bacterial function varies depending on the strain may have caused these results.
Additionally, I. bartlettii was a possible biomarker of not only moderate to severe UC but also left sided or extensive UC. Little is known regarding I. bartlettii except that it is involved in glucose metabolism and its abundance decreases in patients taking metformin [49,50]. Further studies on its relation to intestinal disease are needed.
We also attempted to identify microbial biomarkers for predicting clinical courses. In CD patients, the family Lachnospiraceae and species R. gnavus were significantly more abundant in patients with better prognosis. Lachnospiraceae is a butyrate-producing commensal bacteria, which induces regulatory T cells with anti-inflammatory functions [51-53]. Because Lachnospiraceae has been shown to have a negative association with CD [25], this taxa is suggested to play an important role in disease prevention, and is a target for novel therapy [12]. R. gnavus is known to express beta-glucuronidase activity which induces the formation of toxic compounds in the colon causing local inflammation [54]. Its relation with disease activity and inflammation has previously been identified [55]. CD patients have a higher abundance of R. gnavus compared with healthy individuals, and patients with more extensive disease have a higher abundance of R. gnavus compared with those with isolated disease [25,32,55]. It is unclear why 2 different taxa, which play opposite roles in the inflammatory cascade, were found as potential biomarkers for better prognosis; however, this finding may suggest a complex association between microbiota, inflammation, and disease prognosis.
There were several limitations to the study. First, it was not a longitudinal study. As the fecal samples were not collected serially, for example before and after treatments, it is difficult to identify serial changes in microbiota according to disease fluctuation. Second, the mean age and BMI were significantly lower in CD patients compared to the HC and UC patients, as the HC was selected based on UC patients. Several factors affecting the composition of gut microbiota such as diet, were also not controlled before collecting fecal samples. Third, extract DNA were stored at -80°C for a long time. However, recent study showed that long-term storage at -80°C only limited effect on the microbial community [56]. Fourth, we could not apply time-to-event methods to prognosis evaluation. Since the number of UC (13 patients) and CD (9 patients) patients evaluated as worse prognosis was relatively small, it was difficult to analyze them in consideration of the time when the event occurred. Finally, other inflammatory markers including fecal calprotectin and C-reactive protein were not investigated for the assessment of disease phenotypes. These results therefore need to be interpreted with caution. However, this study advances our knowledge as it identified the fecal microbiota related with the disease phenotypes and prognosis at the species level.
In conclusion, the fecal microbiota profile of IBD patients is different from HC and is characterized according to disease severity and extent. Several bacterial taxa have the potential to be used as biomarkers to assess disease severity and extent, which can be used to determine prognosis. These data may help discriminate disease phenotypes, predict clinical courses, and discover new therapeutic targets for IBD.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Funding Source
This work was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) (Grant/Award No. NRF-2020R1F1A1075489) and a grant of the Korean Association for the Study of Intestinal Diseases for 2009. Lee SC was supported by a CTSA/IIMS UT Health Pilot Grant and holds a Voelcker Fund Young Investigator Award from the Max and Minnie Tomerlin Voelcker Fund.
Author Contribution
Conceptualization: Choi CH, Lee SC. Methodology: Choi CH, Lee SC. Funding acquisition: Choi CH. Project administration: Shin SY, Kim Y, Kim WS, Moon JM, Lee KM, Jung SA, Park H, Huh EY, Kim BC. Writing original draft: Shin SY, Kim Y. Writing-review and editing: Choi CH, Lee SC. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary materials are available at the Intestinal Research website (https://www.irjournal.org).
Supplementary Fig. 1. Beta diversity based on Bray-Curtis index according to the disease extent in patients with ulcerative colitis (UC). HC, healthy control individuals; CD, Crohn’s disease; OUT, operational taxonomic unit.
ir-2021-00168-Supplementary-Fig-1.pdf
Fig. 1.
Diversity of fecal microbiota in a HC, UC patients, and CD patients. (A) Chao 1 index, (B) Shannon index, and (C) beta diversity based on Bray-Curtis dissimilarities. Both richness and diversity were significantly lower in inflammatory bowel disease patients compared with HC, and Shannon diversity index was significantly lower in CD compared with UC. Post hoc analyses using pair-wise comparisons showed that 3 groups were significantly different from each other (HC vs. UC, P=0.001; HC vs. CD, P=0.001; UC vs. CD, P=0.001). HC, healthy control individuals; UC, ulcerative colitis; CD, Crohn’s disease.
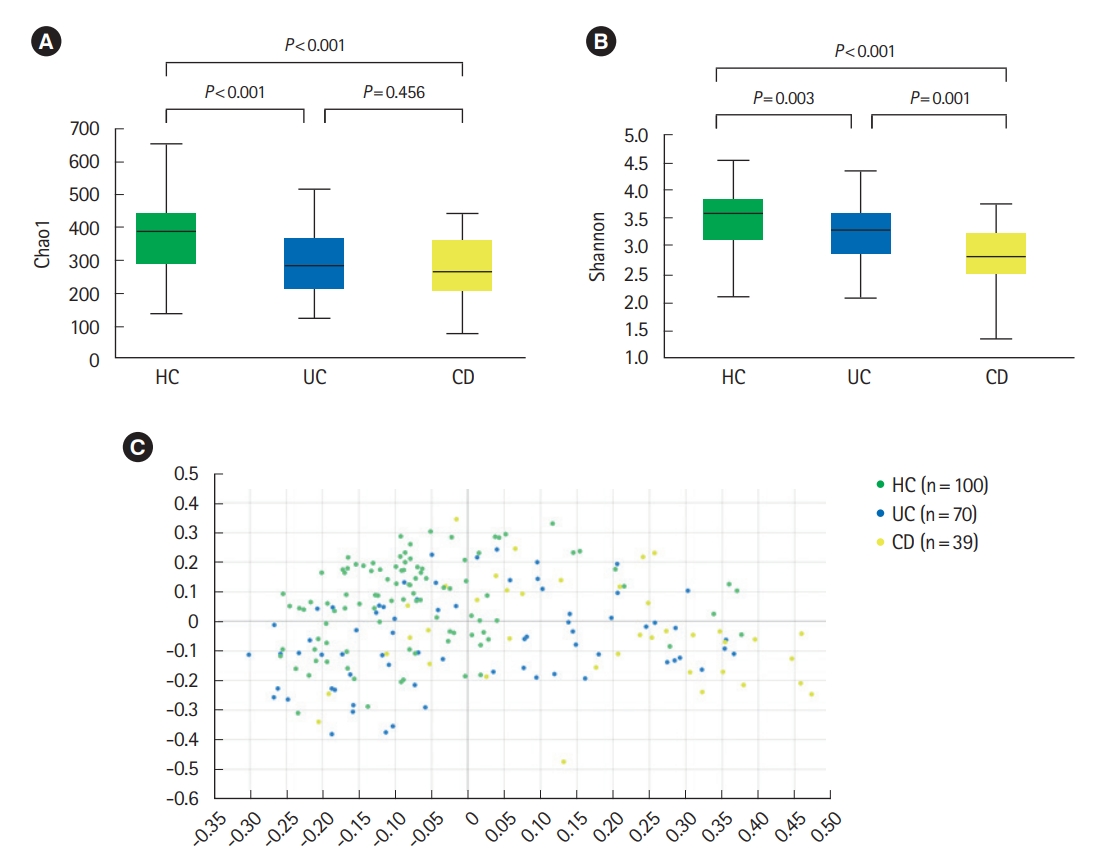
Fig. 2.
Diversity of fecal microbiota in ulcerative colitis (UC) patients according to disease severity (A) and disease extent (B). Alpha diversity decreased as the disease severity and extent deteriorated.

Fig. 3.
Composition of fecal microbiota in HC, UC patients, and CD patients at the phylum (A), genus (B), and species (C) level. Compared to HC and UC patients, CD patients had significantly higher abundances of the phylum Proteobacteria, the genus Escherichia, and the species Escherichia coli. HC, healthy control individuals; UC, ulcerative colitis; CD, Crohn’s disease.

Fig. 4.
Taxa list according to linear discriminate analysis values determined from comparisons between HC and UC patients (A), and between HC and CD patients (B). Effect size estimation analysis identified 9 bacterial taxa that were significantly more abundant in UC patients than HC (A), and 14 bacterial taxa that were significantly more abundant in CD patients than HC. HC, healthy control individuals; UC, ulcerative colitis; CD, Crohn’s disease.
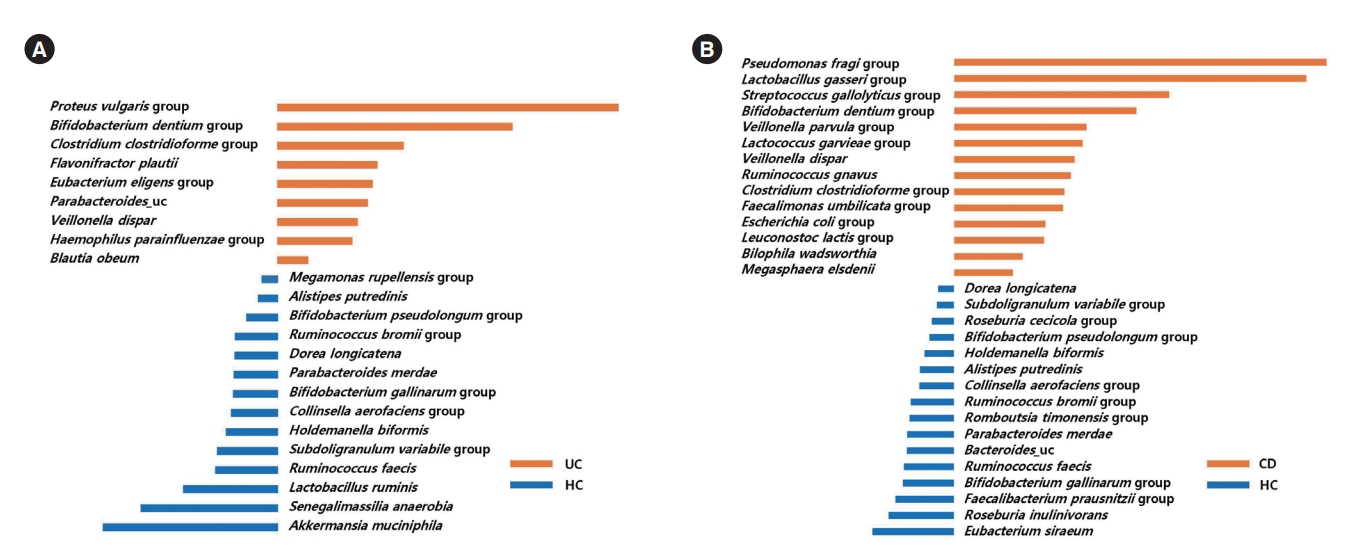
Fig. 5.
Taxa list according to linear discriminate analysis values determined from comparisons according to disease severity and extent in ulcerative colitis (UC) patients. Comparisons between moderate to severe and mild UC (A), between moderate to severe UC and remission (B), and between left sided or extensive UC and proctitis (C). Some bacterial taxa (red color) were identified as potential biomarkers for moderate to severe UC compared to mild UC (A), and remission status (B). Several bacterial taxa (red color) were found to be associated with left sided or extensive UC (C).

Fig. 6.
Taxa list according to linear discriminate analysis values determined from comparisons according to disease severity and extent in Crohn’s disease (CD) patients. Comparisons between remission and active CD (A) and between ileocolonic and small bowel CD (B). Some bacterial taxa (red color) were identified as possible biomarkers for active disease status, compared to remission status (A). Several bacterial taxa (red color) were identified as possible biomarkers for ileocolonic involvement, compared to small bowel involvement only (B).
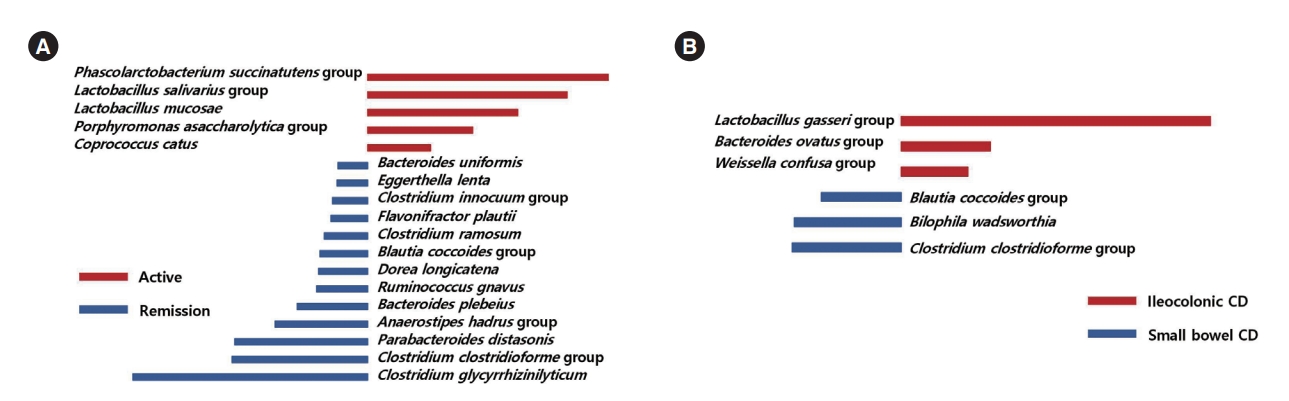
Fig. 7.
Relative abundance of particular taxa in Crohn’s disease (CD) patients based on prognosis. (A) Lachnospiraceae and (B) Ruminococcus gnavus. Better prognosis is defined as patients who did not consume biologic agents including anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α agents or surgical treatment after fecal sampling and worse prognosis is defined as patients who either were administered biologic agents including anti-TNF-α agents or required surgical treatment after fecal sampling (n=9). Lachnospiraceae and R. gnavus were significantly more abundant in the better prognosis group compared to the worse prognosis group.
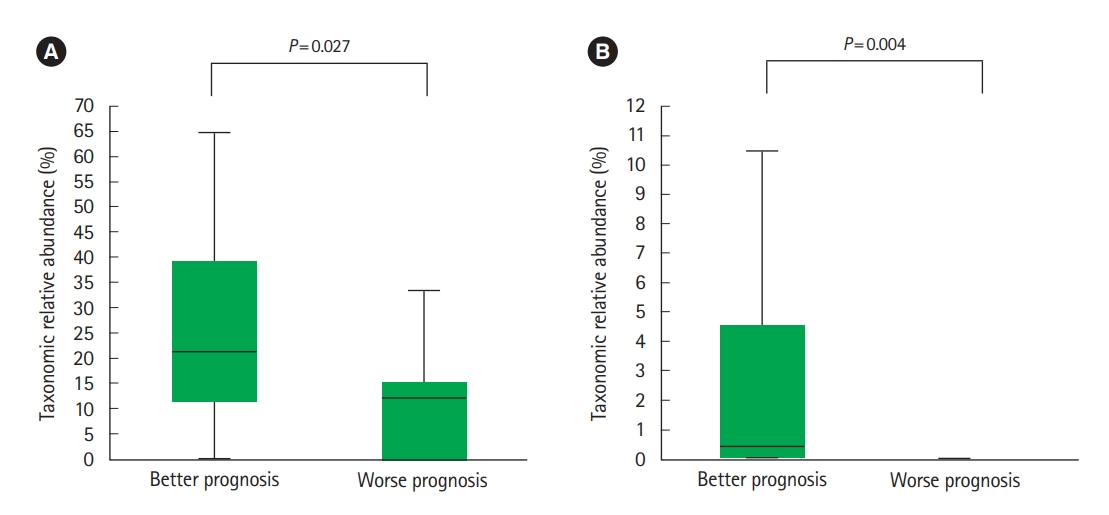
Table 1.
Baseline Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of All Participants
REFERENCES
2. Ungaro R, Mehandru S, Allen PB, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Colombel JF. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet 2017;389:1756-1770.


3. Mizoguchi E, Low D, Ezaki Y, Okada T. Recent updates on the basic mechanisms and pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases in experimental animal models. Intest Res 2020;18:151-167.




4. Ooi CJ, Hilmi I, Banerjee R, et al. Best practices on immunomodulators and biologic agents for ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease in Asia. Intest Res 2019;17:285-310.




5. Watanabe K. Clinical management for small bowel of Crohn’s disease in the treat-to-target era: now is the time to optimize treatment based on the dominant lesion. Intest Res 2020;18:347-354.




6. Toedter GP, Blank M, Lang Y, Chen D, Sandborn WJ, de Villiers WJ. Relationship of C-reactive protein with clinical response after therapy with ustekinumab in Crohn’s disease. Am J Gastroenterol 2009;104:2768-2773.



7. Sands BE. Biomarkers of inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 2015;149:1275-1285.


9. Pittayanon R, Lau JT, Leontiadis GI, et al. Differences in gut microbiota in patients with vs without inflammatory bowel diseases: a systematic review. Gastroenterology 2020;158:930-946.


10. Manichanh C, Rigottier-Gois L, Bonnaud E, et al. Reduced diversity of faecal microbiota in Crohn’s disease revealed by a metagenomic approach. Gut 2006;55:205-211.



11. Zuo T, Ng SC. The gut microbiota in the pathogenesis and therapeutics of inflammatory bowel disease. Front Microbiol 2018;9:2247.



12. Yilmaz B, Juillerat P, Øyås O, et al. Microbial network disturbances in relapsing refractory Crohn’s disease. Nat Med 2019;25:323-336.



13. Franzosa EA, Sirota-Madi A, Avila-Pacheco J, et al. Gut microbiome structure and metabolic activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Microbiol 2019;4:293-305.




14. Neumann C, Blume J, Roy U, et al. c-Maf-dependent Treg cell control of intestinal TH17 cells and IgA establishes host-microbiota homeostasis. Nat Immunol 2019;20:471-481.



15. Mahajan R, Midha V, Singh A, et al. Incidental benefits after fecal microbiota transplant for ulcerative colitis. Intest Res 2020;18:337-340.




16. Sehgal K, Khanna S. Gut microbiome and checkpoint inhibitor colitis. Intest Res 2021;19:360-364.




17. Bamba S, Inatomi O, Nishida A, et al. Relationship between the gut microbiota and bile acid composition in the ileal mucosa of Crohn’s disease. Intest Res 2022;20:370-380.

18. Schroeder KW, Tremaine WJ, Ilstrup DM. Coated oral 5-aminosalicylic acid therapy for mildly to moderately active ulcerative colitis: a randomized study. N Engl J Med 1987;317:1625-1629.


19. Best WR, Becktel JM, Singleton JW, Kern F Jr. Development of a Crohn’s disease activity index. National Cooperative Crohn’s Disease Study. Gastroenterology 1976;70:439-444.


20. Frank DN, Robertson CE, Hamm CM, et al. Disease phenotype and genotype are associated with shifts in intestinal-associated microbiota in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2011;17:179-184.



21. Papa E, Docktor M, Smillie C, et al. Non-invasive mapping of the gastrointestinal microbiota identifies children with inflammatory bowel disease. PLoS One 2012;7:e39242.



22. Satokari R. Contentious host-microbiota relationship in inflammatory bowel disease: can foes become friends again? Scand J Gastroenterol 2015;50:34-42.


23. Vester-Andersen MK, Mirsepasi-Lauridsen HC, Prosberg MV, et al. Increased abundance of proteobacteria in aggressive Crohn’s disease seven years after diagnosis. Sci Rep 2019;9:13473.




24. Alam MT, Amos G, Murphy A, Murch S, Wellington E, Arasaradnam RP. Microbial imbalance in inflammatory bowel disease patients at different taxonomic levels. Gut Pathog 2020;12:1.




25. Gevers D, Kugathasan S, Denson LA, et al. The treatment-naive microbiome in new-onset Crohn’s disease. Cell Host Microbe 2014;15:382-392.



26. Darfeuille-Michaud A, Boudeau J, Bulois P, et al. High prevalence of adherent-invasive Escherichia coli associated with ileal mucosa in Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 2004;127:412-421.


27. Lupp C, Robertson ML, Wickham ME, et al. Host-mediated inflammation disrupts the intestinal microbiota and promotes the overgrowth of Enterobacteriaceae. Cell Host Microbe 2007;2:119-129.


28. Kolho KL, Korpela K, Jaakkola T, et al. Fecal microbiota in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease and its relation to inflammation. Am J Gastroenterol 2015;110:921-930.



29. Pilarczyk-Zurek M, Chmielarczyk A, Gosiewski T, et al. Possible role of Escherichia coli in propagation and perpetuation of chronic inflammation in ulcerative colitis. BMC Gastroenterol 2013;13:61.




30. Mylonaki M, Rayment NB, Rampton DS, Hudspith BN, Brostoff J. Molecular characterization of rectal mucosa-associated bacterial flora in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2005;11:481-487.


31. Zhang SL, Wang SN, Miao CY. Influence of microbiota on intestinal immune system in ulcerative colitis and its intervention. Front Immunol 2017;8:1674.



32. Olbjørn C, Cvancarova Småstuen M, Thiis-Evensen E, et al. Fecal microbiota profiles in treatment-naïve pediatric inflammatory bowel disease: associations with disease phenotype, treatment, and outcome. Clin Exp Gastroenterol 2019;12:37-49.


33. Prosberg M, Bendtsen F, Vind I, Petersen AM, Gluud LL. The association between the gut microbiota and the inflammatory bowel disease activity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand J Gastroenterol 2016;51:1407-1415.


34. O’Mahony L, Feeney M, O’Halloran S, et al. Probiotic impact on microbial flora, inflammation and tumour development in IL-10 knockout mice. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2001;15:1219-1225.



35. Peran L, Camuesco D, Comalada M, et al. Preventative effects of a probiotic, Lactobacillus salivarius ssp. salivarius, in the TNBS model of rat colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2005;11:5185-5192.


36. Feighery LM, Smith P, O’Mahony L, Fallon PG, Brayden DJ. Effects of Lactobacillus salivarius 433118 on intestinal inflammation, immunity status and in vitro colon function in two mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci 2008;53:2495-2506.



37. Bossuyt P, Verhaegen J, Van Assche G, Rutgeerts P, Vermeire S. Increasing incidence of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea in inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis 2009;3:4-7.


38. Singh H, Nugent Z, Yu BN, Lix LM, Targownik LE, Bernstein CN. Higher incidence of Clostridium difficile infection among individuals with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 2017;153:430-438.


39. Rodemann JF, Dubberke ER, Reske KA, Seo DH, Stone CD. Incidence of Clostridium difficile infection in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;5:339-344.


40. Ananthakrishnan AN, Binion DG. Impact of Clostridium difficile on inflammatory bowel disease. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010;4:589-600.


41. Maharshak N, Barzilay I, Zinger H, Hod K, Dotan I. Clostridium difficile infection in hospitalized patients with inflammatory bowel disease: prevalence, risk factors, and prognosis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018;97:e9772.


42. Ben-Horin S, Margalit M, Bossuyt P, et al. Combination immunomodulator and antibiotic treatment in patients with inflammatory bowel disease and Clostridium difficile infection. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009;7:981-987.


43. Peeters M, Joossens S, Vermeire S, Vlietinck R, Bossuyt X, Rutgeerts P. Diagnostic value of anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae and antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies in inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol 2001;96:730-734.


44. Andersen K, Vogt C, Blondin D, et al. Multi-detector CT-colonography in inflammatory bowel disease: prospective analysis of CT-findings to high-resolution video colonoscopy. Eur J Radiol 2006;58:140-146.


45. Scanlan PD, Shanahan F, O’Mahony C, Marchesi JR. Culture-independent analyses of temporal variation of the dominant fecal microbiota and targeted bacterial subgroups in Crohn’s disease. J Clin Microbiol 2006;44:3980-3988.




46. Willing BP, Dicksved J, Halfvarson J, et al. A pyrosequencing study in twins shows that gastrointestinal microbial profiles vary with inflammatory bowel disease phenotypes. Gastroenterology 2010;139:1844-1854.


47. Seksik P, Rigottier-Gois L, Gramet G, et al. Alterations of the dominant faecal bacterial groups in patients with Crohn’s disease of the colon. Gut 2003;52:237-242.



48. Wang W, Chen L, Zhou R, et al. Increased proportions of Bifidobacterium and the Lactobacillus group and loss of butyrate-producing bacteria in inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Microbiol 2014;52:398-406.




49. Song YL, Liu CX, McTeague M, Summanen P, Finegold SM. Clostridium bartlettii sp. nov., isolated from human faeces. Anaerobe 2004;10:179-184.


50. Rosario D, Benfeitas R, Bidkhori G, et al. Understanding the representative gut microbiota dysbiosis in metformin-treated type 2 diabetes patients using genome-scale metabolic modeling. Front Physiol 2018;9:775.



51. Arpaia N, Campbell C, Fan X, et al. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature 2013;504:451-455.




52. Furusawa Y, Obata Y, Fukuda S, et al. Commensal microbe-derived butyrate induces the differentiation of colonic regulatory T cells. Nature 2013;504:446-450.



53. Choi SI, Son JH, Kim N, et al. Changes in cecal microbiota and short-chain fatty acid during lifespan of the rat. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 2021;27:134-146.



54. Beaud D, Tailliez P, Anba-Mondoloni J. Genetic characterization of the beta- glucuronidase enzyme from a human intestinal bacterium, Ruminococcus gnavus. Microbiology (Reading) 2005;151(Pt 7):2323-2330.